Page 20 - Textbook of Practical Laparoscopic Surgery by Dr. R. K. Mishra
P. 20
CHAPTER 6: Abdominal Access Techniques 19
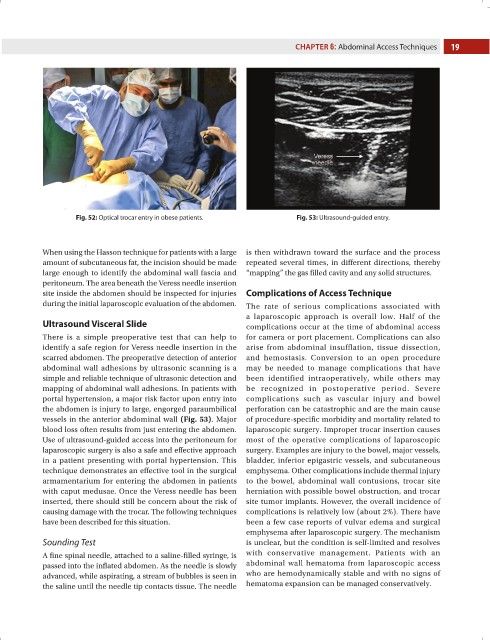
Fig. 52: Optical trocar entry in obese patients. Fig. 53: Ultrasound-guided entry.
When using the Hasson technique for patients with a large is then withdrawn toward the surface and the process
amount of subcutaneous fat, the incision should be made repeated several times, in different directions, thereby
large enough to identify the abdominal wall fascia and “mapping” the gas filled cavity and any solid structures.
peritoneum. The area beneath the Veress needle insertion
site inside the abdomen should be inspected for injuries Complications of Access Technique
during the initial laparoscopic evaluation of the abdomen. The rate of serious complications associated with
a laparoscopic approach is overall low. Half of the
Ultrasound Visceral Slide complications occur at the time of abdominal access
There is a simple preoperative test that can help to for camera or port placement. Complications can also
identify a safe region for Veress needle insertion in the arise from abdominal insufflation, tissue dissection,
scarred abdomen. The preoperative detection of anterior and hemostasis. Conversion to an open procedure
abdominal wall adhesions by ultrasonic scanning is a may be needed to manage complications that have
simple and reliable technique of ultrasonic detection and been identified intraoperatively, while others may
mapping of abdominal wall adhesions. In patients with be recognized in postoperative period. Severe
portal hypertension, a major risk factor upon entry into complications such as vascular injury and bowel
the abdomen is injury to large, engorged paraumbilical perforation can be catastrophic and are the main cause
vessels in the anterior abdominal wall (Fig. 53). Major of procedure-specific morbidity and mortality related to
blood loss often results from just entering the abdomen. laparoscopic surgery. Improper trocar insertion causes
Use of ultrasound-guided access into the peritoneum for most of the operative complications of laparoscopic
laparoscopic surgery is also a safe and effective approach surgery. Examples are injury to the bowel, major vessels,
in a patient presenting with portal hypertension. This bladder, inferior epigastric vessels, and subcutaneous
technique demonstrates an effective tool in the surgical emphysema. Other complications include thermal injury
armamentarium for entering the abdomen in patients to the bowel, abdominal wall contusions, trocar site
with caput medusae. Once the Veress needle has been herniation with possible bowel obstruction, and trocar
inserted, there should still be concern about the risk of site tumor implants. However, the overall incidence of
causing damage with the trocar. The following techniques complications is relatively low (about 2%). There have
have been described for this situation. been a few case reports of vulvar edema and surgical
emphysema after laparoscopic surgery. The mechanism
Sounding Test is unclear, but the condition is self-limited and resolves
A fine spinal needle, attached to a saline-filled syringe, is with conservative management. Patients with an
passed into the inflated abdomen. As the needle is slowly abdominal wall hematoma from laparoscopic access
advanced, while aspirating, a stream of bubbles is seen in who are hemodynamically stable and with no signs of
the saline until the needle tip contacts tissue. The needle hematoma expansion can be managed conservatively.