Page 25 - Textbook of Practical Laparoscopic Surgery by Dr. R. K. Mishra
P. 25
24 SECTION 1: Essentials of Laparoscopy
A B
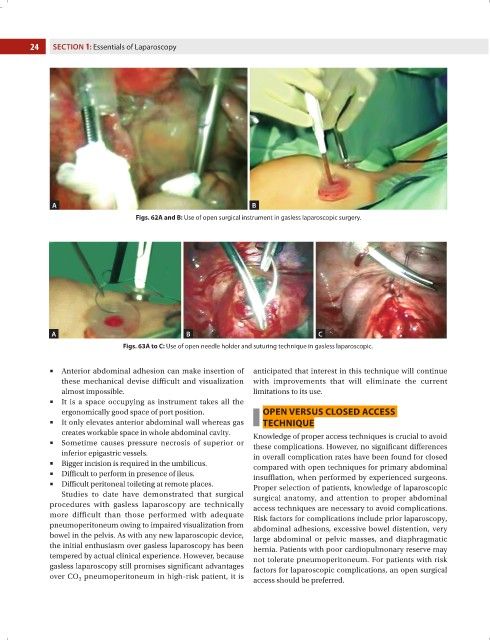
Figs. 62A and B: Use of open surgical instrument in gasless laparoscopic surgery.
A B C
Figs. 63A to C: Use of open needle holder and suturing technique in gasless laparoscopic.
■ ■Anterior abdominal adhesion can make insertion of anticipated that interest in this technique will continue
these mechanical devise difficult and visualization with improvements that will eliminate the current
almost impossible. limitations to its use.
■ ■It is a space occupying as instrument takes all the
ergonomically good space of port position. OPEN VERSUS CLOSED ACCESS
■ ■It only elevates anterior abdominal wall whereas gas TECHNIQUE
creates workable space in whole abdominal cavity. Knowledge of proper access techniques is crucial to avoid
■ ■Sometime causes pressure necrosis of superior or these complications. However, no significant differences
inferior epigastric vessels. in overall complication rates have been found for closed
■ ■Bigger incision is required in the umbilicus. compared with open techniques for primary abdominal
■ ■Difficult to perform in presence of ileus. insufflation, when performed by experienced surgeons.
■ ■Difficult peritoneal toileting at remote places. Proper selection of patients, knowledge of laparoscopic
Studies to date have demonstrated that surgical surgical anatomy, and attention to proper abdominal
procedures with gasless laparoscopy are technically access techniques are necessary to avoid complications.
more difficult than those performed with adequate Risk factors for complications include prior laparoscopy,
pneumoperitoneum owing to impaired visualization from abdominal adhesions, excessive bowel distention, very
bowel in the pelvis. As with any new laparoscopic device, large abdominal or pelvic masses, and diaphragmatic
the initial enthusiasm over gasless laparoscopy has been hernia. Patients with poor cardiopulmonary reserve may
tempered by actual clinical experience. However, because not tolerate pneumoperitoneum. For patients with risk
gasless laparoscopy still promises significant advantages factors for laparoscopic complications, an open surgical
over CO pneumoperitoneum in high-risk patient, it is access should be preferred.
2