Page 23 - Textbook of Practical Laparoscopic Surgery by Dr. R. K. Mishra
P. 23
22 SECTION 1: Essentials of Laparoscopy
A B
Figs. 57A and B: Port closure needle and aneurysm needle.
to use specialized instruments in order to operate on
video images. Abdominal lifting mechanical devices can
provide working space without pneumoperitoneum.
With gasless technique, conventional instruments can be
used, direct visualization of abdominal viscera is possible,
and digital examination of abdominal contents can be
performed without the fear of losing exposure. Since these
procedures are being performed in an isobaric abdominal
cavity, the risk of body fluid contamination to operating
team is diminished when compared to open or traditional
laparoscopic surgery. Gasless laparoscopic surgery is
primarily advocated for the patients who are at high risk
of pneumoperitoneum. A variety of abdominal lift devices
have been developed recently to provide good working
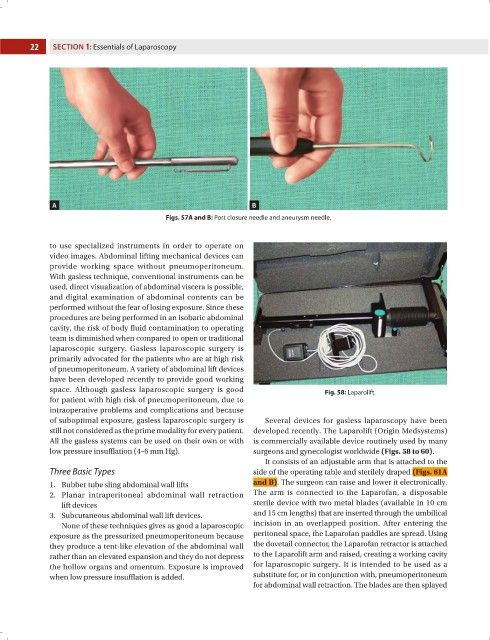
space. Although gasless laparoscopic surgery is good Fig. 58: Laparolift.
for patient with high risk of pneumoperitoneum, due to
intraoperative problems and complications and because
of suboptimal exposure, gasless laparoscopic surgery is Several devices for gasless laparoscopy have been
still not considered as the prime modality for every patient. developed recently. The Laparolift (Origin Medsystems)
All the gasless systems can be used on their own or with is commercially available device routinely used by many
low pressure insufflation (4–6 mm Hg). surgeons and gynecologist worldwide (Figs. 58 to 60).
It consists of an adjustable arm that is attached to the
Three Basic Types side of the operating table and sterilely draped (Figs. 61A
1. Rubber tube sling abdominal wall lifts and B). The surgeon can raise and lower it electronically.
2. Planar intraperitoneal abdominal wall retraction The arm is connected to the Laparofan, a disposable
lift devices sterile device with two metal blades (available in 10 cm
3. Subcutaneous abdominal wall lift devices. and 15 cm lengths) that are inserted through the umbilical
None of these techniques gives as good a laparoscopic incision in an overlapped position. After entering the
exposure as the pressurized pneumoperitoneum because peritoneal space, the Laparofan paddles are spread. Using
they produce a tent-like elevation of the abdominal wall the dovetail connector, the Laparofan retractor is attached
rather than an elevated expansion and they do not depress to the Laparolift arm and raised, creating a working cavity
the hollow organs and omentum. Exposure is improved for laparoscopic surgery. It is intended to be used as a
when low pressure insufflation is added. substitute for, or in conjunction with, pneumoperitoneum
for abdominal wall retraction. The blades are then splayed