Page 23 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 23
Clinical Profile and Laparoscopic Management of Hiatus Hernia
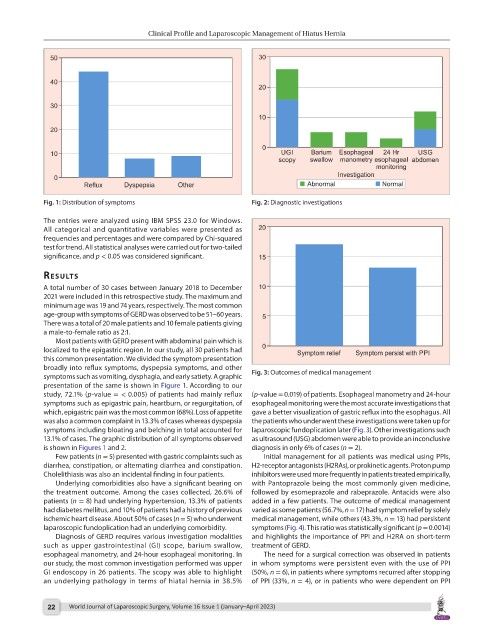
Fig. 1: Distribution of symptoms Fig. 2: Diagnostic investigations
The entries were analyzed using IBM SPSS 23.0 for Windows.
All categorical and quantitative variables were presented as
frequencies and percentages and were compared by Chi-squared
test for trend. All statistical analyses were carried out for two-tailed
significance, and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
results
A total number of 30 cases between January 2018 to December
2021 were included in this retrospective study. The maximum and
minimum age was 19 and 74 years, respectively. The most common
age-group with symptoms of GERD was observed to be 51–60 years.
There was a total of 20 male patients and 10 female patients giving
a male-to-female ratio as 2:1.
Most patients with GERD present with abdominal pain which is
localized to the epigastric region. In our study, all 30 patients had
this common presentation. We divided the symptom presentation
broadly into reflux symptoms, dyspepsia symptoms, and other
symptoms such as vomiting, dysphagia, and early satiety. A graphic Fig. 3: Outcomes of medical management
presentation of the same is shown in Figure 1. According to our
study, 72.1% (p-value = < 0.005) of patients had mainly reflux (p-value = 0.019) of patients. Esophageal manometry and 24-hour
symptoms such as epigastric pain, heartburn, or regurgitation, of esophageal monitoring were the most accurate investigations that
which, epigastric pain was the most common (68%). Loss of appetite gave a better visualization of gastric reflux into the esophagus. All
was also a common complaint in 13.3% of cases whereas dyspepsia the patients who underwent these investigations were taken up for
symptoms including bloating and belching in total accounted for laparoscopic fundoplication later (Fig. 3). Other investigations such
13.1% of cases. The graphic distribution of all symptoms observed as ultrasound (USG) abdomen were able to provide an inconclusive
is shown in Figures 1 and 2. diagnosis in only 6% of cases (n = 2).
Few patients (n = 5) presented with gastric complaints such as Initial management for all patients was medical using PPIs,
diarrhea, constipation, or alternating diarrhea and constipation. H2-receptor antagonists (H2RAs), or prokinetic agents. Proton pump
Cholelithiasis was also an incidental finding in four patients. inhibitors were used more frequently in patients treated empirically,
Underlying comorbidities also have a significant bearing on with Pantoprazole being the most commonly given medicine,
the treatment outcome. Among the cases collected, 26.6% of followed by esomeprazole and rabeprazole. Antacids were also
patients (n = 8) had underlying hypertension, 13.3% of patients added in a few patients. The outcome of medical management
had diabetes mellitus, and 10% of patients had a history of previous varied as some patients (56.7%, n = 17) had symptom relief by solely
ischemic heart disease. About 50% of cases (n = 5) who underwent medical management, while others (43.3%, n = 13) had persistent
laparoscopic fundoplication had an underlying comorbidity. symptoms (Fig. 4). This ratio was statistically significant (p = 0.0014)
Diagnosis of GERD requires various investigation modalities and highlights the importance of PPI and H2RA on short-term
such as upper gastrointestinal (GI) scope, barium swallow, treatment of GERD.
esophageal manometry, and 24-hour esophageal monitoring. In The need for a surgical correction was observed in patients
our study, the most common investigation performed was upper in whom symptoms were persistent even with the use of PPI
GI endoscopy in 26 patients. The scopy was able to highlight (50%, n = 6), in patients where symptoms recurred after stopping
an underlying pathology in terms of hiatal hernia in 38.5% of PPI (33%, n = 4), or in patients who were dependent on PPI
22 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 16 Issue 1 (January–April 2023)