Page 21 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 21
Role of Hysterolaparoscopy in Evaluation of Subfertility
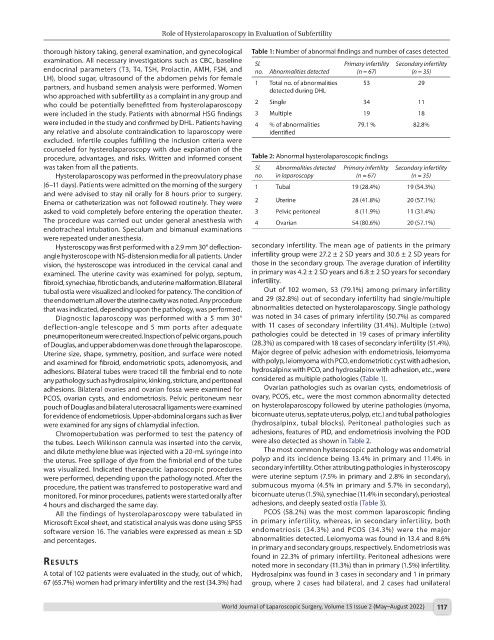
thorough history taking, general examination, and gynecological Table 1: Number of abnormal findings and number of cases detected
examination. All necessary investigations such as CBC, baseline Sl. Primary infertility Secondary infertility
endocrinal parameters (T3, T4, TSH, Prolactin, AMH, FSH, and no. Abnormalities detected (n = 67) (n = 35)
LH), blood sugar, ultrasound of the abdomen pelvis for female
partners, and husband semen analysis were performed. Women 1 Total no. of abnormalities 53 29
detected during DHL
who approached with subfertility as a complaint in any group and
who could be potentially benefitted from hysterolaparoscopy 2 Single 34 11
were included in the study. Patients with abnormal HSG findings 3 Multiple 19 18
were included in the study and confirmed by DHL. Patients having 4 % of abnormalities 79.1 % 82.8%
any relative and absolute contraindication to laparoscopy were identified
excluded. Infertile couples fulfilling the inclusion criteria were
counseled for hysterolaparoscopy with due explanation of the
procedure, advantages, and risks. Written and informed consent Table 2: Abnormal hysterolaparoscopic findings
was taken from all the patients. Sl. Abnormalities detected Primary infertility Secondary infertility
Hysterolaparoscopy was performed in the preovulatory phase no. in laparoscopy (n = 67) (n = 35)
(6–11 days). Patients were admitted on the morning of the surgery 1 Tubal 19 (28.4%) 19 (54.3%)
and were advised to stay nil orally for 8 hours prior to surgery.
Enema or catheterization was not followed routinely. They were 2 Uterine 28 (41.8%) 20 (57.1%)
asked to void completely before entering the operation theater. 3 Pelvic peritoneal 8 (11.9%) 11 (31.4%)
The procedure was carried out under general anesthesia with 4 Ovarian 54 (80.6%) 20 (57.1%)
endotracheal intubation. Speculum and bimanual examinations
were repeated under anesthesia.
Hysteroscopy was first performed with a 2.9 mm 30° deflection- secondary infertility. The mean age of patients in the primary
angle hysteroscope with NS-distension media for all patients. Under infertility group were 27.2 ± 2 SD years and 30.6 ± 2 SD years for
vision, the hysteroscope was introduced in the cervical canal and those in the secondary group. The average duration of infertility
examined. The uterine cavity was examined for polyp, septum, in primary was 4.2 ± 2 SD years and 6.8 ± 2 SD years for secondary
fibroid, synechiae, fibrotic bands, and uterine malformation. Bilateral infertility.
tubal ostia were visualized and looked for patency. The condition of Out of 102 women, 53 (79.1%) among primary infertility
the endometrium all over the uterine cavity was noted. Any procedure and 29 (82.8%) out of secondary infertility had single/multiple
that was indicated, depending upon the pathology, was performed. abnormalities detected on hysterolaparoscopy. Single pathology
Diagnostic laparoscopy was performed with a 5 mm 30° was noted in 34 cases of primary infertility (50.7%) as compared
deflection-angle telescope and 5 mm ports after adequate with 11 cases of secondary infertility (31.4%). Multiple (≥two)
pneumoperitoneum were created. Inspection of pelvic organs, pouch pathologies could be detected in 19 cases of primary infertility
of Douglas, and upper abdomen was done through the laparoscope. (28.3%) as compared with 18 cases of secondary infertility (51.4%).
Uterine size, shape, symmetry, position, and surface were noted Major degree of pelvic adhesion with endometriosis, leiomyoma
and examined for fibroid, endometriotic spots, adenomyosis, and with polyp, leiomyoma with PCO, endometriotic cyst with adhesion,
adhesions. Bilateral tubes were traced till the fimbrial end to note hydrosalpinx with PCO, and hydrosalpinx with adhesion, etc., were
any pathology such as hydrosalpinx, kinking, stricture, and peritoneal considered as multiple pathologies (Table 1).
adhesions. Bilateral ovaries and ovarian fossa were examined for Ovarian pathologies such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis of
PCOS, ovarian cysts, and endometriosis. Pelvic peritoneum near ovary, PCOS, etc., were the most common abnormality detected
pouch of Douglas and bilateral uterosacral ligaments were examined on hysterolaparoscopy followed by uterine pathologies (myoma,
for evidence of endometriosis. Upper-abdominal organs such as liver bicornuate uterus, septate uterus, polyp, etc.) and tubal pathologies
were examined for any signs of chlamydial infection. (hydrosalpinx, tubal blocks). Peritoneal pathologies such as
Chromopertubation was performed to test the patency of adhesions, features of PID, and endometriosis involving the POD
the tubes. Leech Wilkinson cannula was inserted into the cervix, were also detected as shown in Table 2.
and dilute methylene blue was injected with a 20-mL syringe into The most common hysteroscopic pathology was endometrial
the uterus. Free spillage of dye from the fimbrial end of the tube polyp and its incidence being 13.4% in primary and 11.4% in
was visualized. Indicated therapeutic laparoscopic procedures secondary infertility. Other attributing pathologies in hysteroscopy
were performed, depending upon the pathology noted. After the were uterine septum (7.5% in primary and 2.8% in secondary),
procedure, the patient was transferred to postoperative ward and submucous myoma (4.5% in primary and 5.7% in secondary),
monitored. For minor procedures, patients were started orally after bicornuate uterus (1.5%), synechiae (11.4% in secondary), periosteal
4 hours and discharged the same day. adhesions, and deeply seated ostia (Table 3).
All the findings of hysterolaparoscopy were tabulated in PCOS (58.2%) was the most common laparoscopic finding
Microsoft Excel sheet, and statistical analysis was done using SPSS in primary infertility, whereas, in secondary infertility, both
software version 16. The variables were expressed as mean ± SD endometriosis (34.3%) and PCOS (34.3%) were the major
and percentages. abnormalities detected. Leiomyoma was found in 13.4 and 8.6%
in primary and secondary groups, respectively. Endometriosis was
found in 22.3% of primary infertility. Peritoneal adhesions were
results noted more in secondary (11.3%) than in primary (1.5%) infertility.
A total of 102 patients were evaluated in the study, out of which, Hydrosalpinx was found in 3 cases in secondary and 1 in primary
67 (65.7%) women had primary infertility and the rest (34.3%) had group, where 2 cases had bilateral, and 2 cases had unilateral
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 2 (May–August 2022) 117