Page 17 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 17
Comparative Study of the Effect of Various Bariatric Surgery Methods
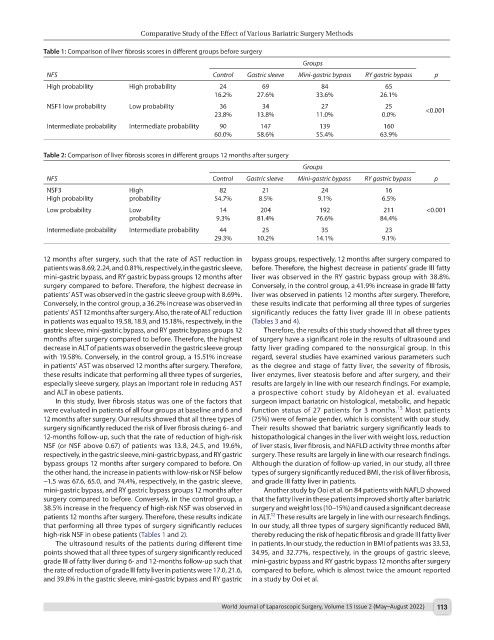
Table 1: Comparison of liver fibrosis scores in different groups before surgery
Groups
NFS Control Gastric sleeve Mini-gastric bypass RY gastric bypass p
High probability High probability 24 69 84 65
16.2% 27.6% 33.6% 26.1%
NSF1 low probability Low probability 36 34 27 25 <0.001
23.8% 13.8% 11.0% 0.0%
Intermediate probability Intermediate probability 90 147 139 160
60.0% 58.6% 55.4% 63.9%
Table 2: Comparison of liver fibrosis scores in different groups 12 months after surgery
Groups
NFS Control Gastric sleeve Mini-gastric bypass RY gastric bypass p
NSF3 High 82 21 24 16
High probability probability 54.7% 8.5% 9.1% 6.5%
Low probability Low 14 204 192 211 <0.001
probability 9.3% 81.4% 76.6% 84.4%
Intermediate probability Intermediate probability 44 25 35 23
29.3% 10.2% 14.1% 9.1%
12 months after surgery, such that the rate of AST reduction in bypass groups, respectively, 12 months after surgery compared to
patients was 8.69, 2.24, and 0.81%, respectively, in the gastric sleeve, before. Therefore, the highest decrease in patients’ grade III fatty
mini-gastric bypass, and RY gastric bypass groups 12 months after liver was observed in the RY gastric bypass group with 38.8%.
surgery compared to before. Therefore, the highest decrease in Conversely, in the control group, a 41.9% increase in grade III fatty
patients’ AST was observed in the gastric sleeve group with 8.69%. liver was observed in patients 12 months after surgery. Therefore,
Conversely, in the control group, a 36.2% increase was observed in these results indicate that performing all three types of surgeries
patients’ AST 12 months after surgery. Also, the rate of ALT reduction significantly reduces the fatty liver grade III in obese patients
in patients was equal to 19.58, 18.9, and 15.18%, respectively, in the (Tables 3 and 4).
gastric sleeve, mini-gastric bypass, and RY gastric bypass groups 12 Therefore, the results of this study showed that all three types
months after surgery compared to before. Therefore, the highest of surgery have a significant role in the results of ultrasound and
decrease in ALT of patients was observed in the gastric sleeve group fatty liver grading compared to the nonsurgical group. In this
with 19.58%. Conversely, in the control group, a 15.51% increase regard, several studies have examined various parameters such
in patients’ AST was observed 12 months after surgery. Therefore, as the degree and stage of fatty liver, the severity of fibrosis,
these results indicate that performing all three types of surgeries, liver enzymes, liver steatosis before and after surgery, and their
especially sleeve surgery, plays an important role in reducing AST results are largely in line with our research findings. For example,
and ALT in obese patients. a prospective cohort study by Aldoheyan et al. evaluated
In this study, liver fibrosis status was one of the factors that surgeon impact bariatric on histological, metabolic, and hepatic
15
were evaluated in patients of all four groups at baseline and 6 and function status of 27 patients for 3 months. Most patients
12 months after surgery. Our results showed that all three types of (75%) were of female gender, which is consistent with our study.
surgery significantly reduced the risk of liver fibrosis during 6- and Their results showed that bariatric surgery significantly leads to
12-months follow-up, such that the rate of reduction of high-risk histopathological changes in the liver with weight loss, reduction
NSF (or NSF above 0.67) of patients was 13.8, 24.5, and 19.6%, of liver stasis, liver fibrosis, and NAFLD activity three months after
respectively, in the gastric sleeve, mini-gastric bypass, and RY gastric surgery. These results are largely in line with our research findings.
bypass groups 12 months after surgery compared to before. On Although the duration of follow-up varied, in our study, all three
the other hand, the increase in patients with low-risk or NSF below types of surgery significantly reduced BMI, the risk of liver fibrosis,
−1.5 was 67.6, 65.0, and 74.4%, respectively, in the gastric sleeve, and grade III fatty liver in patients.
mini-gastric bypass, and RY gastric bypass groups 12 months after Another study by Ooi et al. on 84 patients with NAFLD showed
surgery compared to before. Conversely, in the control group, a that the fatty liver in these patients improved shortly after bariatric
38.5% increase in the frequency of high-risk NSF was observed in surgery and weight loss (10–15%) and caused a significant decrease
12
patients 12 months after surgery. Therefore, these results indicate in ALT. These results are largely in line with our research findings.
that performing all three types of surgery significantly reduces In our study, all three types of surgery significantly reduced BMI,
high-risk NSF in obese patients (Tables 1 and 2). thereby reducing the risk of hepatic fibrosis and grade III fatty liver
The ultrasound results of the patients during different time in patients. In our study, the reduction in BMI of patients was 33.53,
points showed that all three types of surgery significantly reduced 34.95, and 32.77%, respectively, in the groups of gastric sleeve,
grade III of fatty liver during 6- and 12-months follow-up such that mini-gastric bypass and RY gastric bypass 12 months after surgery
the rate of reduction of grade III fatty liver in patients were 17.0, 21.6, compared to before, which is almost twice the amount reported
and 39.8% in the gastric sleeve, mini-gastric bypass and RY gastric in a study by Ooi et al.
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 2 (May–August 2022) 113