Page 39 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 39
Open Mesh Repair vs Laparoscopic Mesh Repair of Umbilical Hernia
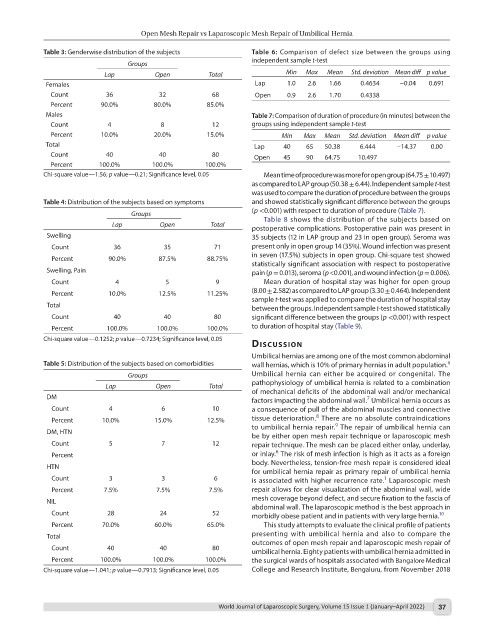
Table 3: Genderwise distribution of the subjects Table 6: Comparison of defect size between the groups using
independent sample t-test
Groups
Lap Open Total Min Max Mean Std. deviation Mean diff p value
Females Lap 1.0 2.6 1.66 0.4634 −0.04 0.691
Count 36 32 68 Open 0.9 2.6 1.70 0.4338
Percent 90.0% 80.0% 85.0%
Males Table 7: Comparison of duration of procedure (in minutes) between the
Count 4 8 12 groups using independent sample t-test
Percent 10.0% 20.0% 15.0% Min Max Mean Std. deviation Mean diff p value
Total Lap 40 65 50.38 6.444 −14.37 0.00
Count 40 40 80 Open 45 90 64.75 10.497
Percent 100.0% 100.0% 100.0%
Chi-square value—1.56; p value—0.21; Significance level, 0.05 Mean time of procedure was more for open group (64.75 ± 10.497)
as compared to LAP group (50.38 ± 6.44). Independent sample t-test
was used to compare the duration of procedure between the groups
Table 4: Distribution of the subjects based on symptoms and showed statistically significant difference between the groups
Groups (p <0.001) with respect to duration of procedure (Table 7).
Table 8 shows the distribution of the subjects based on
Lap Open Total postoperative complications. Postoperative pain was present in
Swelling 35 subjects (12 in LAP group and 23 in open group). Seroma was
Count 36 35 71 present only in open group 14 (35%). Wound infection was present
in seven (17.5%) subjects in open group. Chi-square test showed
Percent 90.0% 87.5% 88.75%
statistically significant association with respect to postoperative
Swelling, Pain pain (p = 0.013), seroma (p <0.001), and wound infection (p = 0.006).
Count 4 5 9 Mean duration of hospital stay was higher for open group
Percent 10.0% 12.5% 11.25% (8.00 ± 2.582) as compared to LAP group (3.30 ± 0.464). Independent
sample t-test was applied to compare the duration of hospital stay
Total between the groups. Independent sample t-test showed statistically
Count 40 40 80 significant difference between the groups (p <0.001) with respect
Percent 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% to duration of hospital stay (Table 9).
Chi-square value—0.1252; p value—0.7234; Significance level, 0.05
dIscussIon
Umbilical hernias are among one of the most common abdominal
6
Table 5: Distribution of the subjects based on comorbidities wall hernias, which is 10% of primary hernias in adult population.
Groups Umbilical hernia can either be acquired or congenital. The
pathophysiology of umbilical hernia is related to a combination
Lap Open Total of mechanical deficits of the abdominal wall and/or mechanical
DM factors impacting the abdominal wall. Umbilical hernia occurs as
7
Count 4 6 10 a consequence of pull of the abdominal muscles and connective
8
Percent 10.0% 15.0% 12.5% tissue deterioration. There are no absolute contraindications
9
to umbilical hernia repair. The repair of umbilical hernia can
DM, HTN
be by either open mesh repair technique or laparoscopic mesh
Count 5 7 12 repair technique. The mesh can be placed either onlay, underlay,
6
Percent or inlay. The risk of mesh infection is high as it acts as a foreign
body. Nevertheless, tension-free mesh repair is considered ideal
HTN
for umbilical hernia repair as primary repair of umbilical hernia
Count 3 3 6 is associated with higher recurrence rate. Laparoscopic mesh
1
Percent 7.5% 7.5% 7.5% repair allows for clear visualization of the abdominal wall, wide
NIL mesh coverage beyond defect, and secure fixation to the fascia of
abdominal wall. The laparoscopic method is the best approach in
Count 28 24 52 morbidly obese patient and in patients with very large hernia.
10
Percent 70.0% 60.0% 65.0% This study attempts to evaluate the clinical profile of patients
Total presenting with umbilical hernia and also to compare the
outcomes of open mesh repair and laparoscopic mesh repair of
Count 40 40 80 umbilical hernia. Eighty patients with umbilical hernia admitted in
Percent 100.0% 100.0% 100.0% the surgical wards of hospitals associated with Bangalore Medical
Chi-square value—1.041; p value—0.7913; Significance level, 0.05 College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, from November 2018
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 1 (January–April 2022) 37