Page 31 - Laparoscopic Journal - WJOLS
P. 31
WJOLS
A Comparative Study of Single Incision vs Conventional Four Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
attention due to the potential to maximize the benefits in reverse Trendelenburg position (30º) with table tilted
of laparoscopic surgery. 8,11 The reported advantages of right up to displace the intraabdominal organs away
SILC include less postoperative pain and minimum or from the gallbladder. A nasogastric tube was placed
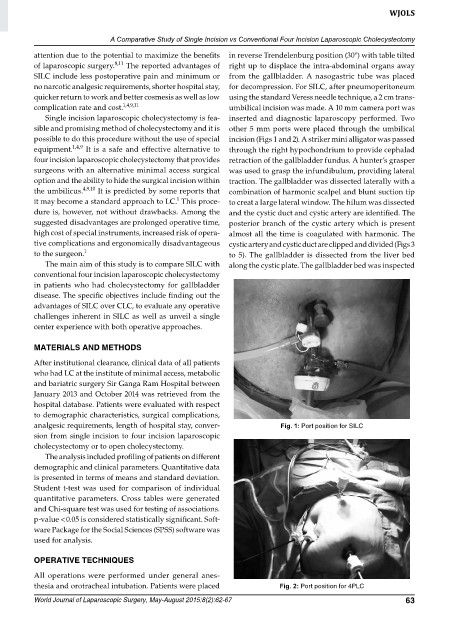
no narcotic analgesic requirements, shorter hospital stay, for decompression. For SILC, after pneumoperitoneum
quicker return to work and better cosmesis as well as low using the standard Veress needle technique, a 2 cm trans
complication rate and cost. 1,4,9,11 umbilical incision was made. A 10 mm camera port was
Single incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy is fea inserted and diagnostic laparoscopy performed. Two
sible and promising method of cholecystectomy and it is other 5 mm ports were placed through the umbilical
possible to do this procedure without the use of special incision (Figs 1 and 2). A striker mini alligator was passed
equipment. 1,4,9 It is a safe and effective alternative to through the right hypochondrium to provide cephalad
four incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy that provides retraction of the gallbladder fundus. A hunter’s grasper
surgeons with an alternative minimal access surgical was used to grasp the infundibulum, providing lateral
option and the ability to hide the surgical incision within traction. The gallbladder was dissected laterally with a
the umbilicus. 4,9,10 It is predicted by some reports that combination of harmonic scalpel and blunt suction tip
1
it may become a standard approach to LC. This proce to creat a large lateral window. The hilum was dissected
dure is, however, not without drawbacks. Among the and the cystic duct and cystic artery are identified. The
suggested disadvantages are prolonged operative time, posterior branch of the cystic artery which is present
high cost of special instruments, increased risk of opera almost all the time is coagulated with harmonic. The
tive complications and ergonomically disadvantageous cystic artery and cystic duct are clipped and divided (Figs 3
to the surgeon. 1 to 5). The gallbladder is dissected from the liver bed
The main aim of this study is to compare SILC with along the cystic plate. The gallbladder bed was inspected
conventional four incision laparoscopic cholecystectomy
in patients who had cholecystectomy for gallbladder
disease. The specific objectives include finding out the
advantages of SILC over CLC, to evaluate any operative
challenges inherent in SILC as well as unveil a single
center experience with both operative approaches.
MATERIALS ANd METHodS
After institutional clearance, clinical data of all patients
who had LC at the institute of minimal access, metabolic
and bariatric surgery Sir Ganga Ram Hospital between
January 2013 and October 2014 was retrieved from the
hospital database. Patients were evaluated with respect
to demographic characteristics, surgical complications,
analgesic requirements, length of hospital stay, conver Fig. 1: port position for silc
sion from single incision to four incision laparoscopic
cholecystectomy or to open cholecystectomy.
The analysis included profiling of patients on different
demographic and clinical parameters. Quantitative data
is presented in terms of means and standard deviation.
Student ttest was used for comparison of individual
quantitative parameters. Cross tables were generated
and Chisquare test was used for testing of associations.
p-value < 0.05 is considered statistically significant. Soft
ware Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software was
used for analysis.
oPERATIVE TECHNIQuES
All operations were performed under general anes
thesia and orotracheal intubation. Patients were placed Fig. 2: port position for 4plc
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2015;8(2):62-67 63