Page 33 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 33
WJOLS
Management of Acute Appendicitis and Left Paraovarian Cyst in a Case of Situs Inversus Totalis by Laparoscopy
A B
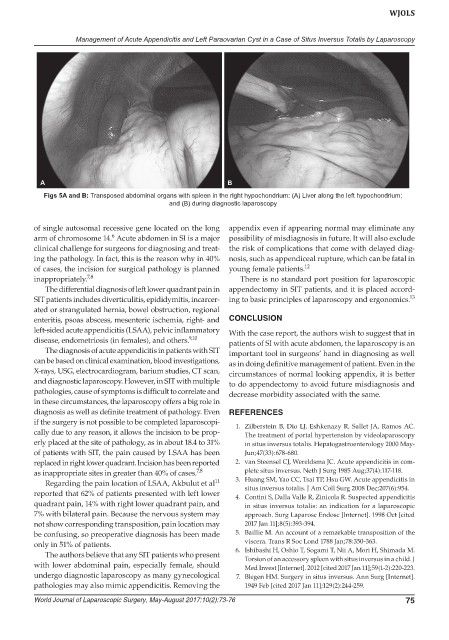
Figs 5A and B: Transposed abdominal organs with spleen in the right hypochondrium: (A) Liver along the left hypochondrium;
and (B) during diagnostic laparoscopy
of single autosomal recessive gene located on the long appendix even if appearing normal may eliminate any
6
arm of chromosome 14. Acute abdomen in SI is a major possibility of misdiagnosis in future. It will also exclude
clinical challenge for surgeons for diagnosing and treat- the risk of complications that come with delayed diag-
ing the pathology. In fact, this is the reason why in 40% nosis, such as appendiceal rupture, which can be fatal in
of cases, the incision for surgical pathology is planned young female patients. 12
inappropriately. 7,8 There is no standard port position for laparoscopic
The differential diagnosis of left lower quadrant pain in appendectomy in SIT patients, and it is placed accord-
SIT patients includes diverticulitis, epididymitis, incarcer- ing to basic principles of laparoscopy and ergonomics. 13
ated or strangulated hernia, bowel obstruction, regional
enteritis, psoas abscess, mesenteric ischemia, right- and CONCLUSION
left-sided acute appendicitis (LSAA), pelvic inflammatory With the case report, the authors wish to suggest that in
disease, endometriosis (in females), and others. 9,10 patients of SI with acute abdomen, the laparoscopy is an
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis in patients with SIT important tool in surgeons’ hand in diagnosing as well
can be based on clinical examination, blood investigations, as in doing definitive management of patient. Even in the
X-rays, USG, electrocardiogram, barium studies, CT scan, circumstances of normal looking appendix, it is better
and diagnostic laparoscopy. However, in SIT with multiple to do appendectomy to avoid future misdiagnosis and
pathologies, cause of symptoms is difficult to correlate and decrease morbidity associated with the same.
in these circumstances, the laparoscopy offers a big role in
diagnosis as well as definite treatment of pathology. Even REFERENCES
if the surgery is not possible to be completed laparoscopi- 1. Zilberstein B, Dio LJ, Eshkenazy R, Sallet JA, Ramos AC.
cally due to any reason, it allows the incision to be prop- The treatment of portal hypertension by videolaparoscopy
erly placed at the site of pathology, as in about 18.4 to 31% in situs inversus totalis. Hepatogastroenterology 2000 May-
of patients with SIT, the pain caused by LSAA has been Jun;47(33):678-680.
replaced in right lower quadrant. Incision has been reported 2. van Steensel CJ, Wereldsma JC. Acute appendicitis in com-
as inappropriate sites in greater than 40% of cases. 7,8 plete situs inversus. Neth J Surg 1985 Aug;37(4):117-118.
11
Regarding the pain location of LSAA, Akbulut et al 3. Huang SM, Yao CC, Tsai TP, Hsu GW. Acute appendicitis in
situs inversus totalis. J Am Coll Surg 2008 Dec;207(6):954.
reported that 62% of patients presented with left lower 4. Contini S, Dalla Valle R, Zinicola R. Suspected appendicitis
quadrant pain, 14% with right lower quadrant pain, and in situs inversus totalis: an indication for a laparoscopic
7% with bilateral pain. Because the nervous system may approach. Surg Laparosc Endosc [Internet]. 1998 Oct [cited
not show corresponding transposition, pain location may 2017 Jan 11];8(5):393-394.
be confusing, so preoperative diagnosis has been made 5. Baillie M. An account of a remarkable transposition of the
only in 51% of patients. viscera. Trans R Soc Lond 1788 Jan;78:350-363.
The authors believe that any SIT patients who present 6. Ishibashi H, Oshio T, Sogami T, Nii A, Mori H, Shimada M.
Torsion of an accessory spleen with situs inversus in a child. J
with lower abdominal pain, especially female, should Med Invest [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2017 Jan 11];59(1-2):220-223.
undergo diagnostic laparoscopy as many gynecological 7. Blegen HM. Surgery in situs inversus. Ann Surg [Internet].
pathologies may also mimic appendicitis. Removing the 1949 Feb [cited 2017 Jan 11];129(2):244-259.
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2017;10(2):73-76 75