Page 28 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 28
Garima Gupta et al
A
B C
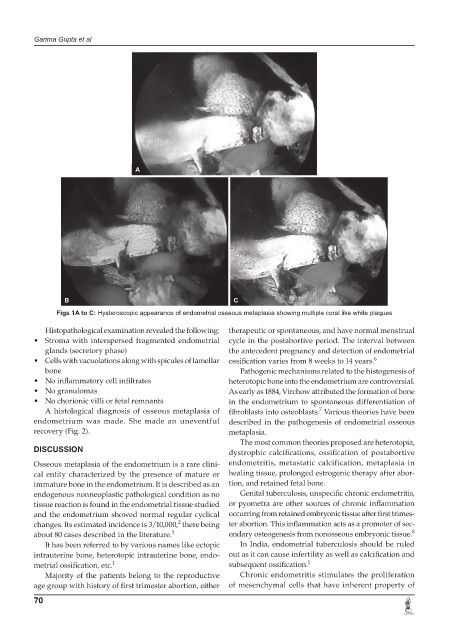
Figs 1A to C: Hysteroscopic appearance of endometrial osseous metaplasia showing multiple coral like white plaques
Histopathological examination revealed the following: therapeutic or spontaneous, and have normal menstrual
• Stroma with interspersed fragmented endometrial cycle in the postabortive period. The interval between
glands (secretory phase) the antecedent pregnancy and detection of endometrial
• Cells with vacuolations along with spicules of lamellar ossification varies from 8 weeks to 14 years. 6
bone Pathogenic mechanisms related to the histogenesis of
• No inflammatory cell infiltrates heterotopic bone into the endometrium are controversial.
• No granulomas As early as 1884, Virchow attributed the formation of bone
• No chorionic villi or fetal remnants in the endometrium to spontaneous differentiation of
7
A histological diagnosis of osseous metaplasia of fibroblasts into osteoblasts. Various theories have been
endometrium was made. She made an uneventful described in the pathogenesis of endometrial osseous
recovery (Fig. 2). metaplasia.
The most common theories proposed are heterotopia,
DISCUSSION dystrophic calcifications, ossification of postabortive
Osseous metaplasia of the endometrium is a rare clini- endometritis, metastatic calcification, metaplasia in
cal entity characterized by the presence of mature or healing tissue, prolonged estrogenic therapy after abor-
immature bone in the endometrium. It is described as an tion, and retained fetal bone.
endogenous nonneoplastic pathological condition as no Genital tuberculosis, unspecific chronic endometritis,
tissue reaction is found in the endometrial tissue studied or pyometra are other sources of chronic inflammation
and the endometrium showed normal regular cyclical occurring from retained embryonic tissue after first trimes-
2
changes. Its estimated incidence is 3/10,000, there being ter abortion. This inflammation acts as a promoter of sec-
about 80 cases described in the literature. 3 ondary osteogenesis from nonosseous embryonic tissue. 8
It has been referred to by various names like ectopic In India, endometrial tuberculosis should be ruled
intrauterine bone, heterotopic intrauterine bone, endo- out as it can cause infertility as well as calcification and
metrial ossification, etc. 1 subsequent ossification. 1
Majority of the patients belong to the reproductive Chronic endometritis stimulates the proliferation
age group with history of first trimester abortion, either of mesenchymal cells that have inherent property of
70