Page 7 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 7
Conversion of LC to Open Surgery
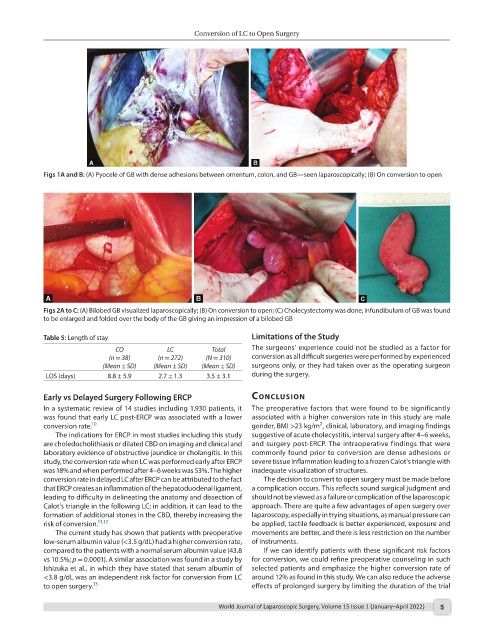
Figs 1A and B: (A) Pyocele of GB with dense adhesions between omentum, colon, and GB—seen laparoscopically; (B) On conversion to open
Figs 2A to C: (A) Bilobed GB visualized laparoscopically; (B) On conversion to open; (C) Cholecystectomy was done, infundibulum of GB was found
to be enlarged and folded over the body of the GB giving an impression of a bilobed GB
Table 5: Length of stay Limitations of the Study
CO LC Total The surgeons’ experience could not be studied as a factor for
(n = 38) (n = 272) (N = 310) conversion as all difficult surgeries were performed by experienced
(Mean ± SD) (Mean ± SD) (Mean ± SD) surgeons only, or they had taken over as the operating surgeon
LOS (days) 8.8 ± 5.9 2.7 ± 1.3 3.5 ± 3.1 during the surgery.
Early vs Delayed Surgery Following ERCP conclusIon
In a systematic review of 14 studies including 1,930 patients, it The preoperative factors that were found to be significantly
was found that early LC post-ERCP was associated with a lower associated with a higher conversion rate in this study are male
2
conversion rate. 10 gender, BMI >23 kg/m , clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings
The indications for ERCP in most studies including this study suggestive of acute cholecystitis, interval surgery after 4–6 weeks,
are choledocholithiasis or dilated CBD on imaging and clinical and and surgery post-ERCP. The intraoperative findings that were
laboratory evidence of obstructive jaundice or cholangitis. In this commonly found prior to conversion are dense adhesions or
study, the conversion rate when LC was performed early after ERCP severe tissue inflammation leading to a frozen Calot’s triangle with
was 18% and when performed after 4–6 weeks was 53%. The higher inadequate visualization of structures.
conversion rate in delayed LC after ERCP can be attributed to the fact The decision to convert to open surgery must be made before
that ERCP creates an inflammation of the hepatoduodenal ligament, a complication occurs. This reflects sound surgical judgment and
leading to difficulty in delineating the anatomy and dissection of should not be viewed as a failure or complication of the laparoscopic
Calot’s triangle in the following LC; in addition, it can lead to the approach. There are quite a few advantages of open surgery over
formation of additional stones in the CBD, thereby increasing the laparoscopy, especially in trying situations, as manual pressure can
risk of conversion. 11,12 be applied, tactile feedback is better experienced, exposure and
The current study has shown that patients with preoperative movements are better, and there is less restriction on the number
low-serum albumin value (<3.5 g/dL) had a higher conversion rate, of instruments.
compared to the patients with a normal serum albumin value (43.8 If we can identify patients with these significant risk factors
vs 10.5%; p = 0.0001). A similar association was found in a study by for conversion, we could refine preoperative counseling in such
Ishizuka et al., in which they have stated that serum albumin of selected patients and emphasize the higher conversion rate of
<3.8 g/dL was an independent risk factor for conversion from LC around 12% as found in this study. We can also reduce the adverse
to open surgery. 13 effects of prolonged surgery by limiting the duration of the trial
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 1 (January–April 2022) 5