Page 14 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 14
Non-appendicitis Pathologies during Appendectomy
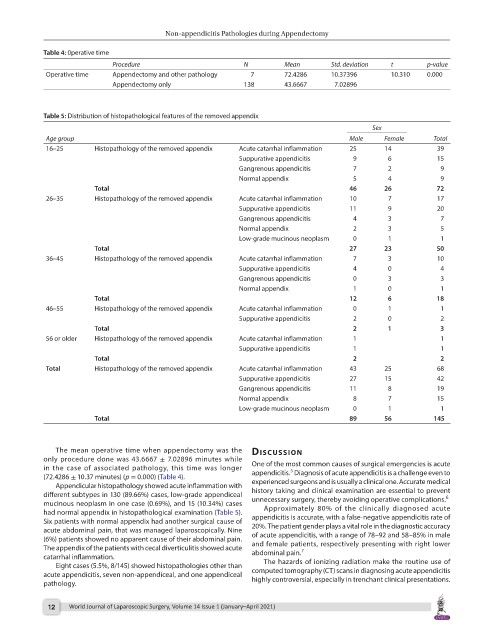
Table 4: 0perative time
Procedure N Mean Std. deviation t p-value
Operative time Appendectomy and other pathology 7 72.4286 10.37396 10.310 0.000
Appendectomy only 138 43.6667 7.02896
Table 5: Distribution of histopathological features of the removed appendix
Sex
Age group Male Female Total
16–25 Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 25 14 39
Suppurative appendicitis 9 6 15
Gangrenous appendicitis 7 2 9
Normal appendix 5 4 9
Total 46 26 72
26–35 Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 10 7 17
Suppurative appendicitis 11 9 20
Gangrenous appendicitis 4 3 7
Normal appendix 2 3 5
Low-grade mucinous neoplasm 0 1 1
Total 27 23 50
36–45 Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 7 3 10
Suppurative appendicitis 4 0 4
Gangrenous appendicitis 0 3 3
Normal appendix 1 0 1
Total 12 6 18
46–55 Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 0 1 1
Suppurative appendicitis 2 0 2
Total 2 1 3
56 or older Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 1 1
Suppurative appendicitis 1 1
Total 2 2
Total Histopathology of the removed appendix Acute catarrhal inflammation 43 25 68
Suppurative appendicitis 27 15 42
Gangrenous appendicitis 11 8 19
Normal appendix 8 7 15
Low-grade mucinous neoplasm 0 1 1
Total 89 56 145
The mean operative time when appendectomy was the dIscussIon
only procedure done was 43.6667 ± 7.02896 minutes while
in the case of associated pathology, this time was longer One of the most common causes of surgical emergencies is acute
5
(72.4286 ± 10.37 minutes) (p = 0.000) (Table 4). appendicitis. Diagnosis of acute appendicitis is a challenge even to
Appendicular histopathology showed acute inflammation with experienced surgeons and is usually a clinical one. Accurate medical
different subtypes in 130 (89.66%) cases, low-grade appendiceal history taking and clinical examination are essential to prevent
6
mucinous neoplasm in one case (0.69%), and 15 (10.34%) cases unnecessary surgery, thereby avoiding operative complications.
had normal appendix in histopathological examination (Table 5). Approximately 80% of the clinically diagnosed acute
Six patients with normal appendix had another surgical cause of appendicitis is accurate, with a false-negative appendicitis rate of
acute abdominal pain, that was managed laparoscopically. Nine 20%. The patient gender plays a vital role in the diagnostic accuracy
(6%) patients showed no apparent cause of their abdominal pain. of acute appendicitis, with a range of 78–92 and 58–85% in male
The appendix of the patients with cecal diverticulitis showed acute and female patients, respectively presenting with right lower
7
catarrhal inflammation. abdominal pain.
Eight cases (5.5%, 8/145) showed histopathologies other than The hazards of ionizing radiation make the routine use of
acute appendicitis, seven non-appendiceal, and one appendiceal computed tomography (CT) scans in diagnosing acute appendicitis
pathology. highly controversial, especially in trenchant clinical presentations.
12 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 1 (January–April 2021)