Page 10 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 10
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling, Clomiphene-resistant PCOS, Treatment Outcome
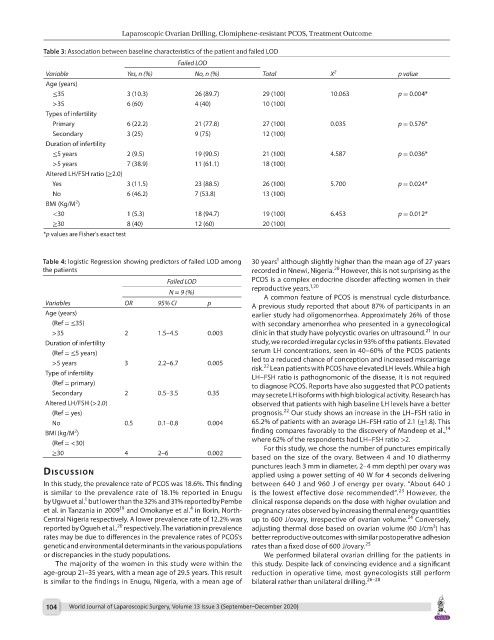
Table 3: Association between baseline characteristics of the patient and failed LOD
Failed LOD
Variable Yes, n (%) No, n (%) Total X 2 p value
Age (years)
≤35 3 (10.3) 26 (89.7) 29 (100) 10.063 p = 0.004*
>35 6 (60) 4 (40) 10 (100)
Types of infertility
Primary 6 (22.2) 21 (77.8) 27 (100) 0.035 p = 0.576*
Secondary 3 (25) 9 (75) 12 (100)
Duration of infertility
≤5 years 2 (9.5) 19 (90.5) 21 (100) 4.587 p = 0.036*
>5 years 7 (38.9) 11 (61.1) 18 (100)
Altered LH/FSH ratio (≥2.0)
Yes 3 (11.5) 23 (88.5) 26 (100) 5.700 p = 0.024*
No 6 (46.2) 7 (53.8) 13 (100)
2
BMI (Kg/M )
<30 1 (5.3) 18 (94.7) 19 (100) 6.453 p = 0.012*
≥30 8 (40) 12 (60) 20 (100)
*p values are Fisher's exact test
1
Table 4: logistic Regression showing predictors of failed LOD among 30 years although slightly higher than the mean age of 27 years
20
the patients recorded in Nnewi, Nigeria. However, this is not surprising as the
Failed LOD PCOS is a complex endocrine disorder affecting women in their
1,20
N = 9 (%) reproductive years.
A common feature of PCOS is menstrual cycle disturbance.
Variables OR 95% CI p A previous study reported that about 87% of participants in an
Age (years) earlier study had oligomenorrhea. Approximately 26% of those
(Ref = ≤35) with secondary amenorrhea who presented in a gynecological
21
>35 2 1.5–4.5 0.003 clinic in that study have polycystic ovaries on ultrasound. In our
Duration of infertility study, we recorded irregular cycles in 93% of the patients. Elevated
(Ref = ≤5 years) serum LH concentrations, seen in 40–60% of the PCOS patients
>5 years 3 2.2–6.7 0.005 led to a reduced chance of conception and increased miscarriage
22
risk. Lean patients with PCOS have elevated LH levels. While a high
Type of infertility LH–FSH ratio is pathognomonic of the disease, it is not required
(Ref = primary) to diagnose PCOS. Reports have also suggested that PCO patients
Secondary 2 0.5–3.5 0.35 may secrete LH isoforms with high biological activity. Research has
Altered LH/FSH (>2.0) observed that patients with high baseline LH levels have a better
22
(Ref = yes) prognosis. Our study shows an increase in the LH–FSH ratio in
No 0.5 0.1–0.8 0.004 65.2% of patients with an average LH–FSH ratio of 2.1 (±1.8). This
14
2
BMI (kg/M ) finding compares favorably to the discovery of Mandeep et al.,
(Ref = <30) where 62% of the respondents had LH–FSH ratio >2.
For this study, we chose the number of punctures empirically
≥30 4 2–6 0.002
based on the size of the ovary. Between 4 and 10 diathermy
punctures (each 3 mm in diameter, 2–4 mm depth) per ovary was
dIscussIon applied using a power setting of 40 W for 4 seconds delivering
In this study, the prevalence rate of PCOS was 18.6%. This finding between 640 J and 960 J of energy per ovary. “About 640 J
23
is similar to the prevalence rate of 18.1% reported in Enugu is the lowest effective dose recommended”. However, the
1
by Ugwu et al. but lower than the 32% and 31% reported by Pembe clinical response depends on the dose with higher ovulation and
19
4
et al. in Tanzania in 2009 and Omokanye et al. in Ilorin, North- pregnancy rates observed by increasing thermal energy quantities
24
Central Nigeria respectively. A lower prevalence rate of 12.2% was up to 600 J/ovary, irrespective of ovarian volume. Conversely,
3
20
reported by Ogueh et al., respectively. The variation in prevalence adjusting thermal dose based on ovarian volume (60 J/cm ) has
rates may be due to differences in the prevalence rates of PCOS’s better reproductive outcomes with similar postoperative adhesion
genetic and environmental determinants in the various populations rates than a fixed dose of 600 J/ovary. 25
or discrepancies in the study populations. We performed bilateral ovarian drilling for the patients in
The majority of the women in this study were within the this study. Despite lack of convincing evidence and a significant
age-group 21–35 years, with a mean age of 29.5 years. This result reduction in operative time, most gynecologists still perform
is similar to the findings in Enugu, Nigeria, with a mean age of bilateral rather than unilateral drilling. 26–28
104 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 13 Issue 3 (September–December 2020)