Page 39 - WALS Journal
P. 39
Sajal Kumar
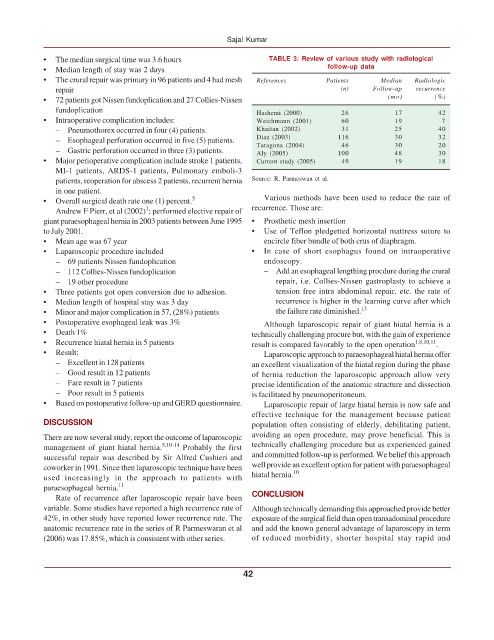
• The median surgical time was 3.6 hours TABLE 3: Review of various study with radiological
• Median length of stay was 2 days follow-up data
• The crural repair was primary in 96 patients and 4 had mesh References Patients Median Radiologic
repair (n) Follow-up recurrence
• 72 patients got Nissen fundoplication and 27 Collies-Nissen (mo) (%)
fundoplication Hashemi (2000) 26 17 42
• Intraoperative complication includes: Weichmann (2001) 60 19 7
– Pneumothorex occurred in four (4) patients. Khaitan (2002) 31 25 40
– Esophageal perforation occurred in five (5) patients. Diaz (2003) 116 30 32
46
– Gastric perforation occurred in three (3) patients. Taragona (2004) 100 30 20
48
Aly (2005)
30
• Major perioperative complication include stroke 1 patients, Current study (2005) 49 19 18
MI-1 patients, ARDS-1 patients, Pulmonary emboli-3
patients, reoperation for abscess 2 patients, recurrent hernia Source: R. Parmeswan et al.
in one patient.
• Overall surgical death rate one (1) percent. 5 Various methods have been used to reduce the rate of
1
Andrew F Pierr, et al (2002) ; performed elective repair of recurrence. Those are:
giant paraesophageal hernia in 2003 patients between June 1995 • Prosthetic mesh insertion
to July 2001. • Use of Teflon pledgetted horizontal mattress suture to
• Mean age was 67 year encircle fiber bundle of both crus of diaphragm.
• Laparoscopic procedure included • In case of short esophagus found on intraoperative
– 69 patients Nissen fundoplication endoscopy.
– 112 Collies-Nissen fundoplication – Add an esophageal lengthing procdure during the crural
– 19 other procedure repair, i.e. Collies-Nissen gastroplasty to achieve a
• Three patients got open conversion due to adhesion. tension free intra abdominal repair, etc. the rate of
• Median length of hospital stay was 3 day recurrence is higher in the learning curve after which
• Minor and major complication in 57, (28%) patients the failure rate diminished. 13
• Postoperative esophageal leak was 3% Although laparoscopic repair of giant hiatal hernia is a
• Death 1% technically challenging procure but, with the gain of experience
• Recurrence hiatal hernia in 5 patients result is compared favorably to the open operation 1,8,10,11 .
• Result; Laparoscopic approach to paraesophageal hiatal hernia offer
– Excellent in 128 patients an excellent visualization of the hiatal region during the phase
– Good result in 12 patients of hernia reduction the laparoscopic approach allow very
– Fare result in 7 patients precise identification of the anatomic structure and dissection
– Poor result in 5 patients is facilitated by pneumoperitoneum.
• Based on postoperative follow-up and GERD questionnaire. Laparoscopic repair of large hiatal hernia is now safe and
effective technique for the management because patient
DISCUSSION population often consisting of elderly, debilitating patient,
There are now several study, report the outcome of laparoscopic avoiding an open procedure, may prove beneficial. This is
management of giant hiatal hernia. 5,10-14 Probably the first technically challenging procedure but as experienced gained
successful repair was described by Sir Alfred Cushieri and and committed follow-up is performed. We belief this approach
coworker in 1991. Since then laparoscopic technique have been well provide an excellent option for patient with paraesophageal
used increasingly in the approach to patients with hiatal hernia. 10
paraesophageal hernia. 11
Rate of recurrence after laparoscopic repair have been CONCLUSION
variable. Some studies have reported a high recurrence rate of Although technically demanding this approached provide better
42%, in other study have reported lower recurrence rate. The exposure of the surgical field than open transadominal procedure
anatomic recurrence rate in the series of R Parmeswaran et al and add the known general advantage of laparoscopy in term
(2006) was 17.85%, which is consistent with other series. of reduced morbidity, shorter hospital stay rapid and
42