Page 25 - WJOLS
P. 25
Elective Laparoscopic Left Colectomy for Diverticular Disease: A Monocentric Study on 205 Consecutive Patients
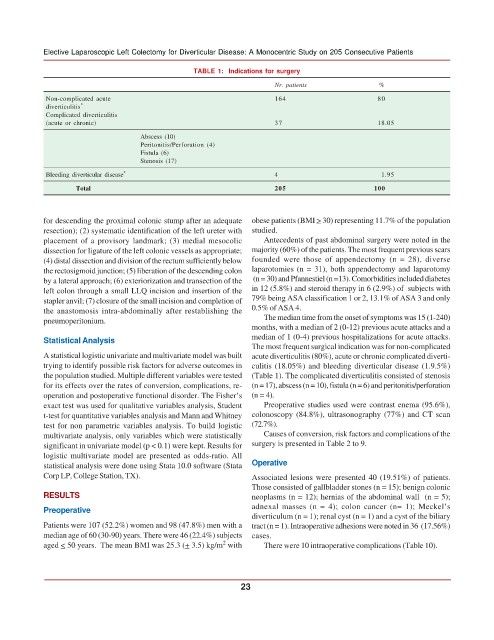
TABLE 1: Indications for surgery
Nr. patients %
Non-complicated acute 164 80
diverticulitis *
Complicated diverticulitis
(acute or chronic) 37 18.05
Abscess (10)
Peritonitis/Perforation (4)
Fistula (6)
Stenosis (17)
Bleeding diverticular disease * 4 1.95
Total 205 100
for descending the proximal colonic stump after an adequate obese patients (BMI > 30) representing 11.7% of the population
resection); (2) systematic identification of the left ureter with studied.
placement of a provisory landmark; (3) medial mesocolic Antecedents of past abdominal surgery were noted in the
dissection for ligature of the left colonic vessels as appropriate; majority (60%) of the patients. The most frequent previous scars
(4) distal dissection and division of the rectum sufficiently below founded were those of appendectomy (n = 28), diverse
the rectosigmoid junction; (5) liberation of the descending colon laparotomies (n = 31), both appendectomy and laparotomy
by a lateral approach; (6) exteriorization and transection of the (n = 30) and Pfannestiel (n =13). Comorbidities included diabetes
left colon through a small LLQ incision and insertion of the in 12 (5.8%) and steroid therapy in 6 (2.9%) of subjects with
stapler anvil; (7) closure of the small incision and completion of 79% being ASA classification 1 or 2, 13.1% of ASA 3 and only
the anastomosis intra-abdominally after restablishing the 0.5% of ASA 4.
pneumoperitonium. The median time from the onset of symptoms was 15 (1-240)
months, with a median of 2 (0-12) previous acute attacks and a
Statistical Analysis median of 1 (0-4) previous hospitalizations for acute attacks.
The most frequent surgical indication was for non-complicated
A statistical logistic univariate and multivariate model was built acute diverticulitis (80%), acute or chronic complicated diverti-
trying to identify possible risk factors for adverse outcomes in culitis (18.05%) and bleeding diverticular disease (1.9.5%)
the population studied. Multiple different variables were tested (Table 1). The complicated diverticulitis consisted of stenosis
for its effects over the rates of conversion, complications, re- (n = 17), abscess (n = 10), fistula (n = 6) and peritonitis/perforation
operation and postoperative functional disorder. The Fisher’s (n = 4).
exact test was used for qualitative variables analysis, Student Preoperative studies used were contrast enema (95.6%),
t-test for quantitative variables analysis and Mann and Whitney colonoscopy (84.8%), ultrasonography (77%) and CT scan
test for non parametric variables analysis. To build logistic (72.7%).
multivariate analysis, only variables which were statistically Causes of conversion, risk factors and complications of the
significant in univariate model (p < 0.1) were kept. Results for surgery is presented in Table 2 to 9.
logistic multivariate model are presented as odds-ratio. All
statistical analysis were done using Stata 10.0 software (Stata Operative
Corp LP, College Station, TX). Associated lesions were presented 40 (19.51%) of patients.
Those consisted of gallbladder stones (n = 15); benign colonic
RESULTS neoplasms (n = 12); hernias of the abdominal wall (n = 5);
Preoperative adnexal masses (n = 4); colon cancer (n= 1); Meckel’s
diverticulum (n = 1); renal cyst (n = 1) and a cyst of the biliary
Patients were 107 (52.2%) women and 98 (47.8%) men with a tract (n = 1). Intraoperative adhesions were noted in 36 (17.56%)
median age of 60 (30-90) years. There were 46 (22.4%) subjects cases.
2
aged < 50 years. The mean BMI was 25.3 (+ 3.5) kg/m with There were 10 intraoperative complications (Table 10).
23