Page 22 - WJOLS
P. 22
Rooh-ul-Muqim et al
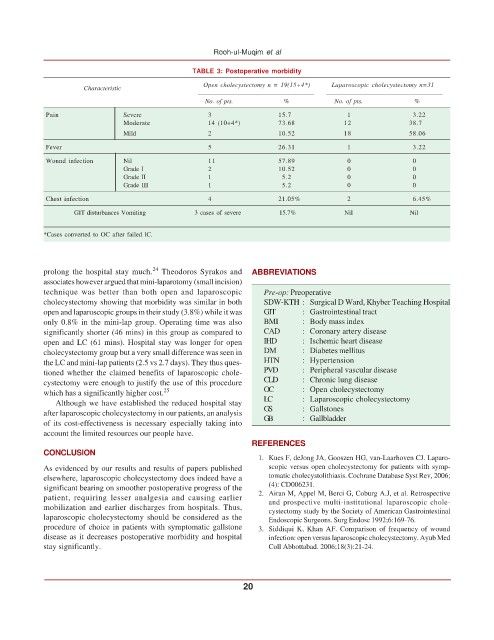
TABLE 3: Postoperative morbidity
Open cholecystectomy n = 19(15+4*) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy n=31
Characteristic
No. of pts. % No. of pts. %
Pain Severe 3 15.7 1 3.22
Moderate 14 (10+4*) 73.68 12 38.7
Mild 2 10.52 18 58.06
Fever 5 26.31 1 3.22
Wound infection Nil 11 57.89 0 0
Grade I 2 10.52 0 0
Grade II 1 5.2 0 0
Grade III 1 5.2 0 0
Chest infection 4 21.05% 2 6.45%
GIT disturbances Vomiting 3 cases of severe 15.7% Nil Nil
*Cases converted to OC after failed lC.
24
prolong the hospital stay much. Theodoros Syrakos and ABBREVIATIONS
associates however argued that mini-laparotomy (small incision)
technique was better than both open and laparoscopic Pre-op: Preoperative
cholecystectomy showing that morbidity was similar in both SDW-KTH : Surgical D Ward, Khyber Teaching Hospital
open and laparoscopic groups in their study (3.8%) while it was GIT : Gastrointestinal tract
only 0.8% in the mini-lap group. Operating time was also BMI : Body mass index
significantly shorter (46 mins) in this group as compared to CAD : Coronary artery disease
open and LC (61 mins). Hospital stay was longer for open IHD : Ischemic heart disease
cholecystectomy group but a very small difference was seen in DM : Diabetes mellitus
the LC and mini-lap patients (2.5 vs 2.7 days). They thus ques- HTN : Hypertension
tioned whether the claimed benefits of laparoscopic chole- PVD : Peripheral vascular disease
cystectomy were enough to justify the use of this procedure CLD : Chronic lung disease
which has a significantly higher cost. 25 OC : Open cholecystectomy
Although we have established the reduced hospital stay LC : Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
after laparoscopic cholecystectomy in our patients, an analysis GS : Gallstones
of its cost-effectiveness is necessary especially taking into GB : Gallbladder
account the limited resources our people have.
REFERENCES
CONCLUSION
1. Kues F, deJong JA, Gooszen HG, van-Laarhoven CJ. Laparo-
As evidenced by our results and results of papers published scopic versus open cholecystectomy for patients with symp-
elsewhere, laparoscopic cholecystectomy does indeed have a tomatic cholecystolithiasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2006;
significant bearing on smoother postoperative progress of the (4): CD006231.
patient, requiring lesser analgesia and causing earlier 2. Airan M, Appel M, Berci G, Coburg A.J, et al. Retrospective
and prospective multi-institutional laparoscopic chole-
mobilization and earlier discharges from hospitals. Thus, cystectomy study by the Society of American Gastrointestinal
laparoscopic cholecystectomy should be considered as the Endoscopic Surgeons. Surg Endosc 1992;6:169-76.
procedure of choice in patients with symptomatic gallstone 3. Siddiqui K, Khan AF. Comparison of frequency of wound
disease as it decreases postoperative morbidity and hospital infection: open versus laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Ayub Med
stay significantly. Coll Abbottabad. 2006;18(3):21-24.
20