Page 5 - Journal of WALS
P. 5
WJOLS
Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair in Patients with Child C Cirrhosis: Our Experience
leak rate of 15%, wound infection of 25% and recurrence use of dual mesh prevents ascitic leak and decreases the
rate of 10%. recurrence rate. It also avoids exposure of viscera reducing
These studies quoted above show that the morbidity and the electrolyte and protein losses in cirrhotic patients and
mortality of open hernia repair in cirrhotic ascetic patients perioperative blood loss is minimal. 11
is high. In a study done by Belli G et al, 14 patients with child
When ventral hernias in patients with ascites have been A cirrhosis with umbilical/incisional hernia underwent
left untreated there have been reports of rupture and laparoscopic mesh hernia repair. There was no conversion
evisceration of omentum due to massive ascites. A sudden to open method with a minor complicatons rate of
increase in intra-abdominal pressure due to vomiting, 78% (seroma, postoperative ileus, skin breakdown etc).
coughing or even straining at stools can cause the rupture There were no recurrences in the follow-up period of
10
of an umbilical hernia. Signs of discoloration, ulceration 8 months.
or sudden rapid increase in size of the umbilical hernia are Another study was conducted by Jitea N et al to evaluate
features of impending rupture. Hence, to avoid this dreaded the efficacy using prolene mesh in laparoscopic umbilical
7
life-threatening complication elective hernia repair should hernia repair. A total of 21 patients were included of which
be planned in all cirrhotic ascitic patients with umbilical five patients had cirrhotic ascites. There were no recurrences
hernia. and morbidity was around 38%. This study has showed that
Safety of laparoscopic surgery is still a debate in cirrhotic laparoscopic repair using prolene intraperitoneal mesh is a
patients and was previously considered a contraindication safe and efficient method and helps to avoid infections and
due to associated coagulation defects, portal hypertension complications in cirrhotic patients. 11
immunosupression and technical difficulties due to massive In our study, a total of three patients with child C
ascites. cirrhosis were included, and all had massive refractory
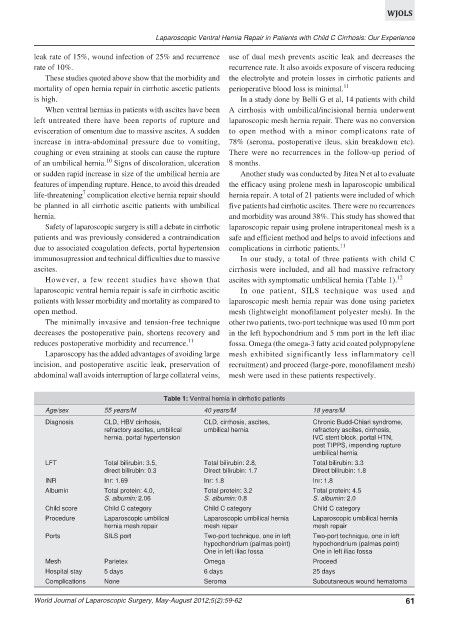
However, a few recent studies have shown that ascites with symptomatic umbilical hernia (Table 1). 12
laparoscopic ventral hernia repair is safe in cirrhotic ascitic In one patient, SILS technique was used and
patients with lesser morbidity and mortality as compared to laparoscopic mesh hernia repair was done using parietex
open method. mesh (lightweight monofilament polyester mesh). In the
The minimally invasive and tension-free technique other two patients, two-port technique was used 10 mm port
decreases the postoperative pain, shortens recovery and in the left hypochondrium and 5 mm port in the left iliac
reduces postoperative morbidity and recurrence. 11 fossa. Omega (the omega-3 fatty acid coated polypropylene
Laparoscopy has the added advantages of avoiding large mesh exhibited significantly less inflammatory cell
incision, and postoperative ascitic leak, preservation of recruitment) and proceed (large-pore, monofilament mesh)
abdominal wall avoids interruption of large collateral veins, mesh were used in these patients respectively.
Table 1: Ventral hernia in cirrhotic patients
Age/sex 55 years/M 40 years/M 18 years/M
Diagnosis CLD, HBV cirrhosis, CLD, cirrhosis, ascites, Chronic Budd-Chiari syndrome,
refractory ascites, umbilical umbilical hernia refractory ascites, cirrhosis,
hernia, portal hypertension IVC stent block, portal HTN,
post TIPPS, impending rupture
umbilical hernia
LFT Total bilirubin: 3.5, Total bilirubin: 2.8, Total bilirubin: 3.3
direct bilirubin: 0.3 Direct bilirubin: 1.7 Direct bilirubin: 1.8
INR Inr: 1.69 Inr: 1.8 Inr: 1.8
Albumin Total protein: 4.0, Total protein: 3.2 Total protein: 4.5
S. albumin: 2.06 S. albumin: 0.8 S. albumin: 2.0
Child score Child C category Child C category Child C category
Procedure Laparoscopic umbilical Laparoscopic umbilical hernia Laparoscopic umbilical hernia
hernia mesh repair mesh repair mesh repair
Ports SILS port Two-port technique, one in left Two-port technique, one in left
hypochondrium (palmas point) hypochondrium (palmas point)
One in left iliac fossa One in left iliac fossa
Mesh Parietex Omega Proceed
Hospital stay 5 days 6 days 25 days
Complications None Seroma Subcutaneous wound hematoma
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2012;5(2):59-62 61