Page 18 - WALS Journal
P. 18
WJOLS
Laparoscopic Management of Renal Hydatid Cyst
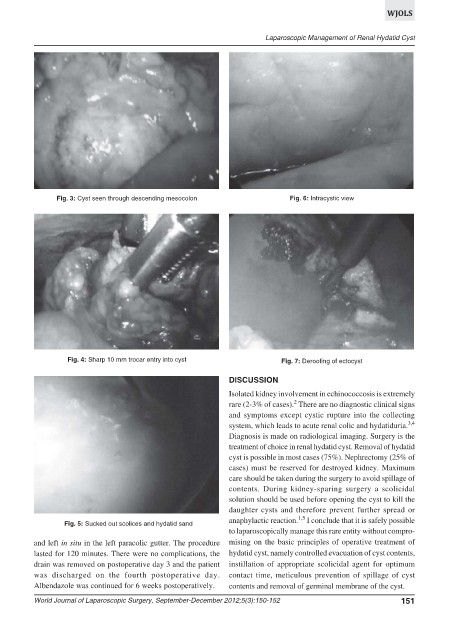
Fig. 3: Cyst seen through descending mesocolon Fig. 6: Intracystic view
Fig. 4: Sharp 10 mm trocar entry into cyst Fig. 7: Deroofing of ectocyst
DISCUSSION
Isolated kidney involvement in echinococcosis is extremely
2
rare (2-3% of cases). There are no diagnostic clinical signs
and symptoms except cystic rupture into the collecting
system, which leads to acute renal colic and hydatiduria. 3,4
Diagnosis is made on radiological imaging. Surgery is the
treatment of choice in renal hydatid cyst. Removal of hydatid
cyst is possible in most cases (75%). Nephrectomy (25% of
cases) must be reserved for destroyed kidney. Maximum
care should be taken during the surgery to avoid spillage of
contents. During kidney-sparing surgery a scolicidal
solution should be used before opening the cyst to kill the
daughter cysts and therefore prevent further spread or
1,5
anaphylactic reaction. I conclude that it is safely possible
Fig. 5: Sucked out scolices and hydatid sand
to laparoscopically manage this rare entity without compro-
and left in situ in the left paracolic gutter. The procedure mising on the basic principles of operative treatment of
lasted for 120 minutes. There were no complications, the hydatid cyst, namely controlled evacuation of cyst contents,
drain was removed on postoperative day 3 and the patient instillation of appropriate scolicidal agent for optimum
was discharged on the fourth postoperative day. contact time, meticulous prevention of spillage of cyst
Albendazole was continued for 6 weeks postoperatively. contents and removal of germinal membrane of the cyst.
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, September-December 2012;5(3):150-152 151