Page 18 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 18
MA Bahram
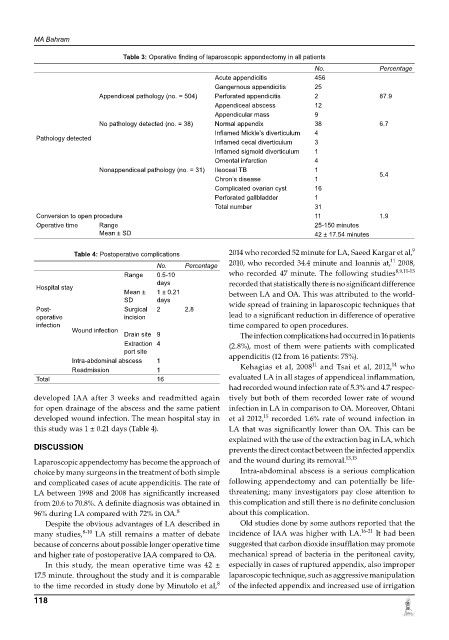
Table 3: operative finding of laparoscopic appendectomy in all patients
No. Percentage
Acute appendicitis 456
Gangernous appendicitis 25
Appendiceal pathology (no. = 504) Perforated appendicitis 2 87.9
Appendiceal abscess 12
Appendicular mass 9
No pathology detected (no. = 38) Normal appendix 38 6.7
Inflamed Mickle’s diverticulum 4
Pathology detected
Inflamed cecal diverticulum 3
Inflamed sigmoid diverticulum 1
omental infarction 4
Nonappendiceal pathology (no. = 31) Ileoceal TB 1 5.4
Chron’s disease 1
Complicated ovarian cyst 16
Perforated gallbladder 1
Total number 31
Conversion to open procedure 11 1.9
operative time range 25150 minutes
Mean ± SD 42 ± 17.54 minutes
9
Table 4: Postoperative complications 2014 who recorded 52 minute forLA,SaeedKargaretal,
11
No. Percentage 2010, who recorded 34.4 minute and Ioannis at, 2008,
range 0.510 who recorded 47 minute. The following studies 8,9,1113
days recordedthatstatisticallythereisnosignificantdifference
Hospital stay
Mean ± 1 ± 0.21 betweenLAandOA.Thiswasattributed to the world
SD days
Post Surgical 2 2.8 wide spread of training in laparoscopic techniques that
operative incision leadtoasignificantreductionindifferenceofoperative
infection time compared to open procedures.
Wound infection
Drain site 9 The infection complications had occurred in 16 patients
extraction 4 (2.8%), most of them were patients with complicated
port site
Intraabdominal abscess 1 appendicitis (12 from 16 patients: 75%). 14
11
Readmission 1 Kehagiasetal,2008 and Tsai et al, 2012, who
Total 16 evaluatedLAinallstagesofappendicealinflammation,
had recor ded wound infection rate of 5.3% and 4.7 respec
developed IAA after 3 weeks and readmitted again tively but both of them recorded lower rate of wound
for open drainage of the abscess and the same patient infectioninLAincomparisontoOA.Moreover,Ohtani
15
developed wound infection. The mean hospital stay in et al 2012, recorded 1.6% rate of wound infection in
this study was 1 ± 0.21 days (Table 4). LAthatwassignificantly lower than OA. This can be
explainedwiththeuseoftheextractionbaginLA,which
dISCuSSIon prevents the direct contact between the infected appendix
Laparoscopicappendectomyhasbecometheapproachof and the wound during its removal. 13,15
choice by many surgeons in the treatment of both simple Intraabdominal abscess is a serious complication
and complicated cases of acute appendicitis. The rate of following appendectomy and can potentially be life
LAbetween1998and2008hassignificantlyincreased threatening; many investigators pay close attention to
from20.6to70.8%.Adefinitediagnosiswasobtainedin thiscomplicationandstillthereisnodefiniteconclusion
96%duringLAcomparedwith72%inOA. 8 about this complication.
DespitetheobviousadvantagesofLAdescribedin Old studies done by some authors reported that the
many studies, 810 LAstillremainsamatterofdebate incidenceofIAAwashigherwithLA. 1621 It had been
because of concerns about possible longer operative time suggestedthatcarbondioxideinsufflationmaypromote
and higher rate of postoperative IAA compared to OA. mechanical spread of bacteria in the peritoneal cavity,
In this study, the mean operative time was 42 ± especially in cases of ruptured appendix, also improper
17.5 minute. throughout the study and it is comparable laparoscopic technique, such as aggressive manipulation
8
to the time recorded in study done by Minutolo et al, of the infected appendix and increased use of irrigation
118