Page 23 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 23
WJOLS
Remission of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
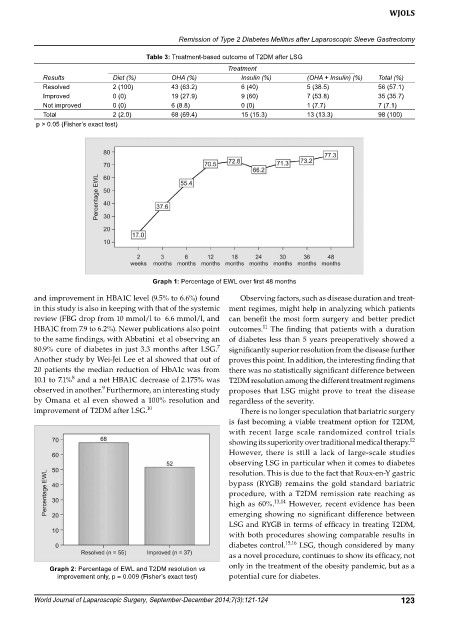
Table 3: Treatment-based outcome of T2DM after LSG
Treatment
Results Diet (%) OHA (%) Insulin (%) (OHA + Insulin) (%) Total (%)
Resolved 2 (100) 43 (63.2) 6 (40) 5 (38.5) 56 (57.1)
Improved 0 (0) 19 (27.9) 9 (60) 7 (53.8) 35 (35.7)
Not improved 0 (0) 6 (8.8) 0 (0) 1 (7.7) 7 (7.1)
Total 2 (2.0) 68 (69.4) 15 (15.3) 13 (13.3) 98 (100)
p > 0.05 (Fisher’s exact test)
Graph 1: Percentage of EWL over first 48 months
and improvement in HBA1C level (9.5% to 6.6%) found Observing factors, such as disease duration and treat
in this study is also in keeping with that of the systemic ment regimes, might help in analyzing which patients
review (FBG drop from 10 mmol/l to 6.6 mmol/l, and can benefit the most form surgery and better predict
11
HBA1C from 7.9 to 6.2%). Newer publications also point outcomes. The finding that patients with a duration
to the same findings, with Abbatini et al observing an of diabetes less than 5 years preoperatively showed a
7
80.9% cure of diabetes in just 3.3 months after LSG. significantly superior resolution from the disease further
Another study by WeiJei Lee et al showed that out of proves this point. In addition, the interesting finding that
20 patients the median reduction of HbA1c was from there was no statistically significant difference between
8
10.1 to 7.1% and a net HBA1C decrease of 2.175% was T2DM resolution among the different treatment regimens
9
observed in another. Furthermore, an interesting study proposes that LSG might prove to treat the disease
by Omana et al even showed a 100% resolution and regardless of the severity.
10
improvement of T2DM after LSG. There is no longer speculation that bariatric surgery
is fast becoming a viable treatment option for T2DM,
with recent large scale randomized control trials
showing its superiority over traditional medical therapy. 12
However, there is still a lack of largescale studies
observing LSG in particular when it comes to diabetes
resolution. This is due to the fact that RouxenY gastric
bypass (RYGB) remains the gold standard bariatric
procedure, with a T2DM remission rate reaching as
high as 60%. 13,14 However, recent evidence has been
emerging showing no significant difference between
LSG and RYGB in terms of efficacy in treating T2DM,
with both procedures showing comparable results in
diabetes control. 15,16 LSG, though considered by many
as a novel procedure, continues to show its efficacy, not
only in the treatment of the obesity pandemic, but as a
Graph 2: Percentage of EWL and T2DM resolution vs
improvement only, p = 0.009 (Fisher’s exact test) potential cure for diabetes.
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, September-December 2014;7(3):121-124 123