Page 39 - WJOLS - Laparoscopic Journal
P. 39
WJOLS
Comparison between Different Entry Techniques in Performing Pneumoperitoneum in Laparoscopic Gynecological Surgery
end points (pops) making their success unpredictable. The Table 1: Incidence of laparoscopic complications according to
description of the landmark technique for performing Veress trocar (total no. 222)
transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block advocated Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
a single entry point, the triangle of Petit, to access a Vascular injury 5
number of abdominal wall nerves hence, providing Visceral injury 0
21
more widespread analgesia. More recently, ultrasound Preperitoneal insufflations 5
0
Gas embolism
guided TAP block has been described with promises of Bradycardia 2
better localization and deposition of the local anesthetic Total 12 (5.40%)
22
with improved accuracy. The Journal of New York
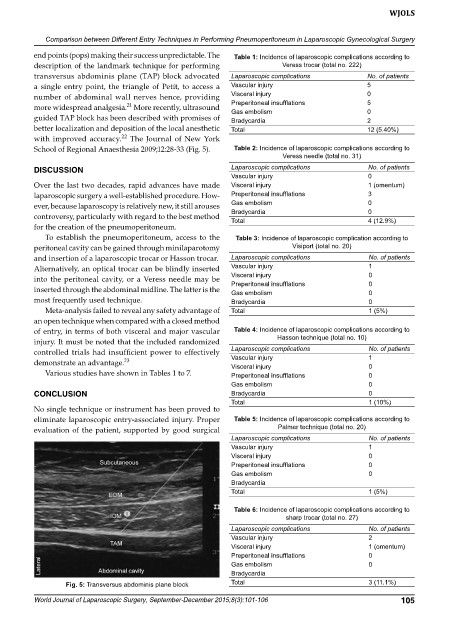
School of Regional Anaesthesia 2009;12:2833 (Fig. 5). Table 2: Incidence of laparoscopic complications according to
Veress needle (total no. 31)
DISCUSSION Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
Vascular injury 0
Over the last two decades, rapid advances have made Visceral injury 1 (omentum)
laparoscopic surgery a wellestablished procedure. How Preperitoneal insufflations 3
ever, because laparoscopy is relatively new, it still arouses Gas embolism 0
controversy, particularly with regard to the best method Bradycardia 0
4 (12.9%)
Total
for the creation of the pneumoperitoneum.
To establish the pneumoperitoneum, access to the Table 3: Incidence of laparoscopic complication according to
peritoneal cavity can be gained through minilaparotomy Visiport (total no. 20)
and insertion of a laparoscopic trocar or Hasson trocar. Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
Alternatively, an optical trocar can be blindly inserted Vascular injury 1
into the peritoneal cavity, or a Veress needle may be Visceral injury 0
Preperitoneal insufflations
0
inserted through the abdominal midline. The latter is the Gas embolism 0
most frequently used technique. Bradycardia 0
Metaanalysis failed to reveal any safety advantage of Total 1 (5%)
an open technique when compared with a closed method
of entry, in terms of both visceral and major vascular Table 4: Incidence of laparoscopic complications according to
injury. It must be noted that the included randomized Hasson technique (total no. 10)
controlled trials had insufficient power to effectively Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
1
Vascular injury
demonstrate an advantage. 23 Visceral injury 0
Various studies have shown in Tables 1 to 7. Preperitoneal insufflations 0
Gas embolism 0
CONCLUSION Bradycardia 0
Total 1 (10%)
No single technique or instrument has been proved to
eliminate laparoscopic entryassociated injury. Proper Table 5: Incidence of laparoscopic complications according to
evaluation of the patient, supported by good surgical Palmer technique (total no. 20)
Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
Vascular injury 1
Visceral injury 0
Preperitoneal insufflations 0
Gas embolism 0
Bradycardia
Total 1 (5%)
Table 6: Incidence of laparoscopic complications according to
sharp trocar (total no. 27)
Laparoscopic complications No. of patients
Vascular injury 2
Visceral injury 1 (omentum)
Preperitoneal insufflations 0
Gas embolism 0
Bradycardia
Fig. 5: Transversus abdominis plane block Total 3 (11.1%)
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, September-December 2015;8(3):101-106 105