Page 42 - WJOLS - Laparoscopic Journal
P. 42
Deepti Shrivastava et al
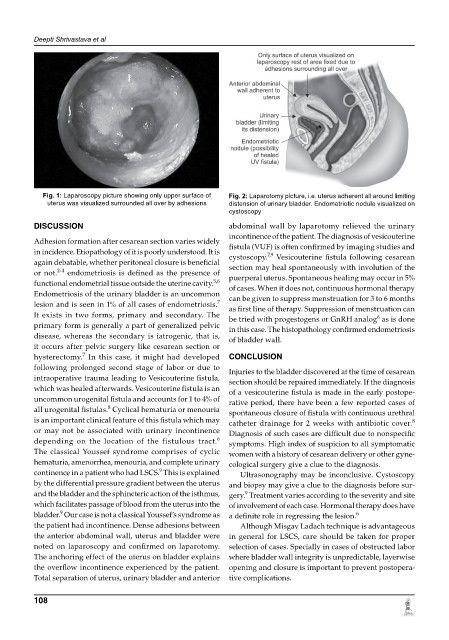
Fig. 1: Laparoscopy picture showing only upper surface of Fig. 2: Laparotomy picture, i.e. uterus adherent all around limiting
uterus was visualized surrounded all over by adhesions distension of urinary bladder. Endometriotic nodule visualized on
cystoscopy
DISCUSSION abdominal wall by laparotomy relieved the urinary
incontinence of the patient. The diagnosis of vesicouterine
Adhesion formation after cesarean section varies widely fistula (VUF) is often confirmed by imaging studies and
in incidence. Etiopathology of it is poorly understood. It is cystoscopy. Vesicouterine fistula following cesarean
7,9
again debatable, whether peritoneal closure is beneficial section may heal spontaneously with involution of the
2-4
or not. endometriosis is defined as the presence of puerperal uterus. Spontaneous healing may occur in 5%
5,6
functional endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity. of cases. When it does not, continuous hormonal therapy
Endometriosis of the urinary bladder is an uncommon can be given to suppress menstruation for 3 to 6 months
7
lesion and is seen in 1% of all cases of endometriosis. as first line of therapy. Suppression of menstruation can
It exists in two forms, primary and secondary. The be tried with progestogens or GnRH analog as is done
6
primary form is generally a part of generalized pelvic in this case. The histopathology confirmed endometriosis
disease, whereas the secondary is iatrogenic, that is, of bladder wall.
it occurs after pelvic surgery like cesarean section or
hysterectomy. In this case, it might had developed CONCLUSION
7
following prolonged second stage of labor or due to Injuries to the bladder discovered at the time of cesarean
intraoperative trauma leading to Vesicouterine fistula, section should be repaired immediately. If the diagnosis
which was healed afterwards. Vesicouterine fistula is an of a vesicouterine fistula is made in the early postope
uncommon urogenital fistula and accounts for 1 to 4% of rative period, there have been a few reported cases of
8
all urogenital fistulas. Cyclical hematuria or menouria spontaneous closure of fistula with continuous urethral
is an important clinical feature of this fistula which may catheter drainage for 2 weeks with antibiotic cover.
8
or may not be associated with urinary incontinence Diagnosis of such cases are difficult due to nonspecific
6
depending on the location of the fistulous tract. symptoms. High index of suspicion to all symptomatic
The classical Youssef syndrome comprises of cyclic women with a history of cesarean delivery or other gyne-
hematuria, amenorrhea, menouria, and complete urinary cological surgery give a clue to the diagnosis.
9
continence in a patient who had LSCS. This is explained Ultrasonography may be inconclusive. Cystoscopy
by the differential pressure gradient between the uterus and biopsy may give a clue to the diagnosis before sur-
9
and the bladder and the sphincteric action of the isthmus, gery. Treatment varies according to the severity and site
which facilitates passage of blood from the uterus into the of involvement of each case. Hormonal therapy does have
9
6
bladder. Our case is not a classical Youssef’s syndrome as a definite role in regressing the lesion.
the patient had incontinence. Dense adhesions between Although Misgav Ladach technique is advantageous
the anterior abdominal wall, uterus and bladder were in general for LSCS, care should be taken for proper
noted on laparoscopy and confirmed on laparotomy. selection of cases. Specially in cases of obstructed labor
The anchoring effect of the uterus on bladder explains where bladder wall integrity is unpredictable, layerwise
the overflow incontinence experienced by the patient. opening and closure is important to prevent postopera-
Total separation of uterus, urinary bladder and anterior tive complications.
108