Page 18 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 18
Sheriff Z Kotb et al
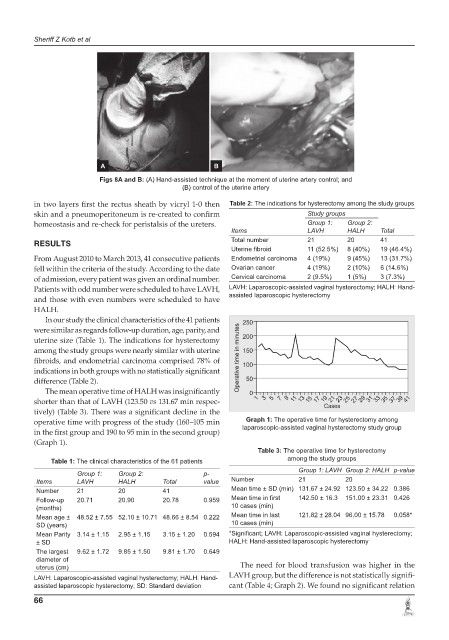
A B
Figs 8A and B: (A) Hand-assisted technique at the moment of uterine artery control; and
(B) control of the uterine artery
in two layers first the rectus sheath by vicryl 1-0 then Table 2: The indications for hysterectomy among the study groups
skin and a pneumoperitoneum is re-created to confirm Study groups
homeostasis and re-check for peristalsis of the ureters. Group 1: Group 2:
Items LAVH HALH Total
RESULTS Total number 21 20 41
Uterine fibroid 11 (52.5%) 8 (40%) 19 (46.4%)
From August 2010 to March 2013, 41 consecutive patients Endometrial carcinoma 4 (19%) 9 (45%) 13 (31.7%)
fell within the criteria of the study. According to the date Ovarian cancer 4 (19%) 2 (10%) 6 (14.6%)
of admission, every patient was given an ordinal number. Cervical carcinoma 2 (9.5%) 1 (5%) 3 (7.3%)
Patients with odd number were scheduled to have LAVH, LAVH: Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy; HALH: Hand-
and those with even numbers were scheduled to have assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy
HALH.
In our study the clinical characteristics of the 41 patients
were similar as regards follow-up duration, age, parity, and
uterine size (Table 1). The indications for hysterectomy
among the study groups were nearly similar with uterine
fibroids, and endometrial carcinoma comprised 78% of
indications in both groups with no statistically significant
difference (Table 2).
The mean operative time of HALH was insignificantly
shorter than that of LAVH (123.50 vs 131.67 min respec-
tively) (Table 3). There was a significant decline in the
Graph 1: The operative time for hysterectomy among
operative time with progress of the study (160–105 min laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy study group
in the first group and 190 to 95 min in the second group)
(Graph 1).
Table 3: The operative time for hysterectomy
Table 1: The clinical characteristics of the 61 patients among the study groups
Group 1: LAVH Group 2: HALH p-value
Group 1: Group 2: p-
Items LAVH HALH Total value Number 21 20
Number 21 20 41 Mean time ± SD (min) 131.67 ± 24.92 123.50 ± 34.22 0.386
Follow-up 20.71 20.90 20.78 0.959 Mean time in first 142.50 ± 16.3 151.00 ± 23.31 0.426
(months) 10 cases (min)
Mean age ± 48.52 ± 7.55 52.10 ± 10.71 48.66 ± 8.54 0.222 Mean time in last 121.82 ± 28.04 96.00 ± 15.78 0.058*
SD (years) 10 cases (min)
Mean Parity 3.14 ± 1.15 2.95 ± 1.15 3.15 ± 1.20 0.594 *Significant; LAVH: Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy;
± SD HALH: Hand-assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy
The largest 9.62 ± 1.72 9.85 ± 1.50 9.81 ± 1.70 0.649
diameter of
uterus (cm) The need for blood transfusion was higher in the
LAVH: Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy; HALH: Hand- LAVH group, but the difference is not statistically signifi-
assisted laparoscopic hysterectomy; SD: Standard deviation cant (Table 4; Graph 2). We found no significant relation
66