Page 11 - WJOLS - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 11
Evaluation of Abdominal Malignancies by Minimal Access Surgery
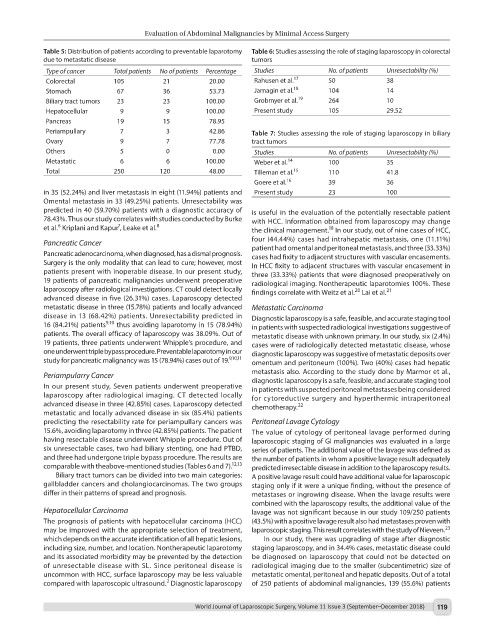
Table 5: Distribution of patients according to preventable laparotomy Table 6: Studies assessing the role of staging laparoscopy in colorectal
due to metastatic disease tumors
Type of cancer Total patients No of patients Percentage Studies No. of patients Unresectability (%)
17
Colorectal 105 21 20.00 Rahusen et al. 50 38
18
Stomach 67 36 53.73 Jarnagin et al. 104 14
19
Biliary tract tumors 23 23 100.00 Grobmyer et al. 264 10
Hepatocellular 9 9 100.00 Present study 105 29.52
Pancreas 19 15 78.95
Periampullary 7 3 42.86 Table 7: Studies assessing the role of staging laparoscopy in biliary
Ovary 9 7 77.78 tract tumors
Others 5 0 0.00 Studies No. of patients Unresectability (%)
Metastatic 6 6 100.00 Weber et al. 100 35
14
Total 250 120 48.00 Tilleman et al. 110 41.8
15
16
Goere et al. 39 36
in 35 (52.24%) and liver metastasis in eight (11.94%) patients and Present study 23 100
Omental metastasis in 33 (49.25%) patients. Unresectability was
predicted in 40 (59.70%) patients with a diagnostic accuracy of is useful in the evaluation of the potentially resectable patient
78.43%. Thus our study correlates with studies conducted by Burke with HCC. Information obtained from laparoscopy may change
7
6
8
et al. Kriplani and Kapur , Leake et al. the clinical management. In our study, out of nine cases of HCC,
18
Pancreatic Cancer four (44.44%) cases had intrahepatic metastasis, one (11.11%)
patient had omental and peritoneal metastasis, and three (33.33%)
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, when diagnosed, has a dismal prognosis. cases had fixity to adjacent structures with vascular encasements.
Surgery is the only modality that can lead to cure; however, most In HCC fixity to adjacent structures with vascular encasement in
patients present with inoperable disease. In our present study, three (33.33%) patients that were diagnosed preoperatively on
19 patients of pancreatic malignancies underwent preoperative radiological imaging. Nontherapeutic laparotomies 100%. These
laparoscopy after radiological investigations. CT could detect locally findings correlate with Weitz et al. Lai et al.
21
20
advanced disease in five (26.31%) cases. Laparoscopy detected
metastatic disease in three (15.78%) patients and locally advanced Metastatic Carcinoma
disease in 13 (68.42%) patients. Unresectability predicted in Diagnostic laparoscopy is a safe, feasible, and accurate staging tool
9,10
16 (84.21%) patients thus avoiding laparotomy in 15 (78.94%) in patients with suspected radiological investigations suggestive of
patients. The overall efficacy of laparoscopy was 38.09%. Out of metastatic disease with unknown primary. In our study, six (2.4%)
19 patients, three patients underwent Whipple’s procedure, and cases were of radiologically detected metastatic disease, whose
one underwent triple bypass procedure. Preventable laparotomy in our diagnostic laparoscopy was suggestive of metastatic deposits over
9,10,11
study for pancreatic malignancy was 15 (78.94%) cases out of 19. omentum and peritoneum (100%). Two (40%) cases had hepatic
Periampularry Cancer metastasis also. According to the study done by Marmor et al.,
diagnostic laparoscopy is a safe, feasible, and accurate staging tool
In our present study, Seven patients underwent preoperative in patients with suspected peritoneal metastases being considered
laparoscopy after radiological imaging. CT detected locally for cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal
advanced disease in three (42.85%) cases. Laparoscopy detected chemotherapy.
22
metastatic and locally advanced disease in six (85.4%) patients
predicting the resectability rate for periampullary cancers was Peritoneal Lavage Cytology
15.6%, avoiding laparotomy in three (42.85%) patients. The patient The value of cytology of peritoneal lavage performed during
having resectable disease underwent Whipple procedure. Out of laparoscopic staging of GI malignancies was evaluated in a large
six unresectable cases, two had biliary stenting, one had PTBD, series of patients. The additional value of the lavage was defined as
and three had undergone triple bypass procedure. The results are the number of patients in whom a positive lavage result adequately
12,13
comparable with theabove-mentioned studies (Tables 6 and 7). predicted irresectable disease in addition to the laparoscopy results.
Biliary tract tumors can be divided into two main categories: A positive lavage result could have additional value for laparoscopic
gallbladder cancers and cholangiocarcinomas. The two groups staging only if it were a unique finding, without the presence of
differ in their patterns of spread and prognosis. metastases or ingrowing disease. When the lavage results were
combined with the laparoscopy results, the additional value of the
Hepatocellular Carcinoma lavage was not significant because in our study 109/250 patients
The prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (43.5%) with a positive lavage result also had metastases proven with
23
may be improved with the appropriate selection of treatment, laparoscopic staging. This result correlates with the study of Nieveen.
which depends on the accurate identification of all hepatic lesions, In our study, there was upgrading of stage after diagnostic
including size, number, and location. Nontherapeutic laparotomy staging laparoscopy, and in 34.4% cases, metastatic disease could
and its associated morbidity may be prevented by the detection be diagnosed on laparoscopy that could not be detected on
of unresectable disease with SL. Since peritoneal disease is radiological imaging due to the smaller (subcentimetric) size of
uncommon with HCC, surface laparoscopy may be less valuable metastatic omental, peritoneal and hepatic deposits. Out of a total
2
compared with laparoscopic ultrasound. Diagnostic laparoscopy of 250 patients of abdominal malignancies, 139 (55.6%) patients
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 11 Issue 3 (September–December 2018) 119