Page 10 - WJOLS - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 10
Evaluation of Abdominal Malignancies by Minimal Access Surgery
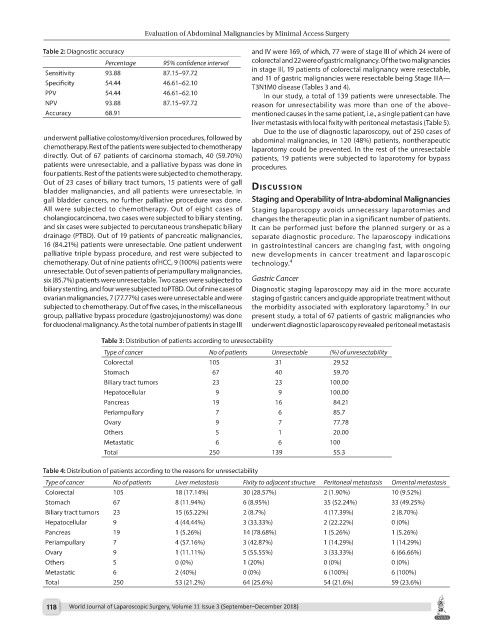
Table 2: Diagnostic accuracy and IV were 169, of which, 77 were of stage III of which 24 were of
Percentage 95% confidence interval colorectal and 22 were of gastric malignancy. Of the two malignancies
Sensitivity 93.88 87.15–97.72 in stage III, 19 patients of colorectal malignancy were resectable,
and 11 of gastric malignancies were resectable being Stage IIIA—
Specificity 54.44 46.61–62.10 T3N1M0 disease (Tables 3 and 4).
PPV 54.44 46.61–62.10 In our study, a total of 139 patients were unresectable. The
NPV 93.88 87.15–97.72 reason for unresectability was more than one of the above-
Accuracy 68.91 mentioned causes in the same patient, i.e., a single patient can have
liver metastasis with local fixity with peritoneal metastasis (Table 5).
Due to the use of diagnostic laparoscopy, out of 250 cases of
underwent palliative colostomy/diversion procedures, followed by abdominal malignancies, in 120 (48%) patients, nontherapeutic
chemotherapy. Rest of the patients were subjected to chemotherapy laparotomy could be prevented. In the rest of the unresectable
directly. Out of 67 patients of carcinoma stomach, 40 (59.70%) patients, 19 patients were subjected to laparotomy for bypass
patients were unresectable, and a palliative bypass was done in procedures.
four patients. Rest of the patients were subjected to chemotherapy.
Out of 23 cases of biliary tract tumors, 15 patients were of gall
bladder malignancies, and all patients were unresectable. In dIscussIon
gall bladder cancers, no further palliative procedure was done. Staging and Operability of Intra-abdominal Malignancies
All were subjected to chemotherapy. Out of eight cases of Staging laparoscopy avoids unnecessary laparotomies and
cholangiocarcinoma, two cases were subjected to biliary stenting, changes the therapeutic plan in a significant number of patients.
and six cases were subjected to percutaneous transhepatic biliary It can be performed just before the planned surgery or as a
drainage (PTBD). Out of 19 patients of pancreatic malignancies, separate diagnostic procedure. The laparoscopy indications
16 (84.21%) patients were unresectable. One patient underwent in gastrointestinal cancers are changing fast, with ongoing
palliative triple bypass procedure, and rest were subjected to new developments in cancer treatment and laparoscopic
4
chemotherapy. Out of nine patients ofHCC, 9 (100%) patients were technology.
unresectable. Out of seven patients of periampullary malignancies,
six (85.7%) patients were unresectable. Two cases were subjected to Gastric Cancer
biliary stenting, and four were subjected toPTBD. Out of nine cases of Diagnostic staging laparoscopy may aid in the more accurate
ovarian malignancies, 7 (77.77%) cases were unresectable and were staging of gastric cancers and guide appropriate treatment without
5
subjected to chemotherapy. Out of five cases, in the miscellaneous the morbidity associated with exploratory laparotomy. In our
group, palliative bypass procedure (gastrojejunostomy) was done present study, a total of 67 patients of gastric malignancies who
for duodenal malignancy. As the total number of patients in stage III underwent diagnostic laparoscopy revealed peritoneal metastasis
Table 3: Distribution of patients according to unresectability
Type of cancer No of patients Unresectable (%) of unresectability
Colorectal 105 31 29.52
Stomach 67 40 59.70
Biliary tract tumors 23 23 100.00
Hepatocellular 9 9 100.00
Pancreas 19 16 84.21
Periampullary 7 6 85.7
Ovary 9 7 77.78
Others 5 1 20.00
Metastatic 6 6 100
Total 250 139 55.3
Table 4: Distribution of patients according to the reasons for unresectability
Type of cancer No of patients Liver metastasis Fixity to adjacent structure Peritoneal metastasis Omental metastasis
Colorectal 105 18 (17.14%) 30 (28.57%) 2 (1.90%) 10 (9.52%)
Stomach 67 8 (11.94%) 6 (8.95%) 35 (52.24%) 33 (49.25%)
Biliary tract tumors 23 15 (65.22%) 2 (8.7%) 4 (17.39%) 2 (8.70%)
Hepatocellular 9 4 (44.44%) 3 (33.33%) 2 (22.22%) 0 (0%)
Pancreas 19 1 (5.26%) 14 (78.68%) 1 (5.26%) 1 (5.26%)
Periampullary 7 4 (57.16%) 3 (42.87%) 1 (14.29%) 1 (14.29%)
Ovary 9 1 (11.11%) 5 (55.55%) 3 (33.33%) 6 (66.66%)
Others 5 0 (0%) 1 (20%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%)
Metastatic 6 2 (40%) 0 (0%) 6 (100%) 6 (100%)
Total 250 53 (21.2%) 64 (25.6%) 54 (21.6%) 59 (23.6%)
118 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 11 Issue 3 (September–December 2018)