Page 50 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 50
The Prevalence of Cancer in Patients Undergoing Appendectomy
13
appendix cancer on average. Pathologically, appendix tumors are Ethics approval: Ethical approval (code: IR. KUMS. REC.1398.185)
diverse, and it seems that the risk of developing various neoplasms was granted from the Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences
of the appendix (except for malignant carcinoid, which involves Ethics Committee.
women three times more than men) is the same for both males
14
and females. Carcinoid is the most common appendix tumor,
while adenocarcinoma, lymphosarcoma, paraganglioma, and Table 1: The frequency distribution of appendix tumors in patients
granular-cellular tumors account for only 10–20% of appendix undergoing appendectomy (n = 41)
15
tumors. Most carcinoid tumors are asymptomatic, and on average, Type of tumor Frequency Percentage
it usually takes 9 years to diagnose the tumor from the time of early Malignant tumors
16
symptoms. When the tumor is located on the appendix base, it
blocks the hole, whereby the patients manifest symptoms similar Adenocarcinoma mucinous 9 34.61
17
to those of appendicitis. The present study aims to examine the Carcinoid 6 23.08
prevalence of malignant tumors of the appendix and determine Adenocarcinoma 5 19.23
its association with demographic and laboratory variables in Mucocele 5 19.23
4940 patients who have undergone appendectomy in Imam Reza
Hospital in Kermanshah, Iran. Cystadenoma 1 3.85
Total 26 100
MAterIAls And Methods Benign tumors
The present study is descriptive cross-sectional, with the study Follicular hyperplasia 9 60
population consisting of all patients who had undergone
appendectomy in 2011–2018 in Imam Reza Hospital in Kermanshah, Lymphoid hyperplasia 3 20
Iran. The exclusion criteria included lack of pathology tests Mucinous cystadenoma 1 6.7
in the file, incomplete information, suffering cancers before Sinus histiocytosis 1 6.7
appendectomy, metastasis to appendix before appendectomy, Follicular lymphoid hyperplasia 1 6.7
taking chemotherapeutic and corticosteroid drugs, radiotherapy,
and use of other immunosuppressive drugs in patients with Total 15 100
acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). From 6086 medical
files of patients undergoing an appendectomy, 1146 were excluded,
and eventually, 4940 files were examined. The required information,
including age, gender, type of tumor, and laboratory information,
was collected from these files.
Data Analysis
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to check the normality
of data distribution. The data were analyzed using descriptive
statistics, including mean and variance for quantitative variables
and frequency/percentage plus two-dimensional contingency
tables for qualitative variables by SPSS 21. The p-value was
considered statistically significant if p ≤0.05.
results
The results indicated that most patients who had undergone
appendectomy in the mentioned hospital were male (n = 3017,
61%), and the rest were female (n = 1923, 39%). The mean age of the
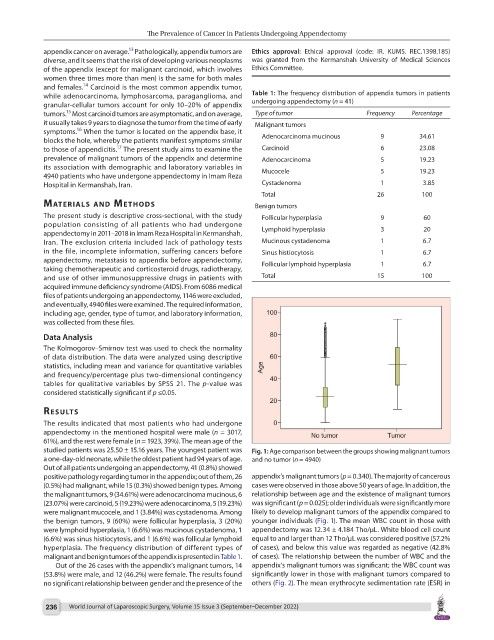
studied patients was 25.50 ± 15.16 years. The youngest patient was Fig. 1: Age comparison between the groups showing malignant tumors
a one-day-old neonate, while the oldest patient had 94 years of age. and no tumor (n = 4940)
Out of all patients undergoing an appendectomy, 41 (0.8%) showed
positive pathology regarding tumor in the appendix; out of them, 26 appendix’s malignant tumors (p = 0.340). The majority of cancerous
(0.5%) had malignant, while 15 (0.3%) showed benign types. Among cases were observed in those above 50 years of age. In addition, the
the malignant tumors, 9 (34.61%) were adenocarcinoma mucinous, 6 relationship between age and the existence of malignant tumors
(23.07%) were carcinoid, 5 (19.23%) were adenocarcinoma, 5 (19.23%) was significant (p = 0.025); older individuals were significantly more
were malignant mucocele, and 1 (3.84%) was cystadenoma. Among likely to develop malignant tumors of the appendix compared to
the benign tumors, 9 (60%) were follicular hyperplasia, 3 (20%) younger individuals (Fig. 1). The mean WBC count in those with
were lymphoid hyperplasia, 1 (6.6%) was mucinous cystadenoma, 1 appendectomy was 12.34 ± 4.184 Tho/µL. White blood cell count
(6.6%) was sinus histiocytosis, and 1 (6.6%) was follicular lymphoid equal to and larger than 12 Tho/µL was considered positive (57.2%
hyperplasia. The frequency distribution of different types of of cases), and below this value was regarded as negative (42.8%
malignant and benign tumors of the appendix is presented in Table 1. of cases). The relationship between the number of WBC and the
Out of the 26 cases with the appendix’s malignant tumors, 14 appendix’s malignant tumors was significant; the WBC count was
(53.8%) were male, and 12 (46.2%) were female. The results found significantly lower in those with malignant tumors compared to
no significant relationship between gender and the presence of the others (Fig. 2). The mean erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in
236 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 3 (September–December 2022)