Page 27 - tmp
P. 27
Intraoperative Finding and Ultrasonographic Scoring for Predicting DLC
Table 5: ROC curve and its AUC for prediction of intraoperative outcome based on preoperative score
Cutoff point AUC (95% CI) p value Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%)
Difficult/very difficult vs easy 5.5 0.974 (0.95–0.99) <0.001 96.9 97.3
Difficult vs easy 5.5 0.975 (0.95–0.99) <0.001 97.7 97.3
Very difficult vs difficult 8.5 0.782 (0.60–0.96) 0.002 75.0 0.62
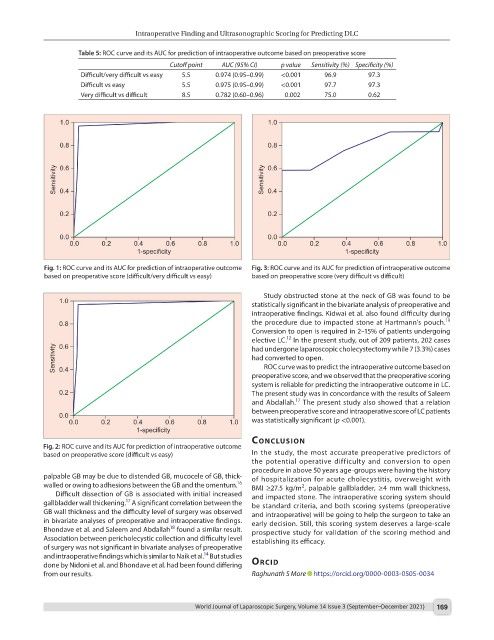
Fig. 1: ROC curve and its AUC for prediction of intraoperative outcome Fig. 3: ROC curve and its AUC for prediction of intraoperative outcome
based on preoperative score (difficult/very difficult vs easy) based on preoperative score (very difficult vs difficult)
Study obstructed stone at the neck of GB was found to be
statistically significant in the bivariate analysis of preoperative and
intraoperative findings. Kidwai et al. also found difficulty during
19
the procedure due to impacted stone at Hartmann’s pouch.
Conversion to open is required in 2–15% of patients undergoing
12
elective LC. In the present study, out of 209 patients, 202 cases
had undergone laparoscopic cholecystectomy while 7 (3.3%) cases
had converted to open.
ROC curve was to predict the intraoperative outcome based on
preoperative score, and we observed that the preoperative scoring
system is reliable for predicting the intraoperative outcome in LC.
The present study was in concordance with the results of Saleem
17
and Abdallah. The present study also showed that a relation
between preoperative score and intraoperative score of LC patients
was statistically significant (p <0.001).
conclusIon
Fig. 2: ROC curve and its AUC for prediction of intraoperative outcome
based on preoperative score (difficult vs easy) In the study, the most accurate preoperative predictors of
the potential operative difficulty and conversion to open
procedure in above 50 years age-groups were having the history
palpable GB may be due to distended GB, mucocele of GB, thick- of hospitalization for acute cholecystitis, overweight with
walled or owing to adhesions between the GB and the omentum. 16 BMI ≥27.5 kg/m , palpable gallbladder, ≥4 mm wall thickness,
2
Difficult dissection of GB is associated with initial increased and impacted stone. The intraoperative scoring system should
17
gallbladder wall thickening. A significant correlation between the be standard criteria, and both scoring systems (preoperative
GB wall thickness and the difficulty level of surgery was observed and intraoperative) will be going to help the surgeon to take an
in bivariate analyses of preoperative and intraoperative findings. early decision. Still, this scoring system deserves a large-scale
18
Bhondave et al. and Saleem and Abdallah found a similar result. prospective study for validation of the scoring method and
Association between pericholecystic collection and difficulty level establishing its efficacy.
of surgery was not significant in bivariate analyses of preoperative
14
and intraoperative findings which is similar to Naik et al. But studies
done by Nidoni et al. and Bhondave et al. had been found differing orcId
from our results. Raghunath S More https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0505-0034
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 3 (September–December 2021) 169