Page 30 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 30
Comparative Outcome of LGI, LSG and LRYGB for Weight Loss and BMI Reduction
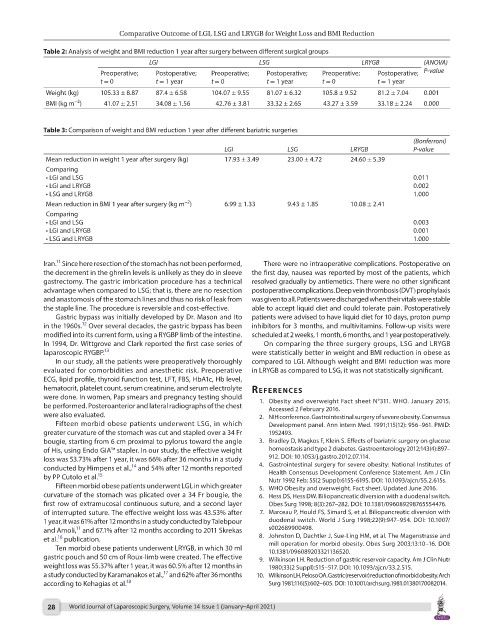
Table 2: Analysis of weight and BMI reduction 1 year after surgery between different surgical groups
LGI LSG LRYGB (ANOVA)
Preoperative; Postoperative; Preoperative; Postoperative; Preoperative; Postoperative; P-value
t = 0 t = 1 year t = 0 t = 1 year t = 0 t = 1 year
Weight (kg) 105.33 ± 8.87 87.4 ± 6.58 104.07 ± 9.55 81.07 ± 6.32 105.8 ± 9.52 81.2 ± 7.04 0.001
−2
BMI (kg m ) 41.07 ± 2.51 34.08 ± 1.56 42.76 ± 3.81 33.32 ± 2.65 43.27 ± 3.59 33.18 ± 2.24 0.000
Table 3: Comparison of weight and BMI reduction 1 year after different bariatric surgeries
(Bonferroni)
LGI LSG LRYGB P-value
Mean reduction in weight 1 year after surgery (kg) 17.93 ± 3.49 23.00 ± 4.72 24.60 ± 5.39
Comparing
• LGI and LSG 0.011
• LGI and LRYGB 0.002
• LSG and LRYGB 1.000
−2
Mean reduction in BMI 1 year after surgery (kg m ) 6.99 ± 1.33 9.43 ± 1.85 10.08 ± 2.41
Comparing
• LGI and LSG 0.003
• LGI and LRYGB 0.001
• LSG and LRYGB 1.000
11
Iran. Since here resection of the stomach has not been performed, There were no intraoperative complications. Postoperative on
the decrement in the ghrelin levels is unlikely as they do in sleeve the first day, nausea was reported by most of the patients, which
gastrectomy. The gastric imbrication procedure has a technical resolved gradually by antiemetics. There were no other significant
advantage when compared to LSG; that is, there are no resection postoperative complications. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis
and anastomosis of the stomach lines and thus no risk of leak from was given to all. Patients were discharged when their vitals were stable
the staple line. The procedure is reversible and cost-effective. able to accept liquid diet and could tolerate pain. Postoperatively
Gastric bypass was initially developed by Dr. Mason and Ito patients were advised to have liquid diet for 10 days, proton pump
12
in the 1960s. Over several decades, the gastric bypass has been inhibitors for 3 months, and multivitamins. Follow-up visits were
modified into its current form, using a RYGBP limb of the intestine. scheduled at 2 weeks, 1 month, 6 months, and 1 year postoperatively.
In 1994, Dr. Wittgrove and Clark reported the first case series of On comparing the three surgery groups, LSG and LRYGB
laparoscopic RYGBP. 13 were statistically better in weight and BMI reduction in obese as
In our study, all the patients were preoperatively thoroughly compared to LGI. Although weight and BMI reduction was more
evaluated for comorbidities and anesthetic risk. Preoperative in LRYGB as compared to LSG, it was not statistically significant.
ECG, lipid profile, thyroid function test, LFT, FBS, HbA1c, Hb level,
hematocrit, platelet count, serum creatinine, and serum electrolyte references
were done. In women, Pap smears and pregnancy testing should 1. Obesity and overweight Fact sheet N°311. WHO. January 2015.
be performed. Posteroanterior and lateral radiographs of the chest Accessed 2 February 2016.
were also evaluated. 2. NIH conference. Gastrointestinal surgery of severe obesity. Consensus
Fifteen morbid obese patients underwent LSG, in which Development panel. Ann intern Med. 1991;115(12): 956–961. PMID:
greater curvature of the stomach was cut and stapled over a 34 Fr 1952493.
bougie, starting from 6 cm proximal to pylorus toward the angle 3. Bradley D, Magkos F, Klein S. Effects of bariatric surgery on glucose
of His, using Endo GIA™ stapler. In our study, the effective weight homeostasis and type 2 diabetes. Gastroenterology 2012;143(4):897–
loss was 53.73% after 1 year, it was 66% after 36 months in a study 912. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.07.114.
14
conducted by Himpens et al., and 54% after 12 months reported 4. Gastrointestinal surgery for severe obesity: National Institutes of
by PP Cutolo et al. 15 Health Consensus Development Conference Statement. Am J Clin
Nutr 1992 Feb; 55(2 Suppl):615S-619S. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/55.2.615s.
Fifteen morbid obese patients underwent LGI, in which greater 5. WHO Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet. Updated June 2016.
curvature of the stomach was plicated over a 34 Fr bougie, the 6. Hess DS, Hess DW. Biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch.
first row of extramucosal continuous suture, and a second layer Obes Surg 1998; 8(3):267–282. DOI: 10.1381/096089298765554476.
of interrupted suture. The effective weight loss was 43.53% after 7. Marceau P, Hould FS, Simard S, et al. Biliopancreatic diversion with
1 year, it was 61% after 12 months in a study conducted by Talebpour duodenal switch. World J Surg 1998;22(9):947–954. DOI: 10.1007/
11
and Amoli, and 67.1% after 12 months according to 2011 Skrekas s002689900498.
16
et al. publication. 8. Johnston D, Dachtler J, Sue-Ling HM, et al. The Magenstrasse and
Ten morbid obese patients underwent LRYGB, in which 30 ml mill operation for morbid obesity. Obes Surg 2003;13:10–16. DOI:
10.1381/096089203321136520.
gastric pouch and 50 cm of Roux-limb were created. The effective 9. Wilkinson LH. Reduction of gastric reservoir capacity. Am J Clin Nutr
weight loss was 55.37% after 1 year, it was 60.5% after 12 months in 1980;33(2 Suppl):515–517. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/33.2.515.
17
a study conducted by Karamanakos et al., and 62% after 36 months 10. Wilkinson LH, Peloso OA. Gastric (reservoir) reduction of morbid obesity. Arch
according to Kehagias et al. 18 Surg 1981;116(5):602–605. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380170082014.
28 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 1 (January–April 2021)