Page 39 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 39
Role of NOTES in the Diagnosis of Women Pelvic Pathologies
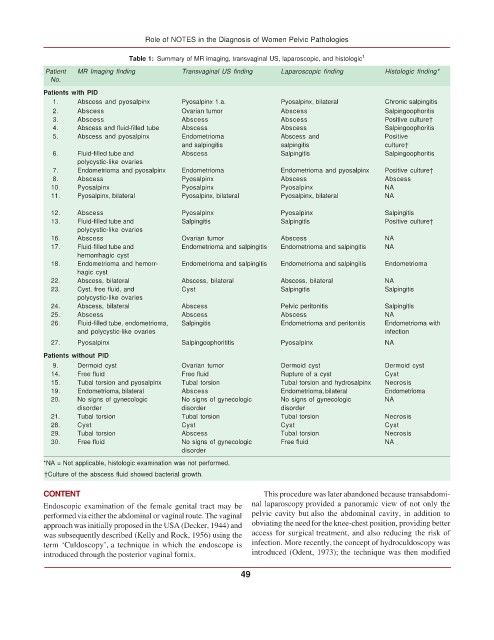
Table 1: Summary of MR imaging, transvaginal US, laparoscopic, and histologic 1
Patient MR Imaging finding Transvaginal US finding Laparoscopic finding Histologic finding*
No.
Patients with PID
1. Abscess and pyosalpinx Pyosalpinx 1.a. Pyosalpinx, bilateral Chronic salpingitis
2. Abscess Ovarian tumor Abscess Salpingoophoritis
3. Abscess Abscess Abscess Positive culture†
4. Abscess and fluid-filled tube Abscess Abscess Salpingoophoritis
5. Abscess and pyosalpinx Endometrioma Abscess and Positive
and salpingitis salpingitis culture†
6. Fluid-filled tube and Abscess Salpingitis Salpingoophoritis
polycystic-like ovaries
7. Endometrioma and pyosalpinx Endometrioma Endometrioma and pyosalpinx Positive culture†
8. Abscess Pyosalpinx Abscess Abscess
10. Pyosalpinx Pyosalpinx Pyosalpinx NA
11. Pyosalpinx, bilateral Pyosalpinx, bilateral Pyosalpinx, bilateral NA
12. Abscess Pyosalpinx Pyosalpinx Salpingitis
13. Fluid-filled tube and Salpingitis Salpingitis Positive culture†
polycystic-like ovaries
16. Abscess Ovarian tumor Abscess NA
17. Fluid-filled tube and Endometrioma and salpingitis Endometrioma and salpingitis NA
hemorrhagic cyst
18. Endometrioma and hemorr- Endometrioma and salpingitis Endometrioma and salpingitis Endometrioma
hagic cyst
22. Abscess, bilateral Abscess, bilateral Abscess, bilateral NA
23. Cyst, free fluid, and Cyst Salpingitis Salpingitis
polycystic-like ovaries
24. Abscess, bilateral Abscess Pelvic peritonitis Salpingitis
25. Abscess Abscess Abscess NA
26. Fluid-filled tube, endometrioma, Salpingitis Endometrioma and peritonitis Endometrioma with
and polycystic-like ovaries infection
27. Pyosalpinx Salpingoophorititis Pyosalpinx NA
Patients without PID
9. Dermoid cyst Ovarian tumor Dermoid cyst Dermoid cyst
14. Free fluid Free fluid Rupture of a cyst Cyst
15. Tubal torsion and pyosalpinx Tubal torsion Tubal torsion and hydrosalpinx Necrosis
19. Endometrioma, bilateral Abscess Endometrioma, bilateral Endometrioma
20. No signs of gynecologic No signs of gynecologic No signs of gynecologic NA
disorder disorder disorder
21. Tubal torsion Tubal torsion Tubal torsion Necrosis
28. Cyst Cyst Cyst Cyst
29. Tubal torsion Abscess Tubal torsion Necrosis
30. Free fluid No signs of gynecologic Free fluid NA
disorder
*NA = Not applicable, histologic examination was not performed.
†Culture of the abscess fluid showed bacterial growth.
CONTENT This procedure was later abandoned because transabdomi-
Endoscopic examination of the female genital tract may be nal laparoscopy provided a panoramic view of not only the
performedvia either the abdominal or vaginal route. The vaginal pelvic cavity but also the abdominal cavity, in addition to
approachwas initially proposed in the USA (Decker, 1944) and obviating the needfor the knee-chest position, providing better
was subsequently described (Kelly and Rock, 1956) using the access for surgical treatment, and also reducing the risk of
term ‘Culdoscopy’, a technique in which the endoscope is infection. More recently, the concept of hydroculdoscopy was
introduced through the posterior vaginal fornix. introduced (Odent, 1973); the technique was then modified
49