Page 7 - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 7
WJOLS
Sleeve Gastrectomy for Morbid Obesity: Robotic vs Standard Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Methods
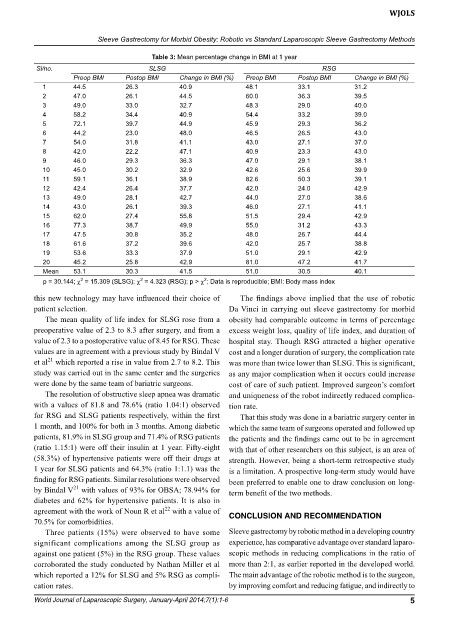
Table 3: mean percentage change in bmi at 1 year
Si/no. SLSG RSG
Preop BMI Postop BMI Change in BMI (%) Preop BMI Postop BMI Change in BMI (%)
1 44.5 26.3 40.9 48.1 33.1 31.2
2 47.0 26.1 44.5 60.0 36.3 39.5
3 49.0 33.0 32.7 48.3 29.0 40.0
4 58.2 34.4 40.9 54.4 33.2 39.0
5 72.1 39.7 44.9 45.9 29.3 36.2
6 44.2 23.0 48.0 46.5 26.5 43.0
7 54.0 31.8 41.1 43.0 27.1 37.0
8 42.0 22.2 47.1 40.9 23.3 43.0
9 46.0 29.3 36.3 47.0 29.1 38.1
10 45.0 30.2 32.9 42.6 25.6 39.9
11 59.1 36.1 38.9 82.6 50.3 39.1
12 42.4 26.4 37.7 42.0 24.0 42.9
13 49.0 28.1 42.7 44.0 27.0 38.6
14 43.0 26.1 39.3 46.0 27.1 41.1
15 62.0 27.4 55.8 51.5 29.4 42.9
16 77.3 38.7 49.9 55.0 31.2 43.3
17 47.5 30.8 35.2 48.0 26.7 44.4
18 61.6 37.2 39.6 42.0 25.7 38.8
19 53.6 33.3 37.9 51.0 29.1 42.9
20 45.2 25.8 42.9 81.0 47.2 41.7
Mean 53.1 30.3 41.5 51.0 30.5 40.1
2
2
2
p = 30.144; c = 15.309 (SLSG); c = 4.323 (RSG); p > c ; Data is reproducible; BMI: body mass index
this new technology may have influenced their choice of The findings above implied that the use of robotic
patient selection. Da Vinci in carrying out sleeve gastrectomy for morbid
The mean quality of life index for SLSG rose from a obesity had comparable outcome in terms of percentage
preoperative value of 2.3 to 8.3 after surgery, and from a excess weight loss, quality of life index, and duration of
value of 2.3 to a postoperative value of 8.45 for RSG. These hospital stay. Though RSG attracted a higher operative
values are in agreement with a previous study by bindal V cost and a longer duration of surgery, the complication rate
21
et al which reported a rise in value from 2.7 to 8.2. This was more than twice lower than SLSG. This is significant,
study was carried out in the same center and the surgeries as any major complication when it occurs could increase
were done by the same team of bariatric surgeons. cost of care of such patient. Improved surgeon’s comfort
The resolution of obstructive sleep apnea was dramatic and uniqueness of the robot indirectly reduced complica-
with a values of 81.8 and 78.6% (ratio 1.04:1) observed tion rate.
for RSG and SLSG patients respectively, within the first That this study was done in a bariatric surgery center in
1 month, and 100% for both in 3 months. Among diabetic which the same team of surgeons operated and followed up
patients, 81.9% in SLSG group and 71.4% of RSG patients the patients and the findings came out to be in agreement
(ratio 1.15:1) were off their insulin at 1 year. Fifty-eight with that of other researchers on this subject, is an area of
(58.3%) of hypertensive patients were off their drugs at strength. However, being a short-term retrospective study
1 year for SLSG patients and 64.3% (ratio 1:1.1) was the is a limitation. A prospective long-term study would have
finding for RSG patients. Similar resolutions were observed been preferred to enable one to draw conclusion on long-
21
by bindal V with values of 93% for ObSA; 78.94% for term benefit of the two methods.
diabetes and 62% for hypertensive patients. It is also in
22
agreement with the work of Noun R et al with a value of COnCLuSIOn And ReCOMMendATIOn
70.5% for comorbidities.
Three patients (15%) were observed to have some Sleeve gastrectomy by robotic method in a developing country
signi ficant complications among the SLSG group as experience, has comparative advantage over standard laparo-
against one patient (5%) in the RSG group. These values scopic methods in reducing complications in the ratio of
corroborated the study conducted by Nathan Miller et al more than 2:1, as earlier reported in the developed world.
which reported a 12% for SLSG and 5% RSG as compli- The main advantage of the robotic method is to the surgeon,
cation rates. by improving comfort and reducing fatigue, and indirectly to
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, January-April 2014;7(1):1-6 5