Page 5 - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 5
WJOLS
Sleeve Gastrectomy for Morbid Obesity: Robotic vs Standard Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy Methods
exclusion Criteria 141.4 to 85.8 kg for RSG patients. Likewise, the mean
preoperative BMI reduced from 83.8 to 30.3 among SLSG
Patients with bMI ≥40 kg/m². Operative technique used patients and 51 to 30.5 at 1 year for RSG patients.
was similar: gastrolysis is performed from 5 cm proximal The mean quality of life for SLSG rose from a preope-
to the pylorus up to the angle of His. Approximately, 100 to rative value of 2.3 to 8.3 after surgery, and from a value of
21
150 ml of sleeve is created over size 38 Fr bougie using 2.3 to a postoperative value of 8.45 for RSG.
Echelon Flex linear stapler with 60 mm. The staple line In this series, 14 out of 20 SLSG patients (70%) and 11
is imbricated with PDS (polydioxanone) 2-0 continuous out of 20 RSG (55%) patients had obstructive sleep apnea.
sutures and peroperative endoscopy is done. The resolution of obstructive sleep apnea was dramatic with
The measures of outcome studied were: duration of a value of 78.6% observed within the first 1 month and 100%
surgery, cost of operation, duration of hospital stay, percen- in 3 months for patients operated by SLSG. 81.8% in 1 month
tage of excess weight loss (%EWL)/bMI, quality of life, 100% in 3 months were observed for RSG patients. Eleven
comorbidity resolution and complications.
out of the 20 (SLSG 55%) and seven out of 20 (RSG 35%)
had diabetes mellitus. There was a noticeable improvement
ReSuLTS
in diabetic status as seen in the reduction in the percentage of
The duration of surgery for SLSG was found to vary from patients on insulin from 81.9% in the first month to 18.1% at
121 to 150 minutes with a mean of 142.7 minutes, while the 1 year for SLSG patients, i.e. 81.9% being off their insulin
overall operative time for RSG was between 132 and 188 at 1 year. A similar drop was noticed for RSG patients from
minutes with an average of 150.4 minutes (Table 1). The 71.4 to 28.6% respectively, with 71.4% of diabetics going
mean docking time was 17.9 minutes. off their insulin at 1 year.
The cost of surgery for SLSG was found to be 7500 USD Sixty percent (12 out of 20) of SLSG patients and 70%
while that of RSG was 9000 USD (Table 1 and Graph 1). The (14 out of 20) of patients operated by RSG were hyperten-
duration of hospital stay for SLSG varied from 3 to 11 days sive. From this value, there was a reduction in the number of
with a mean value of 4.6 days, while for RSG it span from 3 to patient taking antihypertensive agents to control their blood
6 days with a mean value of 3.9 days. pressure from 100% in the first month to 41.7% (58.3% being
The mean percentage excess weight loss for SLSG at off their drugs) at 1 year for SLSG patients and from 100
1 year was 83.8 and 82.0% for RSG (Table 2). The mean to 35.7% (64.3% off drugs) respectively for RSG patients.
preoperative BMI for SLSG and RSG were 53.1 and 51.0 Three patients (15%) were observed to have some significant
respectively (Tables 2 and 3). In this series, the progression complications among the SLSG group as against one patient
of mean percentage excess weight loss by month for SLSG (5%) in the RSG group.
was 23.4% → 45.1% → 58.9% → 83.9%, and 23.7% →
40.8% → 60.8% → 82.8% for RSG at 1, 3, 6 months and dISCuSSIOn
1 year. In this study, the mean preoperative body weight Duration of surgery, cost of operation, duration of hospi-
reduced from 139.2 to 79.6 kg at 1 year for SLSG and from tal stay, %EWL/bMI, QoL, comorbidity resolution and
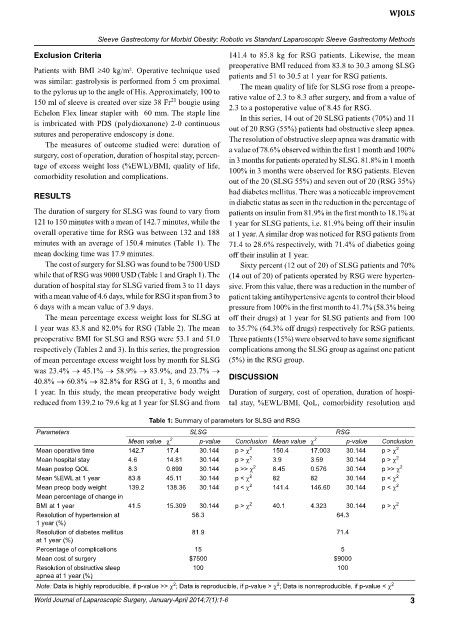
Table 1: Summary of parameters for SLSG and RSG
Parameters SLSG RSG
Mean value c 2 p-value Conclusion Mean value c 2 p-value Conclusion
Mean operative time 142.7 17.4 30.144 p > c 2 150.4 17.003 30.144 p > c 2
Mean hospital stay 4.6 14.81 30.144 p > c 2 3.9 3.59 30.144 p > c 2
Mean postop QOL 8.3 0.899 30.144 p >> c 2 8.45 0.576 30.144 p >> c 2
Mean %EWL at 1 year 83.8 45.11 30.144 p < c 2 82 82 30.144 p < c 2
Mean preop body weight 139.2 138.36 30.144 p < c 2 141.4 146.60 30.144 p < c 2
Mean percentage of change in
BMI at 1 year 41.5 15.309 30.144 p > c 2 40.1 4.323 30.144 p > c 2
Resolution of hypertension at 58.3 64.3
1 year (%)
Resolution of diabetes mellitus 81.9 71.4
at 1 year (%)
Percentage of complications 15 5
Mean cost of surgery $7500 $9000
Resolution of obstructive sleep 100 100
apnea at 1 year (%)
2
2
Note: Data is highly reproducible, if p-value >> c ; Data is reproducible, if p-value > c ; Data is nonreproducible, if p-value < c 2
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, January-April 2014;7(1):1-6 3