Page 20 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 20
M Riyad et al
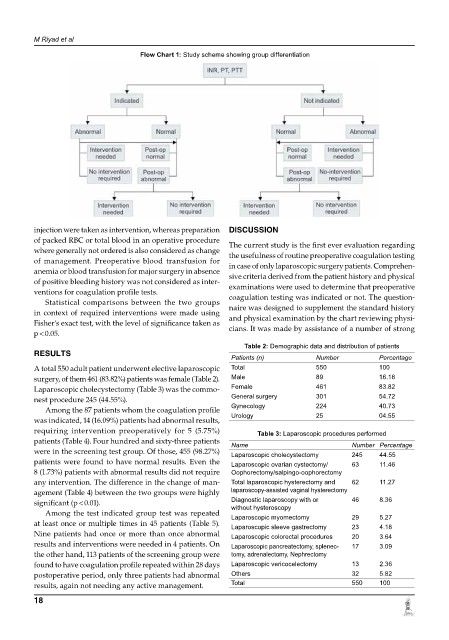
Flow Chart 1: Study scheme showing group differentiation
injection were taken as intervention, whereas preparation diSCUSSion
of packed RBC or total blood in an operative procedure The current study is the first ever evaluation regarding
where generally not ordered is also considered as change the usefulness of routine preoperative coagulation testing
of management. Preoperative blood transfusion for in case of only laparoscopic surgery patients. Comprehen-
anemia or blood transfusion for major surgery in absence sive criteria derived from the patient history and physical
of positive bleeding history was not considered as inter- examinations were used to determine that preoperative
ventions for coagulation profile tests. coagulation testing was indicated or not. The question-
Statistical comparisons between the two groups naire was designed to supplement the standard history
in context of required interventions were made using
Fisher’s exact test, with the level of significance taken as and physical examination by the chart reviewing physi-
p < 0.05. cians. It was made by assistance of a number of strong
Table 2: Demographic data and distribution of patients
RESULTS
Patients (n) Number Percentage
A total 550 adult patient underwent elective laparoscopic Total 550 100
surgery, of them 461 (83.82%) patients was female (Table 2). male 89 16.18
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Table 3) was the commo- female 461 83.82
nest procedure 245 (44.55%). General surgery 301 54.72
Among the 87 patients whom the coagulation profile Gynecology 224 40.73
was indicated, 14 (16.09%) patients had abnormal results, Urology 25 04.55
requiring intervention preoperatively for 5 (5.75%) Table 3: Laparoscopic procedures performed
patients (Table 4). Four hundred and sixty-three patients Name Number Percentage
were in the screening test group. Of those, 455 (98.27%) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy 245 44.55
patients were found to have normal results. Even the Laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy/ 63 11.46
8 (1.73%) patients with abnormal results did not require Oophorectomy/salpingo-oophorectomy
any intervention. The difference in the change of man- Total laparoscopic hysterectomy and 62 11.27
agement (Table 4) between the two groups were highly laparoscopy-assisted vaginal hysterectomy
significant (p < 0.01). Diagnostic laparoscopy with or 46 8.36
without hysteroscopy
Among the test indicated group test was repeated Laparoscopic myomectomy 29 5.27
at least once or multiple times in 45 patients (Table 5). Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy 23 4.18
Nine patients had once or more than once abnormal Laparoscopic colorectal procedures 20 3.64
results and interventions were needed in 4 patients. On Laparoscopic pancreatectomy, splenec- 17 3.09
the other hand, 113 patients of the screening group were tomy, adrenalectomy, Nephrectomy
found to have coagulation profile repeated within 28 days Laparoscopic vericocelectomy 13 2.36
postoperative period, only three patients had abnormal Others 32 5.82
results, again not needing any active management. Total 550 100
18