Page 23 - Laparoscopic Journal - WJOLS
P. 23
WJOLS
A Comparison of Combined Laparoscopic Uterine Artery Ligation and Myomectomy vs Laparoscopic Myomectomy
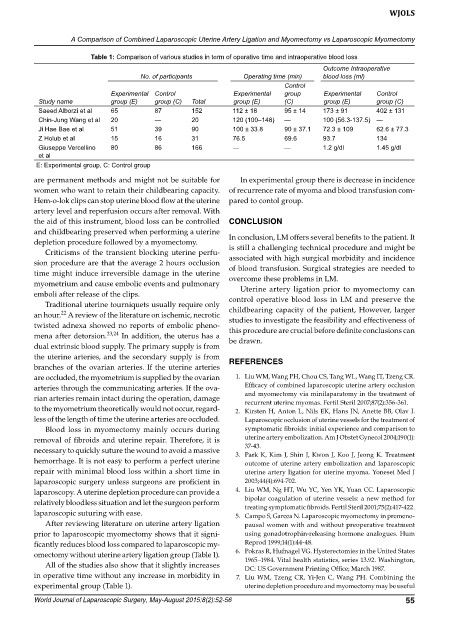
Table 1: Comparison of various studies in term of operative time and intraoperative blood loss
Outcome Intraoperative
No. of participants Operating time (min) blood loss (ml)
Control
Experimental Control Experimental group Experimental Control
Study name group (E) group (C) Total group (E) (C) group (E) group (C)
Saeed Alborzi et al 65 87 152 112 ± 18 95 ± 14 173 ± 91 402 ± 131
Chin-Jung Wang et al 20 — 20 120 (100–148) — 100 (56.3-137.5) —
Ji Hae Bae et al 51 39 90 100 ± 33.8 90 ± 37.1 72.3 ± 109 62.6 ± 77.3
Z Holub et al 15 16 31 76.5 69.6 93.7 134
Giuseppe Vercellino 80 86 166 — — 1.2 g/dl 1.45 g/dl
et al
E: Experimental group, C: Control group
are permanent methods and might not be suitable for In experimental group there is decrease in incidence
women who want to retain their childbearing capacity. of recurrence rate of myoma and blood transfusion com-
Hem-o-lok clips can stop uterine blood flow at the uterine pared to contol group.
artery level and reperfusion occurs after removal. With
the aid of this instrument, blood loss can be controlled ConCLUSion
and childbearing preserved when performing a uterine
depletion procedure followed by a myomectomy. In conclusion, LM offers several benefits to the patient. It
Criticisms of the transient blocking uterine perfu- is still a challenging technical procedure and might be
associated with high surgical morbidity and incidence
sion procedure are that the average 2 hours occlusion
time might induce irreversible damage in the uterine of blood transfusion. Surgical strategies are needed to
myometrium and cause embolic events and pulmonary overcome these problems in LM.
Uterine artery ligation prior to myomectomy can
emboli after release of the clips. control operative blood loss in LM and preserve the
Traditional uterine tourniquets usually require only childbearing capacity of the patient, However, larger
22
an hour. A review of the literature on ischemic, necrotic studies to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of
twisted adnexa showed no reports of embolic pheno- this procedure are crucial before definite conclusions can
mena after detorsion. 23,24 In addition, the uterus has a be drawn.
dual extrinsic blood supply. The primary supply is from
the uterine arteries, and the secondary supply is from REFEREnCES
branches of the ovarian arteries. If the uterine arteries
are occluded, the myometrium is supplied by the ovarian 1. Liu WM, Wang PH, Chou CS, Tang WL, Wang IT, Tzeng CR.
arteries through the communicating arteries. If the ova- Efficacy of combined laparoscopic uterine artery occlusion
rian arteries remain intact during the operation, damage and myomectomy via minilaparatomy in the treatment of
recurrent uterine myomas. Fertil Steril 2007;87(2):356-361.
to the myometrium theoretically would not occur, regard- 2. Kirsten H, Anton L, Nils EK, Hans JN, Anette BB, Olav I.
less of the length of time the uterine arteries are occluded. Laparoscopic occlusion of uterine vessels for the treatment of
Blood loss in myomectomy mainly occurs during symptomatic fibroids: initial experience and comparison to
removal of fibroids and uterine repair. Therefore, it is uterine artery embolization. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004;190(1):
37-43.
necessary to quickly suture the wound to avoid a massive 3. Park K, Kim J, Shin J, Kwon J, Koo J, Jeong K. Treatment
hemorrhage. It is not easy to perform a perfect uterine outcome of uterine artery embolization and laparoscopic
repair with minimal blood loss within a short time in uterine artery ligation for uterine myoma. Yonesei Med J
laparoscopic surgery unless surgeons are proficient in 2003;44(4):694-702.
laparoscopy. A uterine depletion procedure can provide a 4. Liu WM, Ng HT, Wu YC, Yen YK, Yuan CC. Laparoscopic
relatively bloodless situation and let the surgeon perform bipolar coagulation of uterine vessels: a new method for
treating symptomatic fibroids. Fertil Steril 2001;75(2):417-422.
laparoscopic suturing with ease. 5. Campo S, Garcea N. Laparoscopic myomectomy in premeno-
After reviewing literature on uterine artery ligation pausal women with and without preoperative treatment
prior to laparoscopic myomectomy shows that it signi- using gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues. Hum
ficantly reduces blood loss compared to laparoscopic my- Reprod 1999;14(1):44-48.
omectomy without uterine artery ligation group (Table 1). 6. Pokras R, Hufnagel VG. Hysterectomies in the United States
All of the studies also show that it slightly increases 1965–1984. Vital health statistics, series 13.92. Washington,
DC: US Government Printing Office; March 1987.
in operative time without any increase in morbidity in 7. Liu WM, Tzeng CR, Yi-Jen C, Wang PH. Combining the
experimental group (Table 1). uterine depletion procedure and myomectomy may be useful
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2015;8(2):52-56 55