Page 16 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 16
J Rohan Krishna
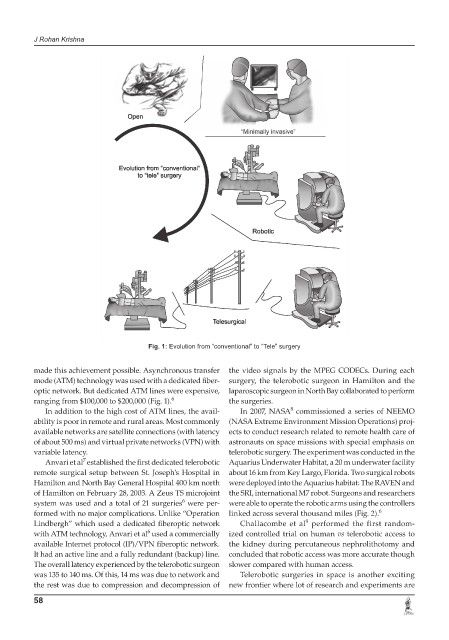
Fig. 1: Evolution from “conventional” to “Tele” surgery
made this achievement possible. Asynchronous transfer the video signals by the MPEG CODECs. During each
mode (ATM) technology was used with a dedicated fiber- surgery, the telerobotic surgeon in Hamilton and the
optic network. But dedicated ATM lines were expensive, laparoscopic surgeon in North Bay collaborated to perform
ranging from $100,000 to $200,000 (Fig. 1). 6 the surgeries.
8
In addition to the high cost of ATM lines, the avail- In 2007, NASA commissioned a series of NEEMO
ability is poor in remote and rural areas. Most commonly (NASA Extreme Environment Mission Operations) proj-
available networks are satellite connections (with latency ects to conduct research related to remote health care of
of about 500 ms) and virtual private networks (VPN) with astronauts on space missions with special emphasis on
variable latency. telerobotic surgery. The experiment was conducted in the
7
Anvari et al established the first dedicated telerobotic Aquarius Underwater Habitat, a 20 m underwater facility
remote surgical setup between St. Joseph’s Hospital in about 16 km from Key Largo, Florida. Two surgical robots
Hamilton and North Bay General Hospital 400 km north were deployed into the Aquarius habitat: The RAVEN and
of Hamilton on February 28, 2003. A Zeus TS microjoint the SRI, international M7 robot. Surgeons and researchers
6
system was used and a total of 21 surgeries were per- were able to operate the robotic arms using the controllers
formed with no major complications. Unlike “Operation linked across several thousand miles (Fig. 2). 6
9
Lindbergh” which used a dedicated fiberoptic network Challacombe et al performed the first random-
6
with ATM technology, Anvari et al used a commercially ized controlled trial on human vs telerobotic access to
available Internet protocol (IP)/VPN fiberoptic network. the kidney during percutaneous nephrolithotomy and
It had an active line and a fully redundant (backup) line. concluded that robotic access was more accurate though
The overall latency experienced by the telerobotic surgeon slower compared with human access.
was 135 to 140 ms. Of this, 14 ms was due to network and Telerobotic surgeries in space is another exciting
the rest was due to compression and decompression of new frontier where lot of research and experiments are
58