Page 30 - wjols
P. 30
Laparoscopic Heminephroureterectomy in Infants Weighing Less Than 10 Kilograms
the likelihood of complications such as hematoma, urinoma, and
the risk of the residual pole pedicle injury. 12,19,20
Laparoscopic heminephrectomy can be performed with
transperitoneal, lateral, or posterior retroperitoneoscopic
approaches. 6,14,21 In addition, robot-assisted approach is reported
in the literature. 11
The limited working space and, consequently, the peritoneal
6
tear risk are the main disadvantages of a retroperitoneal approach.
Wallis et al. described a 15.4% conversion rate and 40% of
functional loss on the residual kidney moiety after retroperitoneal
heminephrectomy. Therefore, they supported the use of open
5
procedures in children under 1 year. Castellan et al. reported that
80% of all complications occurred in patients under 1 year, with a
12.5% conversion rate, so they recommended the TP approach in
6
this group of patients. Miranda et al. described a series of seven
TP heminephrectomies, without complications, in children under
22
2 years. Leclair et al. reported in 21% of the patients, using
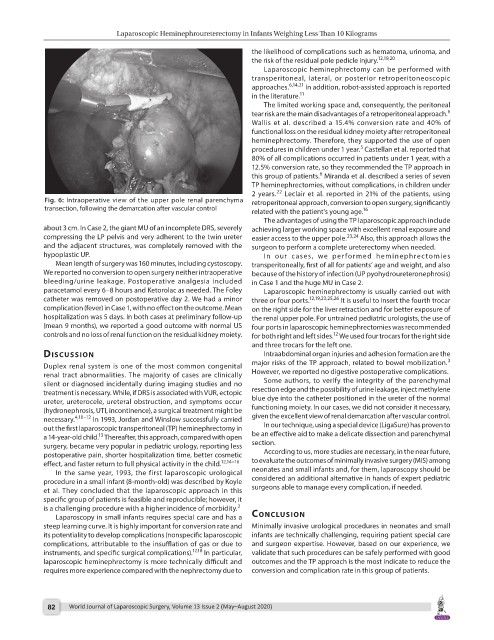
Fig. 6: Intraoperative view of the upper pole renal parenchyma retroperitoneal approach, conversion to open surgery, significantly
transection, following the demarcation after vascular control related with the patient’s young age. 16
The advantages of using the TP laparoscopic approach include
about 3 cm. In Case 2, the giant MU of an incomplete DRS, severely achieving larger working space with excellent renal exposure and
compressing the LP pelvis and very adherent to the twin ureter easier access to the upper pole. 23,24 Also, this approach allows the
and the adjacent structures, was completely removed with the surgeon to perform a complete ureterectomy when needed.
hypoplastic UP. In our cases, we performed heminephrectomies
Mean length of surgery was 160 minutes, including cystoscopy. transperitoneally, first of all for patients’ age and weight, and also
We reported no conversion to open surgery neither intraoperative because of the history of infection (UP pyohydroureteronephrosis)
bleeding/urine leakage. Postoperative analgesia included in Case 1 and the huge MU in Case 2.
paracetamol every 6–8 hours and Ketorolac as needed. The Foley Laparoscopic heminephrectomy is usually carried out with
catheter was removed on postoperative day 2. We had a minor three or four ports. 12,19,23,25,26 It is useful to insert the fourth trocar
complication (fever) in Case 1, with no effect on the outcome. Mean on the right side for the liver retraction and for better exposure of
hospitalization was 5 days. In both cases at preliminary follow-up the renal upper pole. For untrained pediatric urologists, the use of
(mean 9 months), we reported a good outcome with normal US four ports in laparoscopic heminephrectomies was recommended
controls and no loss of renal function on the residual kidney moiety. for both right and left sides. We used four trocars for the right side
12
and three trocars for the left one.
discussion Intraabdominal organ injuries and adhesion formation are the
3
Duplex renal system is one of the most common congenital major risks of the TP approach, related to bowel mobilization.
renal tract abnormalities. The majority of cases are clinically However, we reported no digestive postoperative complications.
silent or diagnosed incidentally during imaging studies and no Some authors, to verify the integrity of the parenchymal
treatment is necessary. While, if DRS is associated with VUR, ectopic resection edge and the possibility of urine leakage, inject methylene
ureter, ureterocele, ureteral obstruction, and symptoms occur blue dye into the catheter positioned in the ureter of the normal
(hydronephrosis, UTI, incontinence), a surgical treatment might be functioning moiety. In our cases, we did not consider it necessary,
necessary. 4,10–12 In 1993, Jordan and Winslow successfully carried given the excellent view of renal demarcation after vascular control.
out the first laparoscopic transperitoneal (TP) heminephrectomy in In our technique, using a special device (LigaSure) has proven to
13
a 14-year-old child. Thereafter, this approach, compared with open be an effective aid to make a delicate dissection and parenchymal
surgery, became very popular in pediatric urology, reporting less section.
postoperative pain, shorter hospitalization time, better cosmetic According to us, more studies are necessary, in the near future,
effect, and faster return to full physical activity in the child. 12,14–16 to evaluate the outcomes of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) among
In the same year, 1993, the first laparoscopic urological neonates and small infants and, for them, laparoscopy should be
procedure in a small infant (8-month-old) was described by Koyle considered an additional alternative in hands of expert pediatric
et al. They concluded that the laparoscopic approach in this surgeons able to manage every complication, if needed.
specific group of patients is feasible and reproducible; however, it
is a challenging procedure with a higher incidence of morbidity. 2
Laparoscopy in small infants requires special care and has a conclusion
steep learning curve. It is highly important for conversion rate and Minimally invasive urological procedures in neonates and small
its potentiality to develop complications (nonspecific laparoscopic infants are technically challenging, requiring patient special care
complications, attributable to the insufflation of gas or due to and surgeon expertise. However, based on our experience, we
instruments, and specific surgical complications). 17,18 In particular, validate that such procedures can be safely performed with good
laparoscopic heminephrectomy is more technically difficult and outcomes and the TP approach is the most indicate to reduce the
requires more experience compared with the nephrectomy due to conversion and complication rate in this group of patients.
82 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 13 Issue 2 (May–August 2020)