Page 38 - WJOLS - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 38
WJOLS
Systematic Review of Laparoscopic Surgery and Simulation-based Training
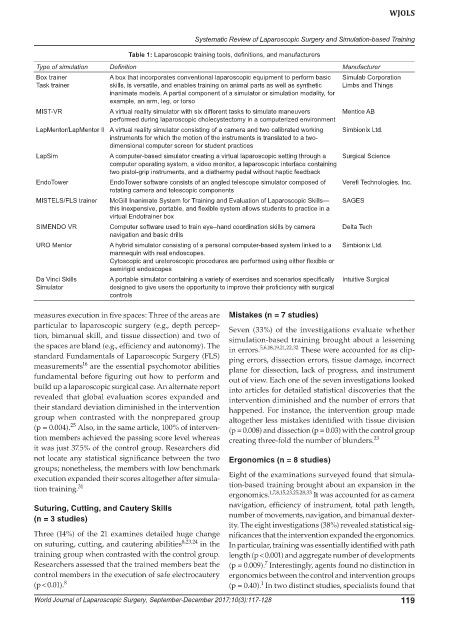
Table 1: Laparoscopic training tools, definitions, and manufacturers
Type of simulation Definition Manufacturer
Box trainer A box that incorporates conventional laparoscopic equipment to perform basic Simulab Corporation
Task trainer skills, is versatile, and enables training on animal parts as well as synthetic Limbs and Things
inanimate models. A partial component of a simulator or simulation modality, for
example, an arm, leg, or torso
MIST-VR A virtual reality simulator with six different tasks to simulate maneuvers Mentice AB
performed during laparoscopic cholecystectomy in a computerized environment
LapMentor/LapMentor II A virtual reality simulator consisting of a camera and two calibrated working Simbionix Ltd.
instruments for which the motion of the instruments is translated to a two-
dimensional computer screen for student practices
LapSim A computer-based simulator creating a virtual laparoscopic setting through a Surgical Science
computer operating system, a video monitor, a laparoscopic interface containing
two pistol-grip instruments, and a diathermy pedal without haptic feedback
EndoTower EndoTower software consists of an angled telescope simulator composed of Verefi Technologies, Inc.
rotating camera and telescopic components
MISTELS/FLS trainer McGill Inanimate System for Training and Evaluation of Laparoscopic Skills— SAGES
this inexpensive, portable, and flexible system allows students to practice in a
virtual Endotrainer box
SIMENDO VR Computer software used to train eye–hand coordination skills by camera Delta Tech
navigation and basic drills
URO Mentor A hybrid simulator consisting of a personal computer-based system linked to a Simbionix Ltd.
mannequin with real endoscopes.
Cytoscopic and ureteroscopic procedures are performed using either flexible or
semirigid endoscopes
Da Vinci Skills A portable simulator containing a variety of exercises and scenarios specifically Intuitive Surgical
Simulator designed to give users the opportunity to improve their proficiency with surgical
controls
measures execution in five spaces: Three of the areas are Mistakes (n = 7 studies)
particular to laparoscopic surgery (e.g., depth percep- Seven (33%) of the investigations evaluate whether
tion, bimanual skill, and tissue dissection) and two of simulation-based training brought about a lessening
the spaces are bland (e.g., efficiency and autonomy). The in errors. 5,6,18,19,21,22,32 These were accounted for as clip-
standard Fundamentals of Laparoscopic Surgery (FLS) ping errors, dissection errors, tissue damage, incorrect
16
measurements are the essential psychomotor abilities plane for dissection, lack of progress, and instrument
fundamental before figuring out how to perform and out of view. Each one of the seven investigations looked
build up a laparoscopic surgical case. An alternate report into articles for detailed statistical discoveries that the
revealed that global evaluation scores expanded and intervention diminished and the number of errors that
their standard deviation diminished in the intervention happened. For instance, the intervention group made
group when contrasted with the nonprepared group altogether less mistakes identified with tissue division
25
(p = 0.004). Also, in the same article, 100% of interven- (p = 0.008) and dissection (p = 0.03) with the control group
tion members achieved the passing score level whereas creating three-fold the number of blunders. 23
it was just 37.5% of the control group. Researchers did
not locate any statistical significance between the two Ergonomics (n = 8 studies)
groups; nonetheless, the members with low benchmark
execution expanded their scores altogether after simula- Eight of the examinations surveyed found that simula-
tion training. 31 tion-based training brought about an expansion in the
ergonomics. 1,7,8,15,23,25,28,33 It was accounted for as camera
Suturing, Cutting, and Cautery Skills navigation, efficiency of instrument, total path length,
(n = 3 studies) number of movements, navigation, and bimanual dexter-
ity. The eight investigations (38%) revealed statistical sig-
Three (14%) of the 21 examines detailed huge change nificances that the intervention expanded the ergonomics.
on suturing, cutting, and cautering abilities 8,23,24 in the In particular, training was essentially identified with path
training group when contrasted with the control group. length (p < 0.001) and aggregate number of developments
7
Researchers assessed that the trained members beat the (p = 0.009). Interestingly, agents found no distinction in
control members in the execution of safe electrocautery ergonomics between the control and intervention groups
(p < 0.01). 8 (p = 0.40). In two distinct studies, specialists found that
1
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, September-December 2017;10(3):117-128 119