Page 10 - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 10
Nidhi Jain et al.
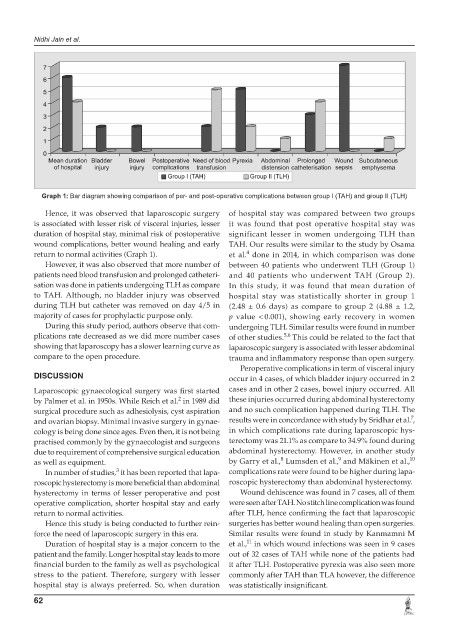
Graph 1: Bar diagram showing comparison of per- and post-operative complications between group I (TAH) and group II (TLH)
Hence, it was observed that laparoscopic surgery of hospital stay was compared between two groups
is associated with lesser risk of visceral injuries, lesser it was found that post operative hospital stay was
duration of hospital stay, minimal risk of postoperative significant lesser in women undergoing TLH than
wound complications, better wound healing and early TAH. Our results were similar to the study by Osama
4
return to normal activities (Graph 1). et al. done in 2014, in which comparison was done
However, it was also observed that more number of between 40 patients who underwent TLH (Group 1)
patients need blood transfusion and prolonged catheteri- and 40 patients who underwent TAH (Group 2).
sation was done in patients undergoing TLH as compare In this study, it was found that mean duration of
to TAH. Although, no bladder injury was observed hospital stay was statistically shorter in group 1
during TLH but catheter was removed on day 4/5 in (2.48 ± 0.6 days) as compare to group 2 (4.88 ± 1.2,
majority of cases for prophylactic purpose only. p value < 0.001), showing early recovery in women
During this study period, authors observe that com- undergoing TLH. Similar results were found in number
5,6
plications rate decreased as we did more number cases of other studies. This could be related to the fact that
showing that laparoscopy has a slower learning curve as laparoscopic surgery is associated with lesser abdominal
compare to the open procedure. trauma and inflammatory response than open surgery.
Peroperative complications in term of visceral injury
DISCUSSION occur in 4 cases, of which bladder injury occurred in 2
Laparoscopic gynaecological surgery was first started cases and in other 2 cases, bowel injury occurred. All
2
by Palmer et al. in 1950s. While Reich et al. in 1989 did these injuries occurred during abdominal hysterectomy
surgical procedure such as adhesiolysis, cyst aspiration and no such complication happened during TLH. The
7
and ovarian biopsy. Minimal invasive surgery in gynae- results were in concordance with study by Sridhar et al. ,
cology is being done since ages. Even then, it is not being in which complications rate during laparoscopic hys-
practised commonly by the gynaecologist and surgeons terectomy was 21.1% as compare to 34.9% found during
due to requirement of comprehensive surgical education abdominal hysterectomy. However, in another study
9
8
10
as well as equipment. by Garry et al., Lumsden et al., and Mäkinen et al.,
3
In number of studies, it has been reported that lapa- complications rate were found to be higher during lapa-
roscopic hysterectomy is more beneficial than abdominal roscopic hysterectomy than abdominal hysterectomy.
hysterectomy in terms of lesser peroperative and post Wound dehiscence was found in 7 cases, all of them
operative complication, shorter hospital stay and early were seen after TAH. No stitch line complication was found
return to normal activities. after TLH, hence confirming the fact that laparoscopic
Hence this study is being conducted to further rein- surgeries has better wound healing than open surgeries.
force the need of laparoscopic surgery in this era. Similar results were found in study by Kanmamni M
11
Duration of hospital stay is a major concern to the et al., in which wound infections was seen in 9 cases
patient and the family. Longer hospital stay leads to more out of 32 cases of TAH while none of the patients had
financial burden to the family as well as psychological it after TLH. Postoperative pyrexia was also seen more
stress to the patient. Therefore, surgery with lesser commonly after TAH than TLA however, the difference
hospital stay is always preferred. So, when duration was statistically insignificant.
62