Page 66 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 66
Laparoscopic Management of Cesarean Scar Pregnancy
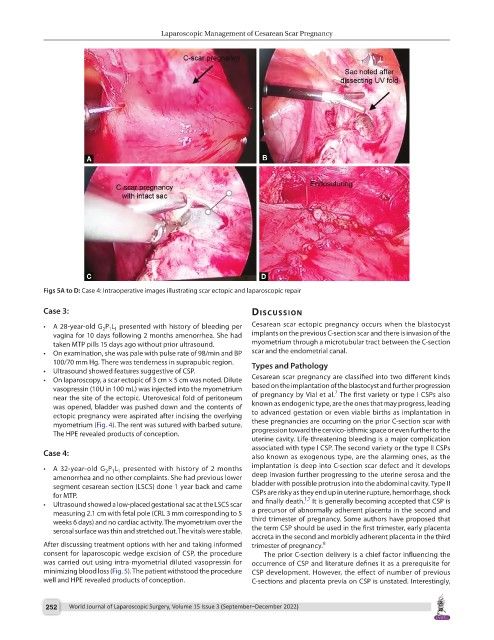
Figs 5A to D: Case 4: Intraoperative images illustrating scar ectopic and laparoscopic repair
Case 3: discussion
• A 28-year-old G P L presented with history of bleeding per Cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy occurs when the blastocyst
2 1 1
vagina for 10 days following 2 months amenorrhea. She had implants on the previous C-section scar and there is invasion of the
taken MTP pills 15 days ago without prior ultrasound. myometrium through a microtubular tract between the C-section
• On examination, she was pale with pulse rate of 98/min and BP scar and the endometrial canal.
100/70 mm Hg. There was tenderness in suprapubic region. Types and Pathology
• Ultrasound showed features suggestive of CSP.
• On laparoscopy, a scar ectopic of 3 cm × 5 cm was noted. Dilute Cesarean scar pregnancy are classified into two different kinds
vasopressin (10U in 100 mL) was injected into the myometrium based on the implantation of the blastocyst and further progression
7
near the site of the ectopic. Uterovesical fold of peritoneum of pregnancy by Vial et al. The first variety or type I CSPs also
was opened, bladder was pushed down and the contents of known as endogenic type, are the ones that may progress, leading
ectopic pregnancy were aspirated after incising the overlying to advanced gestation or even viable births as implantation in
myometrium (Fig. 4). The rent was sutured with barbed suture. these pregnancies are occurring on the prior C-section scar with
The HPE revealed products of conception. progression toward the cervico-isthmic space or even further to the
uterine cavity. Life-threatening bleeding is a major complication
associated with type I CSP. The second variety or the type II CSPs
Case 4: also known as exogenous type, are the alarming ones, as the
• A 32-year-old G P L presented with history of 2 months implantation is deep into C-section scar defect and it develops
2 1 1
amenorrhea and no other complaints. She had previous lower deep invasion further progressing to the uterine serosa and the
segment cesarean section (LSCS) done 1 year back and came bladder with possible protrusion into the abdominal cavity. Type II
for MTP. CSPs are risky as they end up in uterine rupture, hemorrhage, shock
1,7
• Ultrasound showed a low-placed gestational sac at the LSCS scar and finally death. It is generally becoming accepted that CSP is
measuring 2.1 cm with fetal pole (CRL 3 mm corresponding to 5 a precursor of abnormally adherent placenta in the second and
weeks 6 days) and no cardiac activity. The myometrium over the third trimester of pregnancy. Some authors have proposed that
serosal surface was thin and stretched out. The vitals were stable. the term CSP should be used in the first trimester, early placenta
accreta in the second and morbidly adherent placenta in the third
After discussing treatment options with her and taking informed trimester of pregnancy. 8
consent for laparoscopic wedge excision of CSP, the procedure The prior C-section delivery is a chief factor influencing the
was carried out using intra-myometrial diluted vasopressin for occurrence of CSP and literature defines it as a prerequisite for
minimizing blood loss (Fig. 5). The patient withstood the procedure CSP development. However, the effect of number of previous
well and HPE revealed products of conception. C-sections and placenta previa on CSP is unstated. Interestingly,
252 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 3 (September–December 2022)