Page 40 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 40
Laparoscopic vs Robotic Approach for Rectal Cancer: A Meta-analysis
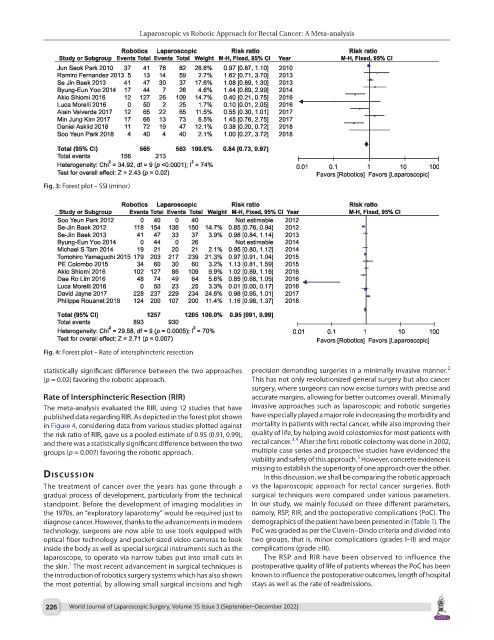
Fig. 3: Forest plot – SSI (minor)
Fig. 4: Forest plot – Rate of intersphincteric resection
2
statistically significant difference between the two approaches precision demanding surgeries in a minimally invasive manner.
(p = 0.02) favoring the robotic approach. This has not only revolutionized general surgery but also cancer
surgery, where surgeons can now excise tumors with precise and
Rate of Intersphincteric Resection (RIR) accurate margins, allowing for better outcomes overall. Minimally
The meta-analysis evaluated the RIR, using 12 studies that have invasive approaches such as laparoscopic and robotic surgeries
published data regarding RIR. As depicted in the forest plot shown have especially played a major role in decreasing the morbidity and
in Figure 4, considering data from various studies plotted against mortality in patients with rectal cancer, while also improving their
the risk ratio of RIR, gave us a pooled estimate of 0.95 (0.91, 0.99), quality of life, by helping avoid colostomies for most patients with
3,4
and there was a statistically significant difference between the two rectal cancer. After the first robotic colectomy was done in 2002,
groups (p = 0.007) favoring the robotic approach. multiple case series and prospective studies have evidenced the
5
viability and safety of this approach. However, concrete evidence is
missing to establish the superiority of one approach over the other.
dIscussIon In this discussion, we shall be comparing the robotic approach
The treatment of cancer over the years has gone through a vs the laparoscopic approach for rectal cancer surgeries. Both
gradual process of development, particularly from the technical surgical techniques were compared under various parameters.
standpoint. Before the development of imaging modalities in In our study, we mainly focused on three different parameters,
the 1970s, an “exploratory laparotomy” would be required just to namely, RSP, RIR, and the postoperative complications (PoC). The
diagnose cancer. However, thanks to the advancements in modern demographics of the patient have been presented in (Table 1). The
technology, surgeons are now able to use tools equipped with PoC was graded as per the Clavein–Dindo criteria and divided into
optical fiber technology and pocket-sized video cameras to look two groups, that is, minor complications (grades I–II) and major
inside the body as well as special surgical instruments such as the complications (grade ≥III).
laparoscope, to operate via narrow tubes put into small cuts in The RSP and RIR have been observed to influence the
1
the skin. The most recent advancement in surgical techniques is postoperative quality of life of patients whereas the PoC has been
the introduction of robotics surgery systems which has also shown known to influence the postoperative outcomes, length of hospital
the most potential, by allowing small surgical incisions and high stays as well as the rate of readmissions.
226 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 3 (September–December 2022)