Page 39 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 39
Laparoscopic vs Robotic Approach for Rectal Cancer: A Meta-analysis
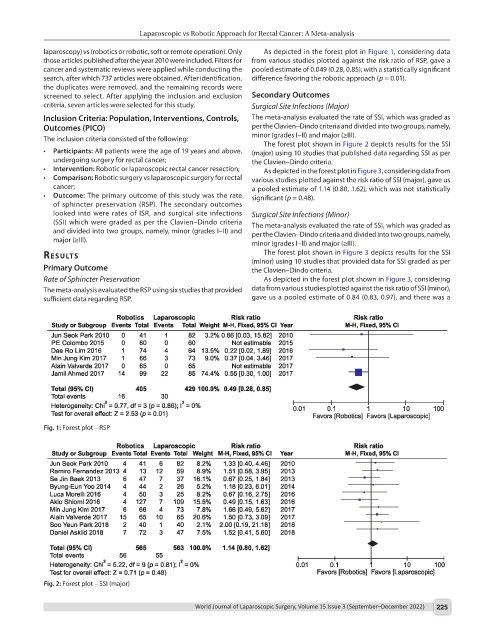
laparoscopy) vs (robotics or robotic, soft or remote operation). Only As depicted in the forest plot in Figure 1, considering data
those articles published after the year 2010 were included. Filters for from various studies plotted against the risk ratio of RSP, gave a
cancer and systematic reviews were applied while conducting the pooled estimate of 0.049 (0.28, 0.85), with a statistically significant
search, after which 737 articles were obtained. After identification, difference favoring the robotic approach (p = 0.01).
the duplicates were removed, and the remaining records were
screened to select. After applying the inclusion and exclusion Secondary Outcomes
criteria, seven articles were selected for this study. Surgical Site Infections (Major)
Inclusion Criteria: Population, Interventions, Controls, The meta-analysis evaluated the rate of SSI, which was graded as
Outcomes (PICO) per the Clavien–Dindo criteria and divided into two groups, namely,
The inclusion criteria consisted of the following: minor (grades I–II) and major (≥III).
The forest plot shown in Figure 2 depicts results for the SSI
• Participants: All patients were the age of 19 years and above, (major) using 10 studies that published data regarding SSI as per
undergoing surgery for rectal cancer; the Clavien–Dindo criteria.
• Intervention: Robotic or laparoscopic rectal cancer resection; As depicted in the forest plot in Figure 3, considering data from
• Comparison: Robotic surgery vs laparoscopic surgery for rectal various studies plotted against the risk ratio of SSI (major), gave us
cancer; a pooled estimate of 1.14 (0.80, 1.62), which was not statistically
• Outcome: The primary outcome of this study was the rate significant (p = 0.48).
of sphincter preservation (RSP). The secondary outcomes
looked into were rates of ISR, and surgical site infections Surgical Site Infections (Minor)
(SSI) which were graded as per the Clavien–Dindo criteria The meta-analysis evaluated the rate of SSI, which was graded as
and divided into two groups, namely, minor (grades I–II) and per the Clavien–Dindo criteria and divided into two groups, namely,
major (≥III). minor (grades I–II) and major (≥III).
The forest plot shown in Figure 3 depicts results for the SSI
results (minor) using 10 studies that provided data for SSI graded as per
Primary Outcome the Clavien–Dindo criteria.
Rate of Sphincter Preservation As depicted in the forest plot shown in Figure 3, considering
The meta-analysis evaluated the RSP using six studies that provided data from various studies plotted against the risk ratio of SSI (minor),
sufficient data regarding RSP. gave us a pooled estimate of 0.84 (0.83, 0.97), and there was a
Fig. 1: Forest plot – RSP
Fig. 2: Forest plot – SSI (major)
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 15 Issue 3 (September–December 2022) 225