Page 6 - tmp
P. 6
Intraoperative Cholangiography vs Laparoscopic Ultrasound
However, LUS failed to detect CD junction anomalies in all Table 3: IOC accuracy indexes
patients, while IOC detected these anomalies in 4 patients (8%) CBD stone (s) CBD stone (s) not Total
out of 50 patients. The anomalies found were medial insertion IOC present N (%) present N (%) N (%)
of cystic duct in one patient (2%) and low insertion of cystic duct Positive 4 (8%) 3 (6%) 7 (14%)
in three patients (6%). The incidence of these anomalies was
statistically insignificant (p-value = 0.05). While LUS detected Negative 1 (2%) 42 (84%) 43 (86%)
vascular structures in 52 patients (98.11%) with an OR of 1.554, it Total 5 (10%) 45 (90%) 50 (100%)
failed to demonstrate anomalies in the vascular structures in all
patients (Table 1).
Postoperative CBD Stones
Within the 6-month follow-up period, we suspected postoperative
CBD stones in 7 patients (13.2%) among the 53 total sample.
Of those seven patients, one patient presented with biliary
pancreatitis and was treated conservatively. Two patients had
persistent elevation of LFTs. Three patients underwent magnetic
resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) postoperatively,
who were both IOC and LUS positive for CBD stones and MRCP
confirmed the presence of stones. One patient had CBD dilatation
on transabdominal US, who also was LUS and IOC positive. These
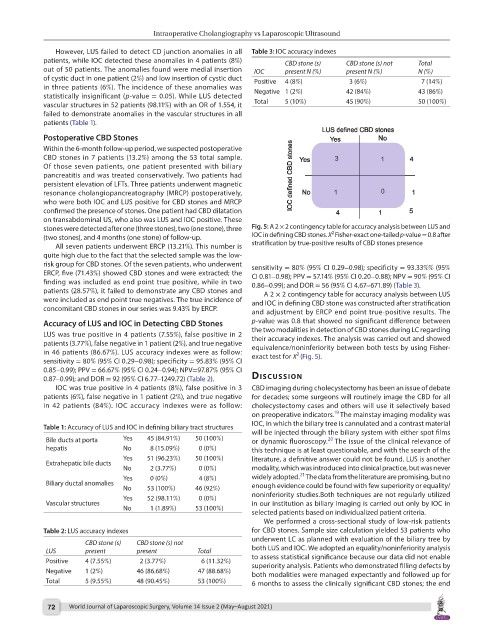
stones were detected after one (three stones), two (one stone), three Fig. 5: A 2 × 2 contingency table for accuracy analysis between LUS and
2
(two stones), and 4 months (one stone) of follow-up. IOC in defining CBD stones. X Fisher-exact one-tailed p-value = 0.8 after
All seven patients underwent ERCP (13.21%). This number is stratification by true-positive results of CBD stones presence
quite high due to the fact that the selected sample was the low-
risk group for CBD stones. Of the seven patients, who underwent sensitivity = 80% (95% CI 0.29–0.98); specificity = 93.33%% (95%
ERCP, five (71.43%) showed CBD stones and were extracted; the CI 0.81–0.98); PPV = 57.14% (95% CI 0.20–0.88); NPV = 90% (95% CI
finding was included as end point true positive, while in two 0.86–0.99); and DOR = 56 (95% CI 4.67–671.89) (Table 3).
patients (28.57%), it failed to demonstrate any CBD stones and A 2 × 2 contingency table for accuracy analysis between LUS
were included as end point true negatives. The true incidence of and IOC in defining CBD stone was constructed after stratification
concomitant CBD stones in our series was 9.43% by ERCP. and adjustment by ERCP end point true-positive results. The
Accuracy of LUS and IOC in Detecting CBD Stones p-value was 0.8 that showed no significant difference between
LUS was true positive in 4 patients (7.55%), false positive in 2 the two modalities in detection of CBD stones during LC regarding
their accuracy indexes. The analysis was carried out and showed
patients (3.77%), false negative in 1 patient (2%), and true negative equivalence/noninferiority between both tests by using Fisher-
in 46 patients (86.67%). LUS accuracy indexes were as follow: exact test for X (Fig. 5).
2
sensitivity = 80% (95% CI 0.29–0.98); specificity = 95.83% (95% CI
0.85–0.99); PPV = 66.67% (95% CI 0.24–0.94); NPV=97.87% (95% CI
0.87–0.99); and DOR = 92 (95% CI 6.77–1249.72) (Table 2). dIscussIon
IOC was true positive in 4 patients (8%), false positive in 3 CBD imaging during cholecystectomy has been an issue of debate
patients (6%), false negative in 1 patient (2%), and true negative for decades; some surgeons will routinely image the CBD for all
in 42 patients (84%). IOC accuracy indexes were as follow: cholecystectomy cases and others will use it selectively based
19
on preoperative indicators. The mainstay imaging modality was
IOC, in which the biliary tree is cannulated and a contrast material
Table 1: Accuracy of LUS and IOC in defining biliary tract structures
will be injected through the biliary system with either spot films
20
Bile ducts at porta Yes 45 (84.91%) 50 (100%) or dynamic fluoroscopy. The issue of the clinical relevance of
hepatis No 8 (15.09%) 0 (0%) this technique is at least questionable, and with the search of the
Yes 51 (96.23%) 50 (100%) literature, a definitive answer could not be found. LUS is another
Extrahepatic bile ducts
No 2 (3.77%) 0 (0%) modality, which was introduced into clinical practice, but was never
21
Yes 0 (0%) 4 (8%) widely adopted. The data from the literature are promising, but no
Biliary ductal anomalies enough evidence could be found with few superiority or equality/
No 53 (100%) 46 (92%)
Yes 52 (98.11%) 0 (0%) noninferiority studies.Both techniques are not regularly utilized
Vascular structures in our institution as biliary imaging is carried out only by IOC in
No 1 (1.89%) 53 (100%)
selected patients based on individualized patient criteria.
We performed a cross-sectional study of low-risk patients
Table 2: LUS accuracy indexes for CBD stones. Sample size calculation yielded 53 patients who
underwent LC as planned with evaluation of the biliary tree by
CBD stone (s) CBD stone (s) not
LUS present present Total both LUS and IOC. We adopted an equality/noninferiority analysis
to assess statistical significance because our data did not enable
Positive 4 (7.55%) 2 (3.77%) 6 (11.32%) superiority analysis. Patients who demonstrated filling defects by
Negative 1 (2%) 46 (86.68%) 47 (88.68%) both modalities were managed expectantly and followed up for
Total 5 (9.55%) 48 (90.45%) 53 (100%) 6 months to assess the clinically significant CBD stones; the end
72 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 14 Issue 2 (May–August 2021)