Page 21 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 21
Safety and Feasibility of Sleeve Gastrectomy with Loop Duodenal Switch
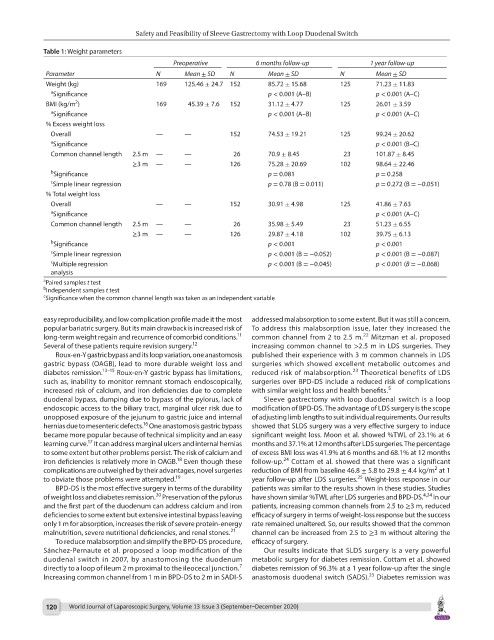
Table 1: Weight parameters
Preoperative 6 months follow-up 1 year follow-up
Parameter N Mean ± SD N Mean ± SD N Mean ± SD
Weight (kg) 169 125.46 ± 24.7 152 85.72 ± 15.68 125 71.23 ± 11.83
a Significance p < 0.001 (A–B) p < 0.001 (A–C)
2
BMI (kg/m ) 169 45.39 ± 7.6 152 31.12 ± 4.77 125 26.01 ± 3.59
a Significance p < 0.001 (A–B) p < 0.001 (A–C)
% Excess weight loss
Overall — — 152 74.53 ± 19.21 125 99.24 ± 20.62
a Significance p < 0.001 (B–C)
Common channel length 2.5 m — — 26 70.9 ± 8.45 23 101.87 ± 8.45
≥3 m — — 126 75.28 ± 20.69 102 98.64 ± 22.46
b Significance p = 0.081 p = 0.258
c Simple linear regression p = 0.78 (B = 0.011) p = 0.272 (B = −0.051)
% Total weight loss
Overall — — 152 30.91 ± 4.98 125 41.86 ± 7.63
a Significance p < 0.001 (A–C)
Common channel length 2.5 m — — 26 35.98 ± 5.49 23 51.23 ± 6.55
≥3 m — — 126 29.87 ± 4.18 102 39.75 ± 6.13
b Significance p < 0.001 p < 0.001
c Simple linear regression p < 0.001 (B = −0.052) p < 0.001 (B = −0.087)
c Multiple regression p < 0.001 (B = −0.045) p < 0.001 (B = −0.068)
analysis
a Paired samples t test
b Independent samples t test
c Significance when the common channel length was taken as an independent variable
easy reproducibility, and low complication profile made it the most addressed malabsorption to some extent. But it was still a concern.
popular bariatric surgery. But its main drawback is increased risk of To address this malabsorption issue, later they increased the
22
11
long-term weight regain and recurrence of comorbid conditions. common channel from 2 to 2.5 m. Mitzman et al. proposed
Several of these patients require revision surgery. 12 increasing common channel to >2.5 m in LDS surgeries. They
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and its loop variation, one anastomosis published their experience with 3 m common channels in LDS
gastric bypass (OAGB), lead to more durable weight loss and surgeries which showed excellent metabolic outcomes and
23
diabetes remission. 13–15 Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has limitations, reduced risk of malabsorption. Theoretical benefits of LDS
such as, inability to monitor remnant stomach endoscopically, surgeries over BPD-DS include a reduced risk of complications
increased risk of calcium, and iron deficiencies due to complete with similar weight loss and health benefits. 5
duodenal bypass, dumping due to bypass of the pylorus, lack of Sleeve gastrectomy with loop duodenal switch is a loop
endoscopic access to the biliary tract, marginal ulcer risk due to modification of BPD-DS. The advantage of LDS surgery is the scope
unopposed exposure of the jejunum to gastric juice and internal of adjusting limb lengths to suit individual requirements. Our results
16
hernias due to mesenteric defects. One anastomosis gastric bypass showed that SLDS surgery was a very effective surgery to induce
became more popular because of technical simplicity and an easy significant weight loss. Moon et al. showed %TWL of 23.1% at 6
17
learning curve. It can address marginal ulcers and internal hernias months and 37.1% at 12 months after LDS surgeries. The percentage
to some extent but other problems persist. The risk of calcium and of excess BMI loss was 41.9% at 6 months and 68.1% at 12 months
24
18
iron deficiencies is relatively more in OAGB. Even though these follow-up. Cottam et al. showed that there was a significant
2
complications are outweighed by their advantages, novel surgeries reduction of BMI from baseline 46.8 ± 5.8 to 29.8 ± 4.4 kg/m at 1
25
to obviate those problems were attempted. 19 year follow-up after LDS surgeries. Weight-loss response in our
BPD-DS is the most effective surgery in terms of the durability patients was similar to the results shown in these studies. Studies
20
of weight loss and diabetes remission. Preservation of the pylorus have shown similar %TWL after LDS surgeries and BPD-DS. 4,24 In our
and the first part of the duodenum can address calcium and iron patients, increasing common channels from 2.5 to ≥3 m, reduced
deficiencies to some extent but extensive intestinal bypass leaving efficacy of surgery in terms of weight-loss response but the success
only 1 m for absorption, increases the risk of severe protein-energy rate remained unaltered. So, our results showed that the common
malnutrition, severe nutritional deficiencies, and renal stones. 21 channel can be increased from 2.5 to ≥3 m without altering the
To reduce malabsorption and simplify the BPD-DS procedure, efficacy of surgery.
Sánchez-Pernaute et al. proposed a loop modification of the Our results indicate that SLDS surgery is a very powerful
duodenal switch in 2007, by anastomosing the duodenum metabolic surgery for diabetes remission. Cottam et al. showed
7
directly to a loop of ileum 2 m proximal to the ileocecal junction. diabetes remission of 96.3% at a 1 year follow-up after the single
25
Increasing common channel from 1 m in BPD-DS to 2 m in SADI-S anastomosis duodenal switch (SADS). Diabetes remission was
120 World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, Volume 13 Issue 3 (September–December 2020)