Page 34 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 34
Alaa H Ali
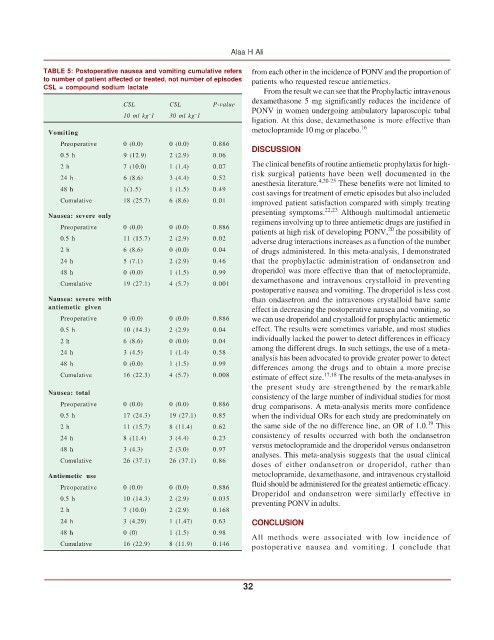
TABLE 5: Postoperative nausea and vomiting cumulative refers from each other in the incidence of PONV and the proportion of
to number of patient affected or treated, not number of episodes patients who requested rescue antiemetics.
CSL = compound sodium lactate
From the result we can see that the Prophylactic intravenous
dexamethasone 5 mg significantly reduces the incidence of
CSL CSL P-value PONV in women undergoing ambulatory laparoscopic tubal
–
–
10 ml kg 1 30 ml kg 1
ligation. At this dose, dexamethasone is more effective than
metoclopramide 10 mg or placebo. 16
Vomiting
Preoperative 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.886
DISCUSSION
0.5 h 9 (12.9) 2 (2.9) 0.06
The clinical benefits of routine antiemetic prophylaxis for high-
2 h 7 (10.0) 1 (1.4) 0.07
risk surgical patients have been well documented in the
24 h 6 (8.6) 3 (4.4) 0.52
anesthesia literature. 4,20-25 These benefits were not limited to
48 h 1(1.5) 1 (1.5) 0.49
cost savings for treatment of emetic episodes but also included
Cumulative 18 (25.7) 6 (8.6) 0.01 improved patient satisfaction compared with simply treating
presenting symptoms. 22,23 Although multimodal antiemetic
Nausea: severe only
regimens involving up to three antiemetic drugs are justified in
Preoperative 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.886 20
patients at high risk of developing PONV, the possibility of
0.5 h 11 (15.7) 2 (2.9) 0.02 adverse drug interactions increases as a function of the number
2 h 6 (8.6) 0 (0.0) 0.04 of drugs administered. In this meta-analysis, I demonstrated
24 h 5 (7.1) 2 (2.9) 0.46 that the prophylactic administration of ondansetron and
48 h 0 (0.0) 1 (1.5) 0.99 droperidol was more effective than that of metoclopramide,
dexamethasone and intravenous crystalloid in preventing
Cumulative 19 (27.1) 4 (5.7) 0.001
postoperative nausea and vomiting. The droperidol is less cost
Nausea: severe with than ondasetron and the intravenous crystalloid have same
antiemetic given effect in decreasing the postoperative nausea and vomiting, so
Preoperative 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.886 we can use droperidol and crystalloid for prophylactic antiemetic
0.5 h 10 (14.3) 2 (2.9) 0.04 effect. The results were sometimes variable, and most studies
individually lacked the power to detect differences in efficacy
2 h 6 (8.6) 0 (0.0) 0.04
among the different drugs. In such settings, the use of a meta-
24 h 3 (4.5) 1 (1.4) 0.58
analysis has been advocated to provide greater power to detect
48 h 0 (0.0) 1 (1.5) 0.99
differences among the drugs and to obtain a more precise
Cumulative 16 (22.3) 4 (5.7) 0.008 estimate of effect size. 17,18 The results of the meta-analyses in
the present study are strengthened by the remarkable
Nausea: total
consistency of the large number of individual studies for most
Preoperative 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.886 drug comparisons. A meta-analysis merits more confidence
0.5 h 17 (24.3) 19 (27.1) 0.85 when the individual ORs for each study are predominately on
19
2 h 11 (15.7) 8 (11.4) 0.62 the same side of the no difference line, an OR of 1.0. This
consistency of results occurred with both the ondansetron
24 h 8 (11.4) 3 (4.4) 0.23
versus metoclopramide and the droperidol versus ondansetron
48 h 3 (4.3) 2 (3.0) 0.97
analyses. This meta-analysis suggests that the usual clinical
Cumulative 26 (37.1) 26 (37.1) 0.86
doses of either ondansetron or droperidol, rather than
Antiemetic use metoclopramide, dexamethasone, and intravenous crystalloid
fluid should be administered for the greatest antiemetic efficacy.
Preoperative 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0.886
Droperidol and ondansetron were similarly effective in
0.5 h 10 (14.3) 2 (2.9) 0.035
preventing PONV in adults.
2 h 7 (10.0) 2 (2.9) 0.168
24 h 3 (4.29) 1 (1.47) 0.63 CONCLUSION
48 h 0 (0) 1 (1.5) 0.98
All methods were associated with low incidence of
Cumulative 16 (22.9) 8 (11.9) 0.146 postoperative nausea and vomiting. I conclude that
32