Page 38 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 38
Hanom Husni Syam
of compressed muscular fibres and diverted uterine vessels.
This allows healthy adjacent myometrium to be preserved and
damage avoided to the peri-myomatous vessels which are often
distended due to compression by the myoma and could be the
origin of considerable hemorrhage.
Electrocoagulation must be used as sparingly as possible
to achieve hemostasis of the edges after myomectomy. Certain
cases of uterine rupture during pregnancy reported after LM
and after myolysis suggest that the use of electrocoagulation
may induce necrosis of the myometrium resulting in a
postoperative fistula.
Suture of the hysterotomy must always respect a certain
number of principles. Indeed any technical deficiency when
carrying it out may result in uterine rupture during a subsequent
pregnancy. Apart from pedunculated myomata, the
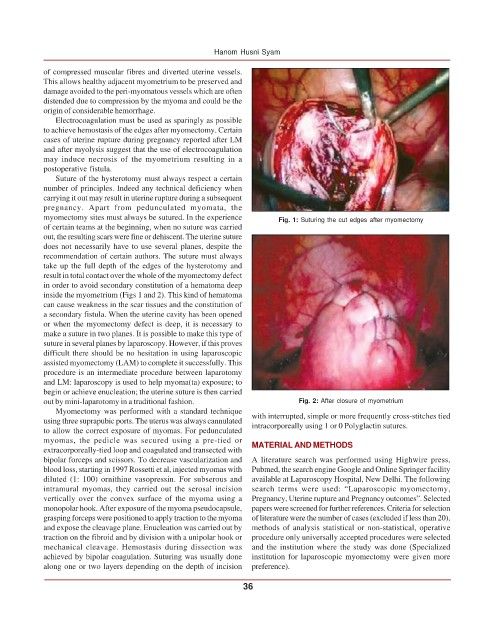
myomectomy sites must always be sutured. In the experience Fig. 1: Suturing the cut edges after myomectomy
of certain teams at the beginning, when no suture was carried
out, the resulting scars were fine or dehiscent. The uterine suture
does not necessarily have to use several planes, despite the
recommendation of certain authors. The suture must always
take up the full depth of the edges of the hysterotomy and
result in total contact over the whole of the myomectomy defect
in order to avoid secondary constitution of a hematoma deep
inside the myometrium (Figs 1 and 2). This kind of hematoma
can cause weakness in the scar tissues and the constitution of
a secondary fistula. When the uterine cavity has been opened
or when the myomectomy defect is deep, it is necessary to
make a suture in two planes. It is possible to make this type of
suture in several planes by laparoscopy. However, if this proves
difficult there should be no hesitation in using laparoscopic
assisted myomectomy (LAM) to complete it successfully. This
procedure is an intermediate procedure between laparotomy
and LM: laparoscopy is used to help myoma(ta) exposure; to
begin or achieve enucleation; the uterine suture is then carried
out by mini-laparotomy in a traditional fashion. Fig. 2: After closure of myometrium
Myomectomy was performed with a standard technique
using three suprapubic ports. The uterus was always cannulated with interrupted, simple or more frequently cross-stitches tied
intracorporeally using 1 or 0 Polyglactin sutures.
to allow the correct exposure of myomas. For pedunculated
myomas, the pedicle was secured using a pre-tied or MATERIAL AND METHODS
extracorporeally-tied loop and coagulated and transected with
bipolar forceps and scissors. To decrease vascularization and A literature search was performed using Highwire press,
blood loss, starting in 1997 Rossetti et al, injected myomas with Pubmed, the search engine Google and Online Springer facility
diluted (1: 100) ornithine vasopressin. For subserous and available at Laparoscopy Hospital, New Delhi. The following
intramural myomas, they carried out the serosal incision search terms were used: “Laparoscopic myomectomy,
vertically over the convex surface of the myoma using a Pregnancy, Uterine rupture and Pregnancy outcomes”. Selected
monopolar hook. After exposure of the myoma pseudocapsule, papers were screened for further references. Criteria for selection
grasping forceps were positioned to apply traction to the myoma of literature were the number of cases (excluded if less than 20),
and expose the cleavage plane. Enucleation was carried out by methods of analysis statistical or non-statistical, operative
traction on the fibroid and by division with a unipolar hook or procedure only universally accepted procedures were selected
mechanical cleavage. Hemostasis during dissection was and the institution where the study was done (Specialized
achieved by bipolar coagulation. Suturing was usually done institution for laparoscopic myomectomy were given more
along one or two layers depending on the depth of incision preference).
36