Page 19 - World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery
P. 19
R Dennis et al
as a postoperative bile leak managed by laparoscopy, washout DISCUSSION
and laparoscopic repair of a CBD injury. The second, a hepatic This series demonstrates that laparoscopic cholecystectomy is
duct injury complicating laparoscopic bile duct exploration, was safe and efficacious in the patients over 80 years. Thirty seven
recognized at the time of surgery and repaired laparoscopically. (54%) of our patients with an age range 80 to 91 years left
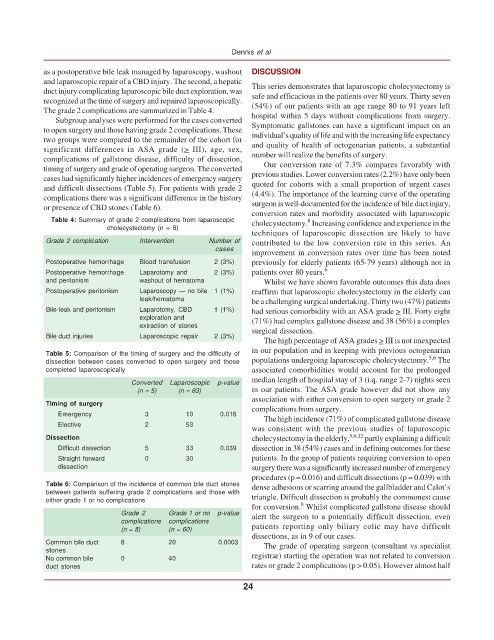
The grade 2 complications are summarized in Table 4. hospital within 5 days without complications from surgery.
Subgroup analyses were performed for the cases converted
to open surgery and those having grade 2 complications. These Symptomatic gallstones can have a significant impact on an
two groups were compared to the remainder of the cohort for individual’s quality of life and with the increasing life expectancy
significant differences in ASA grade (> III), age, sex, and quality of health of octogenarian patients, a substantial
complications of gallstone disease, difficulty of dissection, number will realize the benefits of surgery.
timing of surgery and grade of operating surgeon. The converted Our conversion rate of 7.3% compares favorably with
cases had significantly higher incidences of emergency surgery previous studies. Lower conversion rates (2.2%) have only been
and difficult dissections (Table 5). For patients with grade 2 quoted for cohorts with a small proportion of urgent cases
complications there was a significant difference in the history (4.4%). The importance of the learning curve of the operating
or presence of CBD stones (Table 6). surgeon is well-documented for the incidence of bile duct injury,
conversion rates and morbidity associated with laparoscopic
Table 4: Summary of grade 2 complications from laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Increasing confidence and experience in the
8
cholecystectomy (n = 8)
techniques of laparoscopic dissection are likely to have
Grade 2 complication Intervention Number of contributed to the low conversion rate in this series. An
cases
improvement in conversion rates over time has been noted
Postoperative hemorrhage Blood transfusion 2 (3%) previously for elderly patients (65-79 years) although not in
Postoperative hemorrhage Laparotomy and 2 (3%) patients over 80 years. 6
and peritonism washout of hematoma Whilst we have shown favorable outcomes this data does
Postoperative peritonism Laparoscopy — no bile 1 (1%) reaffirm that laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the elderly can
leak/hematoma be a challenging surgical undertaking. Thirty two (47%) patients
Bile-leak and peritonism Laparotomy, CBD 1 (1%) had serious comorbidity with an ASA grade > III. Forty eight
exploration and (71%) had complex gallstone disease and 38 (56%) a complex
extraction of stones surgical dissection.
Bile duct injuries Laparoscopic repair 2 (3%)
The high percentage of ASA grades > III is not unexpected
in our population and in keeping with previous octogenarian
Table 5: Comparison of the timing of surgery and the difficulty of 5,6
dissection between cases converted to open surgery and those populations undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The
completed laparoscopically associated comorbidities would account for the prolonged
median length of hospital stay of 3 (i.q. range 2-7) nights seen
Converted Laparoscopic p-value
(n = 5) (n = 63) in our patients. The ASA grade however did not show any
association with either conversion to open surgery or grade 2
Timing of surgery
complications from surgery.
Emergency 3 10 0.016
The high incidence (71%) of complicated gallstone disease
Elective 2 53
was consistent with the previous studies of laparoscopic
Dissection cholecystectomy in the elderly, 5,6,12 partly explaining a difficult
Difficult dissection 5 33 0.039 dissection in 38 (54%) cases and in defining outcomes for these
Straight forward 0 30 patients. In the group of patients requiring conversion to open
dissection surgery there was a significantly increased number of emergency
procedures (p = 0.016) and difficult dissections (p = 0.039) with
Table 6: Comparison of the incidence of common bile duct stones dense adhesions or scarring around the gallbladder and Calot’s
between patients suffering grade 2 complications and those with triangle. Difficult dissection is probably the commonest cause
either grade 1 or no complications
8
for conversion. Whilst complicated gallstone disease should
Grade 2 Grade 1 or no p-value alert the surgeon to a potentially difficult dissection, even
complications complications patients reporting only biliary colic may have difficult
(n = 8) (n = 60)
dissections, as in 9 of our cases.
Common bile duct 8 20 0.0003 The grade of operating surgeon (consultant vs specialist
stones
No common bile 0 40 registrar) starting the operation was not related to conversion
duct stones rates or grade 2 complications (p > 0.05). However almost half
24