Page 49 - Journal of WALS
P. 49
Meha Jabeen
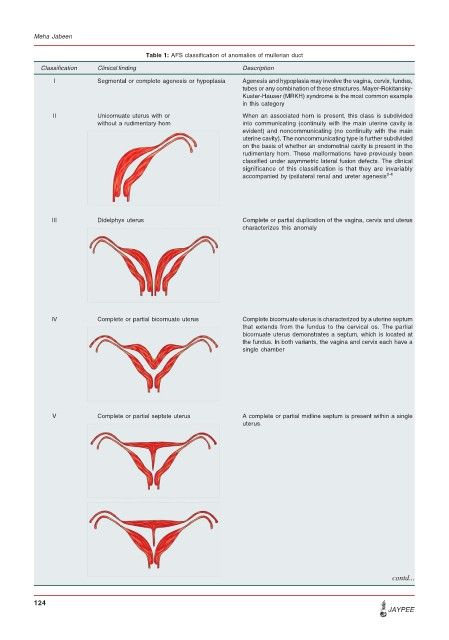
Table 1: AFS classification of anomalies of mullerian duct
Classification Clinical finding Description
I Segmental or complete agenesis or hypoplasia Agenesis and hypoplasia may involve the vagina, cervix, fundus,
tubes or any combination of these structures. Mayer-Rokitansky-
Kuster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome is the most common example
in this category
II Unicornuate uterus with or When an associated horn is present, this class is subdivided
without a rudimentary horn into communicating (continuity with the main uterine cavity is
evident) and noncommunicating (no continuity with the main
uterine cavity). The noncommunicating type is further subdivided
on the basis of whether an endometrial cavity is present in the
rudimentary horn. These malformations have previously been
classified under asymmetric lateral fusion defects. The clinical
significance of this classification is that they are invariably
accompanied by ipsilateral renal and ureter agenesis 2-4
III Didelphys uterus Complete or partial duplication of the vagina, cervix and uterus
characterizes this anomaly
IV Complete or partial bicornuate uterus Complete bicornuate uterus is characterized by a uterine septum
that extends from the fundus to the cervical os. The partial
bicornuate uterus demonstrates a septum, which is located at
the fundus. In both variants, the vagina and cervix each have a
single chamber
V Complete or partial septate uterus A complete or partial midline septum is present within a single
uterus.
contd...
124
JAYPEE