Page 44 - Journal of WALS
P. 44
WJOLS
Subfascial Endoscopic Perforator Surgery in Perforator Vein Insufficiency
The perforating veins may be visible immediately or may and the operated leg is wrapped with a compression bandage
require some amount of blunt dissection and exploration. Skin extending from the forefoot to the upper calf or leg.
markings done with the help of duplex venous studies are useful Usually, patients are discharged on the same day of surgery
in guiding the surgeon to the location of the perforators. Once and advised routine follow-up in outpatient department 1 week
identified, each perforating vein is double clipped with the after surgery.
8 mm titanium clips with a 5 mm clip applier. Generally, all
perforating veins which can be identified are clipped (Fig. 6D). POSTOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
As the perforator continuity is interruped by the clips, the Once the effect of anesthetic wears off, the patients are
veins are usually not divided. However, division of the perforator encouraged to ambulate and are discharged on the same day or
between the clips can be performed, when desired, with the day after surgery. Patients receive two postoperative doses
endoscopic shears to facilitate distal exposure. 8-12 of antibiotics in addition to the intraoperative intravenous
When interruption and/or division of the perforators is antibiotic. First 24 hours after surgery, they are provided with
complete, the trocars are removed, the skin incisions are closed adequate parenteral analgesia, this is changed to oral analgesia
with interrupted mattress stitches using monofilament sutures. upon discharge. Postoperative instructions stress on the need
Superficial ligation and stripping can be performed in the for active ambulation, elevation of the operated limb and
standard fashion in patients with superficial venous maintenance of the elastic bandage regularly. Patients are seen
insufficiency, nonadherent dressing are covered to all wounds, for removal of skin sutures in the outpatient department a week
A
A
B B
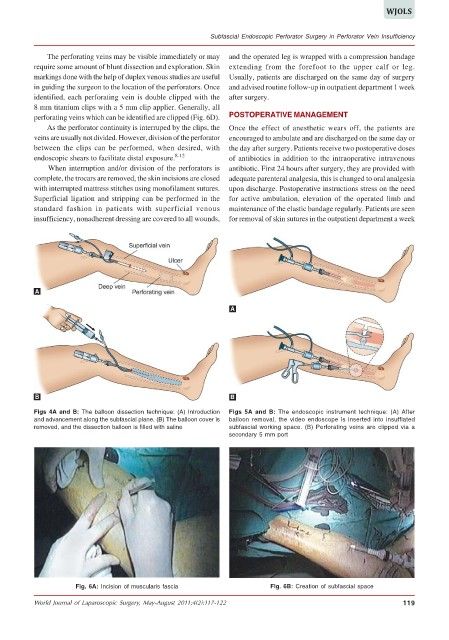
Figs 4A and B: The balloon dissection technique: (A) Introduction Figs 5A and B: The endoscopic instrument technique: (A) After
and advancement along the subfascial plane. (B) The balloon cover is balloon removal, the video endoscope is inserted into insufflated
removed, and the dissection balloon is filled with saline subfascial working space. (B) Perforating veins are clipped via a
secondary 5 mm port
Fig. 6A: Incision of muscularis fascia Fig. 6B: Creation of subfascial space
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, May-August 2011;4(2):117-122 119