Page 24 - World Association of Laparoscopic Surgeons - Journal
P. 24
WJOLS
Role of Falloposcopy in the Management of Subfertility
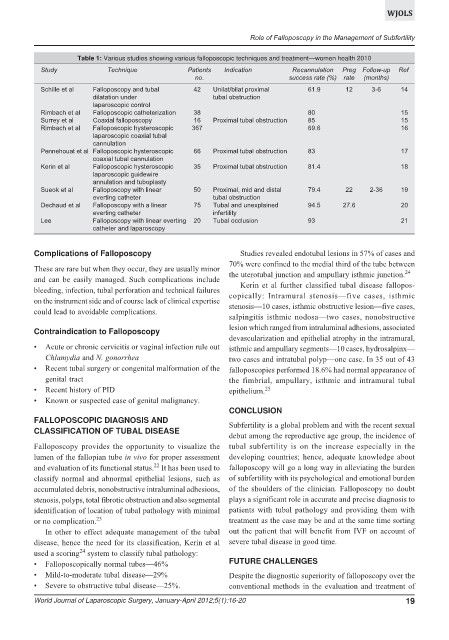
Table 1: Various studies showing various falloposcopic techniques and treatment—women health 2010
Study Technique Patients Indication Recannulation Preg Follow-up Ref
no. success rate (%) rate (months)
Schille et al Falloposcopy and tubal 42 Unilat/bilat proximal 61.9 12 3-6 14
dilatation under tubal obstruction
laparoscopic control
Rimbach et al Falloposcopic catheterization 38 80 15
Surrey et al Coaxial falloposcopy 16 Proximal tubal obstruction 85 15
Rimbach et al Falloposcopic hysteroscopic 367 69.6 16
laparoscopic coaxial tubal
cannulation
Pennehouat et al Falloposcopic hysteroscopic 66 Proximal tubal obstruction 83 17
coaxial tubal cannulation
Kerin et al Falloposcopic hysteroscopic 35 Proximal tubal obstruction 81.4 18
laparoscopic guidewire
annulation and tuboplasty
Sueok et al Falloposcopy with linear 50 Proximal, mid and distal 79.4 22 2-36 19
everting catheter tubal obstruction
Dechaud et al Falloposcopy with a linear 75 Tubal and unexplained 94.5 27.6 20
everting catheter infertility
Lee Falloposcopy with linear everting 20 Tubal occlusion 93 21
catheter and laparoscopy
Complications of Falloposcopy Studies revealed endotubal lesions in 57% of cases and
70% were confined to the medial third of the tube between
These are rare but when they occur, they are usually minor 24
the uterotubal junction and ampullary isthmic junction.
and can be easily managed. Such complications include
Kerin et al further classified tubal disease fallopos-
bleeding, infection, tubal perforation and technical failures
copically: Intramural stenosis—five cases, isthmic
on the instrument side and of course lack of clinical expertise
stenosis—10 cases, isthmic obstructive lesion—five cases,
could lead to avoidable complications.
salpingitis isthmic nodosa—two cases, nonobstructive
lesion which ranged from intraluminal adhesions, associated
Contraindication to Falloposcopy
devascularization and epithelial atrophy in the intramural,
Acute or chronic cervicitis or vaginal infection rule out isthmic and ampullary segments—10 cases, hydrosalpinx—
Chlamydia and N. gonorrhea two cases and intratubal polyp—one case. In 35 out of 43
Recent tubal surgery or congenital malformation of the falloposcopies performed 18.6% had normal appearance of
genital tract the fimbrial, ampullary, isthmic and intramural tubal
Recent history of PID epithelium. 25
Known or suspected case of genital malignancy.
CONCLUSION
FALLOPOSCOPIC DIAGNOSIS AND
Subfertility is a global problem and with the recent sexual
CLASSIFICATION OF TUBAL DISEASE
debut among the reproductive age group, the incidence of
Falloposcopy provides the opportunity to visualize the tubal subfertility is on the increase especially in the
lumen of the fallopian tube in vivo for proper assessment developing countries; hence, adequate knowledge about
22
and evaluation of its functional status. It has been used to falloposcopy will go a long way in alleviating the burden
classify normal and abnormal epithelial lesions, such as of subfertility with its psychological and emotional burden
accumulated debris, nonobstructive intraluminal adhesions, of the shoulders of the clinician. Falloposcopy no doubt
stenosis, polyps, total fibrotic obstruction and also segmental plays a significant role in accurate and precise diagnosis to
identification of location of tubal pathology with minimal patients with tubal pathology and providing them with
or no complication. 23 treatment as the case may be and at the same time sorting
In other to effect adequate management of the tubal out the patient that will benefit from IVF on account of
disease, hence the need for its classification, Kerin et al severe tubal disease in good time.
24
used a scoring system to classify tubal pathology:
FUTURE CHALLENGES
Falloposcopically normal tubes—46%
Mild-to-moderate tubal disease—29% Despite the diagnostic superiority of falloposcopy over the
Severe to obstructive tubal disease—25%. conventional methods in the evaluation and treatment of
World Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery, January-April 2012;5(1):16-20 19