Page 50 - Journal of Laparoscopic Surgery - WALS Journal
P. 50
Sadashivayya S Soppimath
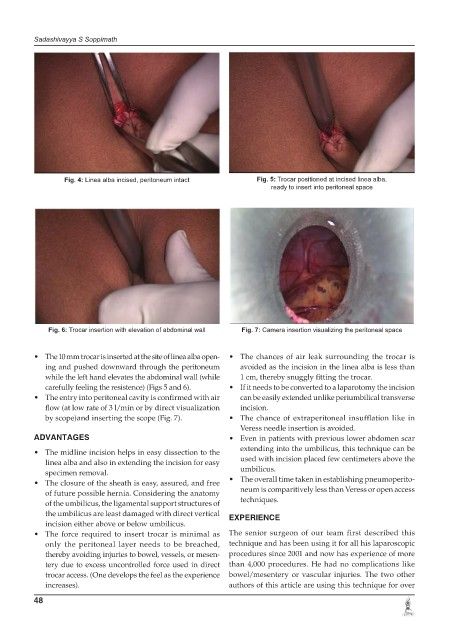
Fig. 4: Linea alba incised, peritoneum intact Fig. 5: Trocar positioned at incised linea alba,
ready to insert into peritoneal space
Fig. 6: Trocar insertion with elevation of abdominal wall Fig. 7: Camera insertion visualizing the peritoneal space
• The 10 mm trocar is inserted at the site of linea alba open- • The chances of air leak surrounding the trocar is
ing and pushed downward through the peritoneum avoided as the incision in the linea alba is less than
while the left hand elevates the abdominal wall (while 1 cm, thereby snuggly fitting the trocar.
carefully feeling the resistence) (Figs 5 and 6). • If it needs to be converted to a laparotomy the incision
• The entry into peritoneal cavity is confirmed with air can be easily extended unlike periumbilical transverse
flow (at low rate of 3 l/min or by direct visualization incision.
by scope)and inserting the scope (Fig. 7). • The chance of extraperitoneal insufflation like in
Veress needle insertion is avoided.
ADVANTAGES • Even in patients with previous lower abdomen scar
extending into the umbilicus, this technique can be
• The midline incision helps in easy dissection to the
linea alba and also in extending the incision for easy used with incision placed few centimeters above the
specimen removal. umbilicus.
• The closure of the sheath is easy, assured, and free • The overall time taken in establishing pneumoperito-
of future possible hernia. Considering the anatomy neum is comparitively less than Veress or open access
of the umbilicus, the ligamental support structures of techniques.
the umbilicus are least damaged with direct vertical EXPERIENCE
incision either above or below umbilicus.
• The force required to insert trocar is minimal as The senior surgeon of our team first described this
only the peritoneal layer needs to be breached, technique and has been using it for all his laparoscopic
thereby avoiding injuries to bowel, vessels, or mesen- procedures since 2001 and now has experience of more
tery due to excess uncontrolled force used in direct than 4,000 procedures. He had no complications like
trocar access. (One develops the feel as the experience bowel/mesentery or vascular injuries. The two other
increases). authors of this article are using this technique for over
48