-- ALL Newsletter --
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019
2020
2021
2022
2023
2024
2025
Dr. Sudhir Srivastava Founder, Chairman & CEO of the Company Making SSi Mantra Robot
Dr. Sudhir Srivastava, a highly renowned robotic cardiac surgeon, has made significant contributions to the field of medical technology through his leadership at SS Innovations International Inc. As the founder, chairman, and CEO of this pioneering company, Dr. Srivastava has been instrumental in developing the SSi Mantra, a groundbreaking surgical robotic system. This system represents a major advancement in the field of cardiothoracic surgery, particularly in robotic procedures.

The SSi Mantra, created under Dr. Srivastava's guidance, is notable for its role in revolutionizing medical robotic surgery practices not only in India but also internationally. As a product of an Indian med-tech startup, it carries the distinction of being the first-ever 'Made in India' surgical robot. This innovative technology is a testament to Dr. Srivastava's vision of making advanced surgical procedures more affordable and accessible, particularly for underserved populations around the world.
Dr. Srivastava's career is marked by his expertise in robotic surgery, holding the record for the most robotic Beating Heart Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB) surgeries. His work has been pivotal in decentralizing excellence in the medical field, bringing high-quality healthcare to a broader range of patients.
The SSi Mantra has been installed in prestigious institutions like the Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Center in New Delhi (RGCI), marking a significant milestone in India's medical technology landscape. It is designed to be more modular, flexible, and versatile compared to existing global surgical systems, which is particularly important in a market that was previously dominated by expensive alternatives.

What sets the SSi Mantra apart is its cost-effectiveness and the range of surgical procedures it can support. These include various operations in urology, gynecology, cardiac, thoracic, general, gastro-intestinal, and head & neck surgeries. The system's introduction into the market is a result of extensive research and development efforts, along with collaborations with talented engineers from India and experienced global scientists.

In summary, Dr. Sudhir Srivastava's work with SS Innovations and the development of the SSi Mantra stands as a significant contribution to the global field of robotic surgery, particularly in making such advanced technologies more accessible and affordable.
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, has significantly transformed the landscape of modern surgical procedures. This advanced technique utilizes robotic systems to enhance the precision, flexibility, and control of surgeons during complex operations. Robotic surgery is most commonly associated with minimally invasive surgery, where procedures are performed through tiny incisions, but it is also sometimes applied in traditional open surgical procedures.
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery is its ability to facilitate surgery through smaller incisions. This approach offers several benefits, including reduced pain and discomfort, lower risk of infection, minimized blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and smaller scars. The robotic arms used in these surgeries exhibit a high degree of dexterity, allowing surgeons to operate in very tight spaces within the body that would be challenging or impossible to access through open surgery.
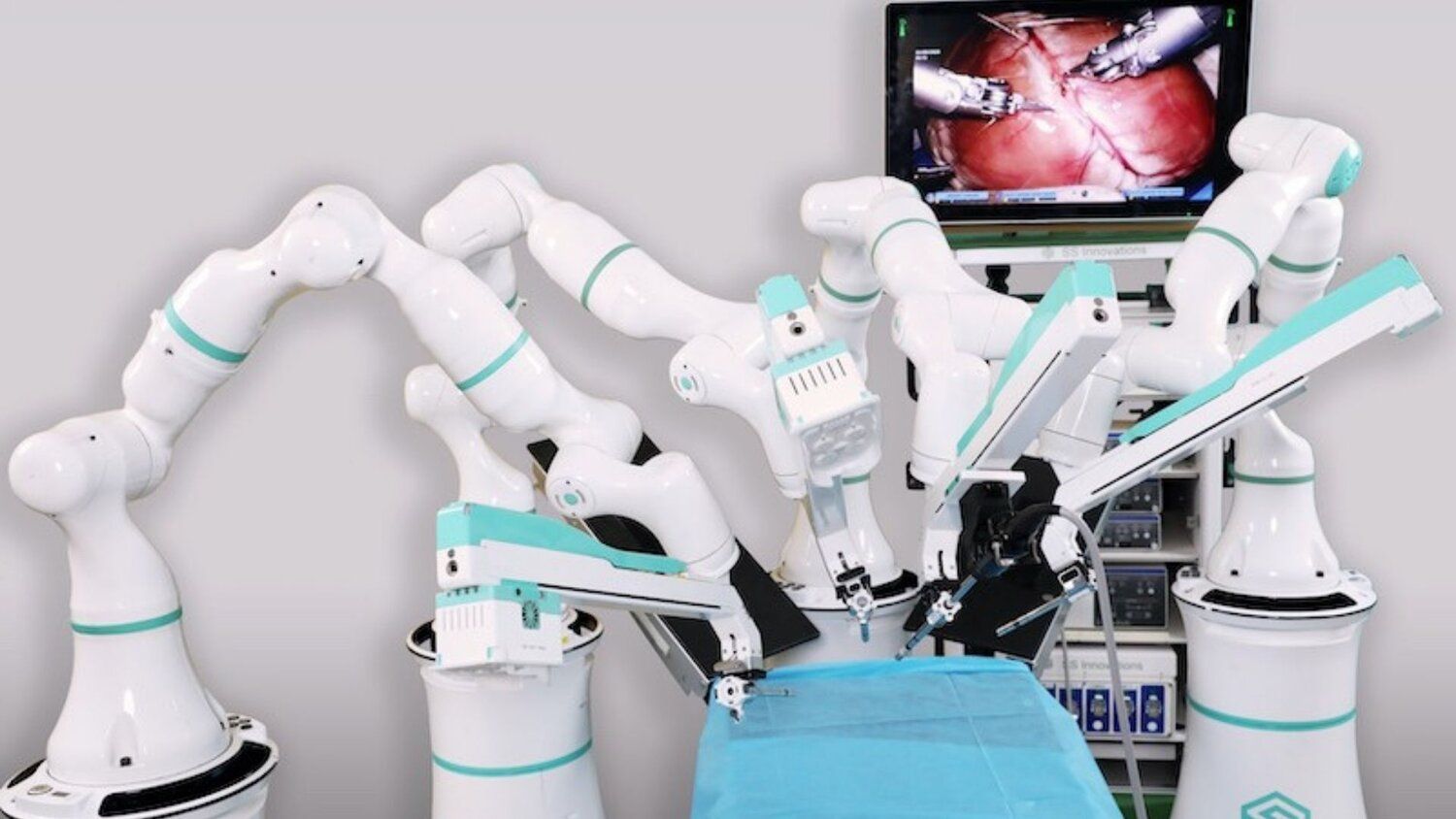
During robotic surgery, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions and inserts ports (thin tubes) through these incisions. The robotic system, which includes a camera and surgical instruments, is then attached to these ports. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console situated in the operating room, which provides a magnified, high-definition, 3D view of the surgical site. This setup offers better visualization and precision, allowing surgeons to perform delicate and complex procedures more effectively.
Robotic surgery is utilized across various specialties, including gynecologic surgery (e.g., endometriosis resection, hysterectomy, pelvic organ prolapse repair), thoracic surgery (e.g., lung resection, mediastinal mass reduction, thymectomy), urologic surgery (e.g., cystectomy, partial nephrectomy, radical prostatectomy), and even heart surgery. In heart surgery, for example, robotic arms enable small, precise movements, enhancing the surgeon's ability to perform the operation.
Despite its numerous advantages, robotic surgery does have some limitations and risks. These include the requirement for centers to afford the technology and have specially trained surgeons, the potential need to convert to an open procedure if complications arise, the risk of nerve damage and compression, and the extremely rare chance of robotic malfunction.
The recovery from robotic surgery is generally much quicker compared to traditional surgery. Patients can often get out of bed shortly after the anesthesia wears off, eat within a few hours of surgery, and may go home the same day or the next day. However, postoperative care is crucial, and patients should closely follow their healthcare provider's instructions, including monitoring for signs of infection or blood clots.
It's important for patients to discuss with their healthcare providers the suitability of robotic surgery for their specific medical condition, as it may not be an option for everyone. The availability of this technology also varies by geographic location and medical facility capabilities.

The SSi Mantra, created under Dr. Srivastava's guidance, is notable for its role in revolutionizing medical robotic surgery practices not only in India but also internationally. As a product of an Indian med-tech startup, it carries the distinction of being the first-ever 'Made in India' surgical robot. This innovative technology is a testament to Dr. Srivastava's vision of making advanced surgical procedures more affordable and accessible, particularly for underserved populations around the world.
Dr. Srivastava's career is marked by his expertise in robotic surgery, holding the record for the most robotic Beating Heart Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB) surgeries. His work has been pivotal in decentralizing excellence in the medical field, bringing high-quality healthcare to a broader range of patients.
The SSi Mantra has been installed in prestigious institutions like the Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Center in New Delhi (RGCI), marking a significant milestone in India's medical technology landscape. It is designed to be more modular, flexible, and versatile compared to existing global surgical systems, which is particularly important in a market that was previously dominated by expensive alternatives.

What sets the SSi Mantra apart is its cost-effectiveness and the range of surgical procedures it can support. These include various operations in urology, gynecology, cardiac, thoracic, general, gastro-intestinal, and head & neck surgeries. The system's introduction into the market is a result of extensive research and development efforts, along with collaborations with talented engineers from India and experienced global scientists.

In summary, Dr. Sudhir Srivastava's work with SS Innovations and the development of the SSi Mantra stands as a significant contribution to the global field of robotic surgery, particularly in making such advanced technologies more accessible and affordable.
Robotic surgery, also known as robot-assisted surgery, has significantly transformed the landscape of modern surgical procedures. This advanced technique utilizes robotic systems to enhance the precision, flexibility, and control of surgeons during complex operations. Robotic surgery is most commonly associated with minimally invasive surgery, where procedures are performed through tiny incisions, but it is also sometimes applied in traditional open surgical procedures.
One of the primary advantages of robotic surgery is its ability to facilitate surgery through smaller incisions. This approach offers several benefits, including reduced pain and discomfort, lower risk of infection, minimized blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and smaller scars. The robotic arms used in these surgeries exhibit a high degree of dexterity, allowing surgeons to operate in very tight spaces within the body that would be challenging or impossible to access through open surgery.

During robotic surgery, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions and inserts ports (thin tubes) through these incisions. The robotic system, which includes a camera and surgical instruments, is then attached to these ports. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console situated in the operating room, which provides a magnified, high-definition, 3D view of the surgical site. This setup offers better visualization and precision, allowing surgeons to perform delicate and complex procedures more effectively.
Robotic surgery is utilized across various specialties, including gynecologic surgery (e.g., endometriosis resection, hysterectomy, pelvic organ prolapse repair), thoracic surgery (e.g., lung resection, mediastinal mass reduction, thymectomy), urologic surgery (e.g., cystectomy, partial nephrectomy, radical prostatectomy), and even heart surgery. In heart surgery, for example, robotic arms enable small, precise movements, enhancing the surgeon's ability to perform the operation.
Despite its numerous advantages, robotic surgery does have some limitations and risks. These include the requirement for centers to afford the technology and have specially trained surgeons, the potential need to convert to an open procedure if complications arise, the risk of nerve damage and compression, and the extremely rare chance of robotic malfunction.
The recovery from robotic surgery is generally much quicker compared to traditional surgery. Patients can often get out of bed shortly after the anesthesia wears off, eat within a few hours of surgery, and may go home the same day or the next day. However, postoperative care is crucial, and patients should closely follow their healthcare provider's instructions, including monitoring for signs of infection or blood clots.
It's important for patients to discuss with their healthcare providers the suitability of robotic surgery for their specific medical condition, as it may not be an option for everyone. The availability of this technology also varies by geographic location and medical facility capabilities.